Chapter 18
Financial Statements
By Boundless

Companies prepare three financial statements according to GAAP rules: the income statement, the balance sheet, and the cash flow statement.

Profitability ratios are used to assess a business's ability to generate earnings.

Liquidity ratios measure how quickly assets can be turned into cash in order to pay the company's short-term obligations.
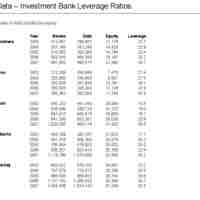
Debt ratios provide information about a company's long-term financial health.

Most financial ratios have no universal benchmarks, so meaningful analysis involves comparisons with competitors and industry averages.
Valuation ratios describe the value of shares to shareholders, and include the EPS ratio, the P/E ratio, and the dividend yield ratio.
Activity ratios provide useful insights regarding an organization's ability to leverage existing assets efficiently.
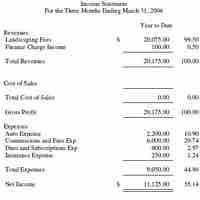
Most of the ratios discussed can be calculated using information found in the three main financial statements.
Accounting is the vehicle for reporting financial information about a business entity to many different groups of people.
Through integrating accounting knowledge with strategic decision-making, organizations can improve performance, refine strategy, and mitigate risk.
Financial accounting is a core organizational function in which accountants prepare a variety of documents to inform stakeholders of the financial health of operations.
Tax accounting couples legal obligations with financial accounting to ensure adherence to current tax laws.

Governmental and nonprofit accounting follow different rules from those of commercial enterprises.
Most of a company's stakeholders consume its accounting information in one form or another.
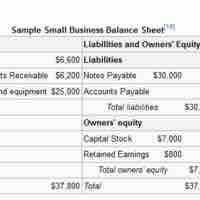
The accounting equation is a general rule used in business transactions where the sum of liabilities and owners' equity equals assets.

A double-entry bookkeeping system requires that every transaction be recorded in at least two different nominal ledger accounts.
The accounting cycle includes analysis of transactions, transferring journal entries into a general ledger, revenue, and expense closed.

The balance sheet is a summary of the financial balances of a company.
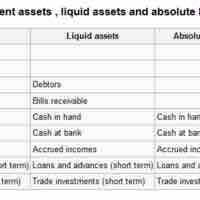
Assets are resources as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the enterprise.
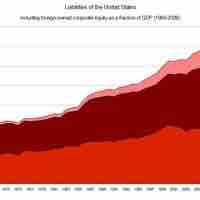
A "liability" is an obligation of an entity, the settlement of which may result in the yielding of economic benefits in future.

Shareholders' equity is the difference between total assets and total liabilities.
The income statements reports the revenues, expenses, and overall net profit or loss over a given reporting period.
Revenue is cash inflows or other enhancements of assets derived by delivering or producing goods.
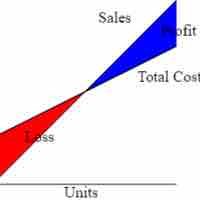
The cost of goods sold, calculated and recorded in the income statement, is a useful indicator of overall production costs and efficiency.
General and administrative non-production related costs provide a good indication of overall operational efficiency.
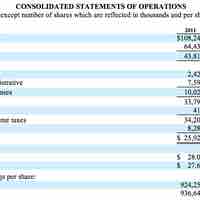
Net income in accounting is an entity's income minus expenses for an accounting period.
The income statement displays the revenues recognized for a specified period and the costs and expenses charged against these revenues.
Organizations must carefully manage their cash flow statements to ensure appropriate liquidity to avoid missing investment opportunities.
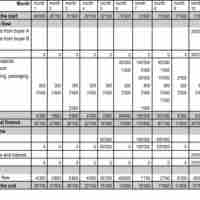
Cash flow statements can be measured via the direct method and the indirect method to determine overall liquidity.