Chapter 8
Periodic Properties
By Boundless

The periodic table is a methodical arrangement of the chemical elements, organized on the basis of their electron configurations.

Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells.

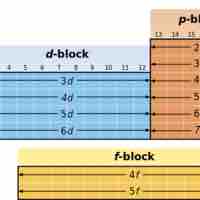
The d-block elements are commonly known as transition metals or transition elements.
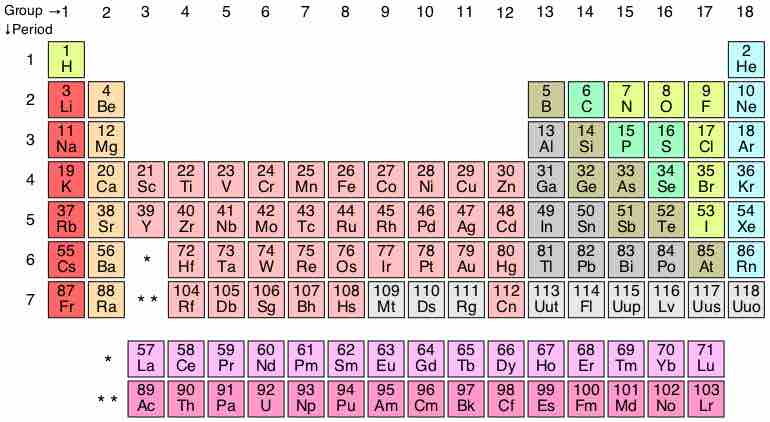
The periodic table currently contains 7 periods, but theorists predict that two additional periods may exist.
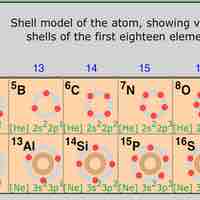
The position of elements on the periodic table is directly related to their electron configurations.
The elements on the periodic table exhibit different levels of reactivity based on the number of electrons in their highest energy shells.
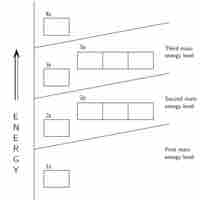
An atom's electrons exist in discrete atomic orbitals, and the atom's electron configuration can be determined using a set of guidelines.

The Aufbau principle determines an atom's electron configuration by adding electrons to atomic orbitals following a defined set of rules.
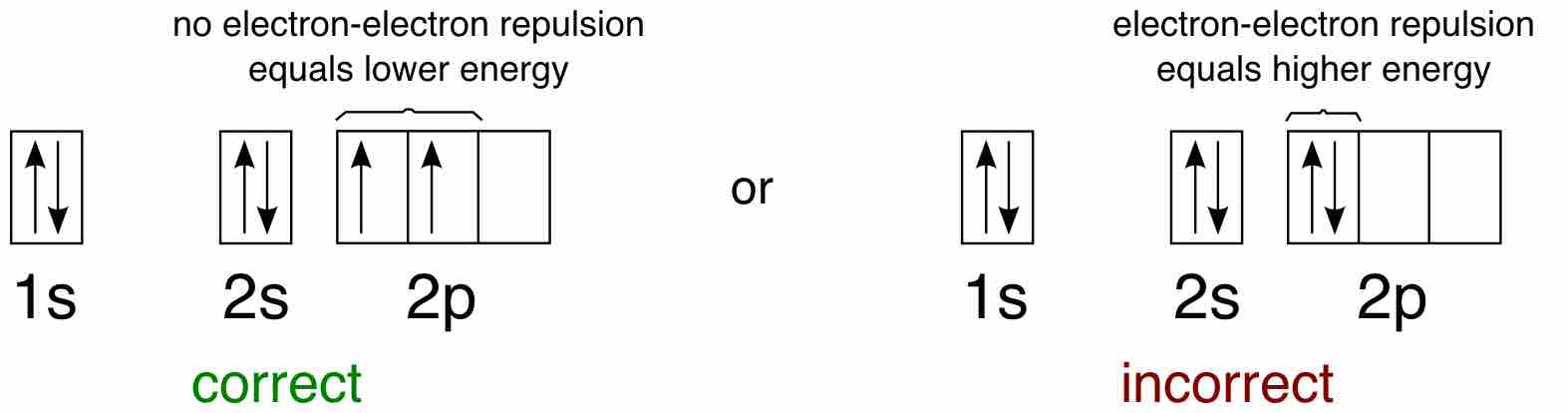
Hund's Rule defines the behavior of unpaired valence shell electrons, providing insight into an atom's reactivity and stability.

