Chapter 10
Advanced Concepts of Chemical Bonding
By Boundless
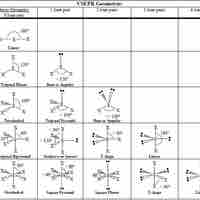
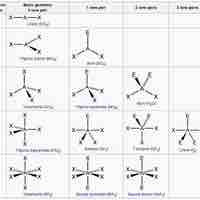
The VSPER theory detremines molecular geometries (linear, trigonal, trigonal bipyramidal, tetrahedral, and octahedral).
The VSEPR theory describes five main shapes of simple molecules: linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral.
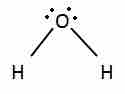
Nonbonding electrons are in orbitals that occupy space, repel the other orbitals, and change a molecule's shape.
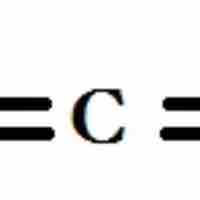
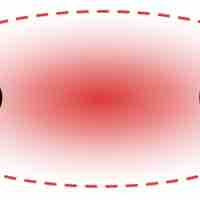
A dipole exists when a molecule has areas of asymmetrical positive and negative charge.

Bond polarity exists when two bonded atoms unequally share electrons, resulting in a negative and a positive end.
Chemical bonds are more varied than terminology might suggest; they exist on a spectrum between purely ionic and purely covalent bonds.
Valence bond theory states that overlap between two atomic orbitals forms a covalent bond between two atoms.
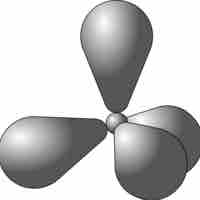
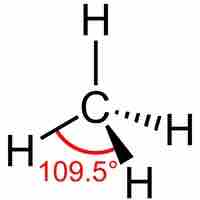
sp3 hybrid orbitals form when a single s and three p orbitals hybridize.
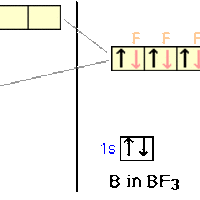
sp2 hybridization occurs between one s-orbital and two p-orbitals.
sp hybrid orbitals form from one s-orbital and one p-orbital.

sp2, sp hybridizations, and pi-bonding can be used to describe the chemical bonding in molecules with double and triple bonds.
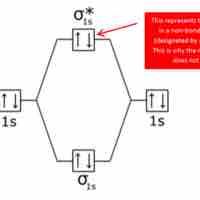
Bonding and antibonding orbitals are illustrated in MO diagrams, and are useful for predicting the strength and existence of chemical bonds.

Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms.
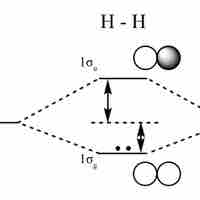
An LCAO approximation is a quantum superposition of atomic orbitals, used to calculate molecular orbitals in quantum chemistry.

Homonuclear diatomic molecules are composed of only one element.
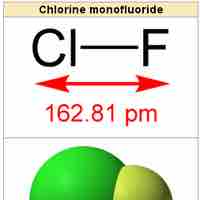
Heteronuclear diatomic molecules are composed of two atoms of two different elements.
A polyatomic molecule is a single entity composed of at least three covalently-bonded atoms.