Chapter 9
Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
By Boundless
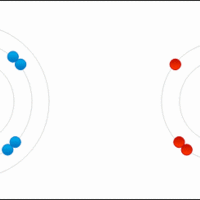
An ionic bond results from the transfer of an electron from a metal atom to a non-metal atom.
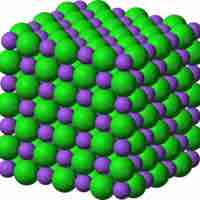
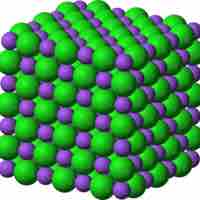
Lattice energy is a measure of the bond strength in an ionic compound.
Ionic formulas must satisfy the noble gas configurations for the constituent ions and the product compound must be electrically neutral.
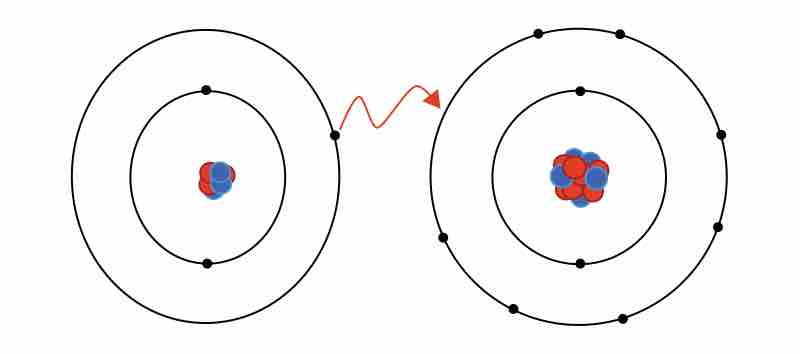
Ionic bonds can have some covalent character.
Covalent and ionic compounds have distinct physical properties.
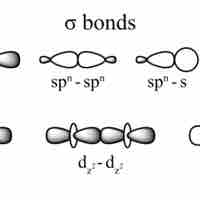
Single covalent bonds are sigma bonds, which occur when one pair of electrons is shared between atoms.
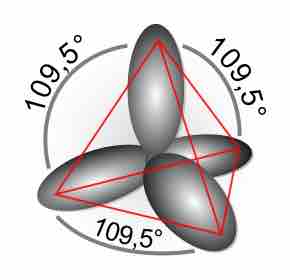
Double and triple bonds, comprised of sigma and pi bonds, increase the stability and restrict the geometry of a compound.
The covalent bonding model helps predict many of the physical properties of compounds.
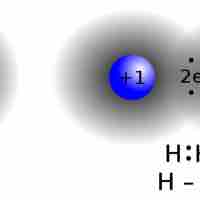
Lewis symbols use dots to visually represent the valence electrons of an atom.
The Lewis symbol for an atom depicts its valence electrons as dots around the symbol for the element.
In covalent molecules, atoms share pairs of electrons in order to achieve a full valence level.
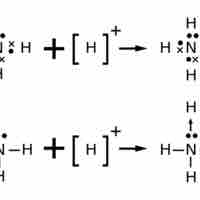
The Lewis structure of an ion is placed in brackets and its charge is written as a superscript outside of the brackets, on the upper right.

Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom/molecule to attract electrons; oxidation number is an indicator of its bonding environment.
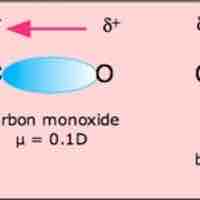
Molecular polarity is dependent on the presence of polar covalent bonds and the molecule's three-dimensional structure.
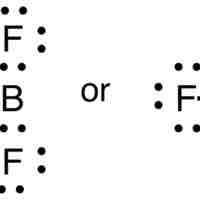
While most elements below atomic number 20 follow the octet rule, several exceptions exist, including compounds of boron and aluminum.
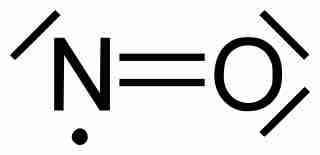
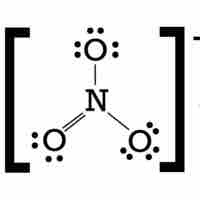
Molecules with an odd number of electrons disobey the octet rule.
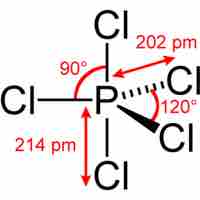
Main group elements in the third period and below form compounds that deviate from the octet rule by having more than 8 valence electrons.
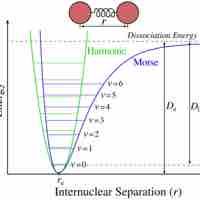
Bond energy is the measure of bond strength. In order to turn one mole of a molecule into its constituent atoms, an amount of heat equal to the bond energy needs to be put into the system.
.jpg)
Bond enthalpy is defined as the enthalpy change when a covalent bond is cleaved by homolysis.

Bond length between two atoms depends on factors such as the orbital hybridization and the electronic nature of the components.