The shielding effect, approximated by the effective nuclear charge, is due to inner electrons shielding valence electrons from the nucleus.

Diamagnetic atoms have only paired electrons, whereas paramagnetic atoms, which can be made magnetic, have at least one unpaired electron.
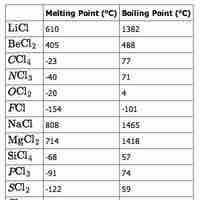
The physical properties of elements vary across a period, mostly as a function of bonding.

The physical properties (notably, melting and boiling points) of the elements in a given group vary as you move down the table.
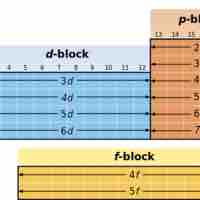
The electron configuration of a given element can be predicted based on its location in the periodic table.
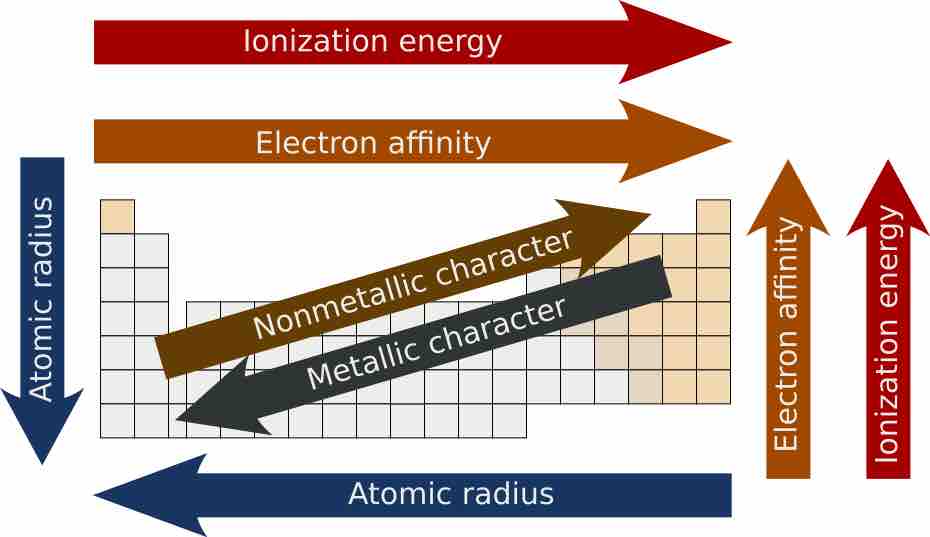
Atomic radii decrease from left to right across a period and increase from top to bottom along a group.

Similarly charged ions tend to decrease in size across a period (row) and increase in size down a group (column).

The ionization energy tends to increase as one moves from left to right across a given period or up a group in the periodic table.

The electron affinity of the elements generally increases across a period and sometimes decreases down a group in the periodic table.
In the periodic table, the elements are placed from left to right in each period in the sequence of their atomic numbers.

The halogens are a series of highly reactive, nonmetal elements from Group 17 of the periodic table.

Noble gases are the six chemical elements of Group 18 of the periodic table, being monatomic and (with very limited exceptions) inert.
- The Nature of Light
- Bohr's Theory
- Quantum Mechanical Description of the Atomic Orbital
- Orbital Shapes