In financial accounting, assets are economic resources. Anything tangible or intangible that is capable of being owned or controlled to produce value and that is held to have positive economic value is considered an asset.
Simply stated, assets represent ownership of value that can be converted into cash (although cash itself is also considered an asset). The balance sheet of a firm records the monetary value of the assets owned by the firm . It is money and other valuables belonging to an individual or business. Two major classes are tangible assets and intangible assets .
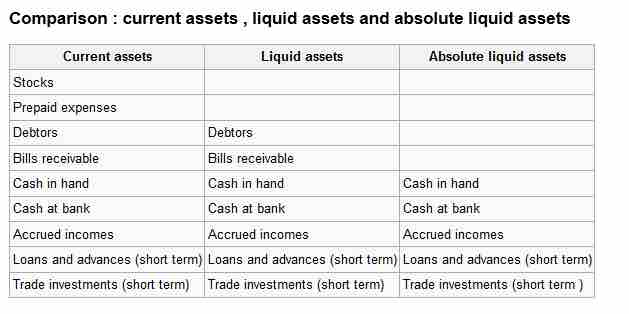
Comparison of Various types of Assets
Current assets vs. liquid assets vs. absolute liquid assets.
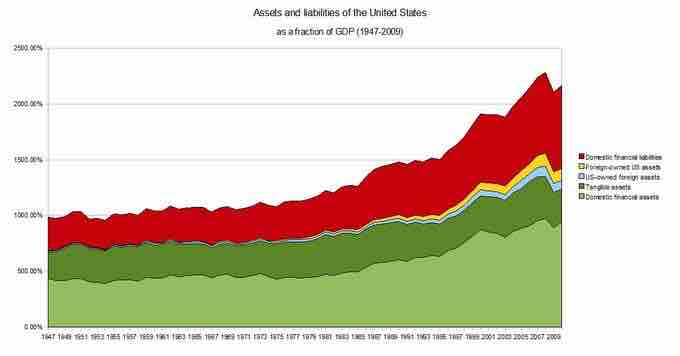
Assets and Liabilities of the US
Assets and liabilities of the US as a fraction of the GDP 1945-2009.
Tangible assets contain various subclasses, including current and fixed assets. Current assets include inventory, while fixed assets include such items as buildings and equipment.
Intangible assets are nonphysical resources and rights that have a value to the firm because they give the firm some kind of advantage in the market place. Examples of intangible assets are goodwill, copyrights, trademarks, patents, computer programs, and financial assets, including such items as accounts receivable, bonds and stocks.
The accounting equation relates assets, liabilities, and owner's equity:
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity (Owners' Equity)
That is, the total value of a firm's assets are always equal to the combined value of its "equity" and "liabilities. " In other words, the accounting equation is the mathematical structure of the balance sheet.
Probably the most accepted accounting definition of asset is the one used by the International Accounting Standards Board. The following is a quotation from the IFRS Framework:
"An asset is a resource controlled by the enterprise as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the enterprise. "