The total number of electrons represented in a Lewis structure is equal to the sum of the numbers of valence electrons in each individual atom. Non-valence electrons are not represented in Lewis structures. After the total number of available electrons has been determined, electrons must be placed into the structure.
Lewis structures for polyatomic ions are drawn by the same methods that we have already learned. When counting electrons, negative ions should have extra electrons placed in their Lewis structures; positive ions should have fewer electrons than an uncharged molecule. When the Lewis structure of an ion is written, the entire structure is placed in brackets, and the charge is written as a superscript on the upper right, outside of the brackets. For example, consider the ammonium ion, NH4+, which contains 9 (5 from N and 1 from each of the four H atoms) –1 = 8 electrons. One electron is subtracted because the entire molecule has a +1 charge.
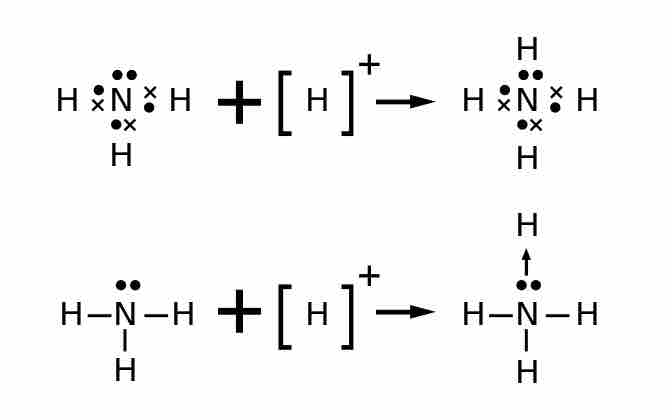
Coordinate covalent bonding
The ammonium ion, NH4+, contains 9–1 = 8 electrons.
Negative ions follow the same procedure. The chlorite ion, ClO2–, contains 19 (7 from the Cl and 6 from each of the two O atoms) +1 = 20 electrons. One electron is added because the entire molecule has a -1 charge.

Hypochlorite ion Lewis structure
The hypochlorite ion, ClO−, contains 13 + 1 = 14 electrons.