This article was medically reviewed by Janice Litza, MD. Dr. Litza is a board certified Family Medicine Physician in Wisconsin. She is a practicing Physician and taught as a Clinical Professor for 13 years, after receiving her MD from the University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health in 1998.
There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 80% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 85,782 times.
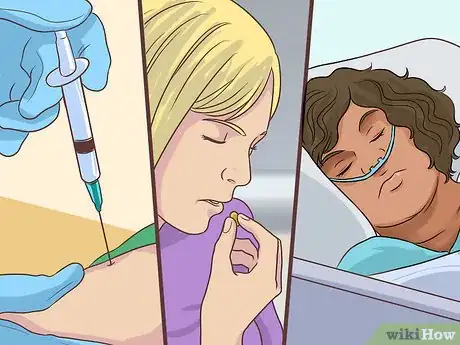
The flu, or influenza, can be a serious and potentially deadly illness that attacks the respiratory system.[1] The flu is highly contagious. Most cases of the flu go away without medication or complications. Many people now get an annual flu vaccine to prevent the illness or serious complications. The flu vaccine is generally safe, but some people may have adverse reactions to the injection.[2] You can treat an adverse reaction to the flu vaccine by seeking medical attention for allergic reactions or relieving less serious side effects at home.
Steps
Seeking Medical Attention for Severe Reactions
-
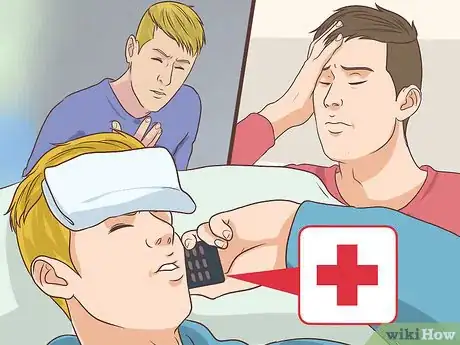
1Get immediate medical care for severe allergic reactions. In rare cases, the flu vaccine can cause a severe or life threatening allergic reaction.[3] This usually develops within a few minutes to hours of receiving the vaccine. If you have any of the following symptoms and they are severe, call emergency medical services or get to the nearest hospital as soon as possible:[4]
- Difficulty breathing.
- Hoarseness or wheezing.
- Swelling around the eyes, lips, or throat.
- Hives.
- Paleness.
- Weakness.
- Rapid heartbeat or dizziness.
-
2Contact your doctor for possible allergic reactions. Even if you don’t have symptoms of a severe or life threatening allergic reaction to the flu vaccine, you may still experience serious side effects. These also require medical attention. Call your doctor about how to proceed if you have any of the follow serious side effects:[5]Advertisement
-
3Receive medication to relieve reaction. Medical treatment depends on the type of adverse or serious reaction you have. Your doctor may give you medication or require that you stay at a hospital for monitoring. You may receive one of the following treatments for a serious reaction:[8]
- Injections of epinephrine for anaphylaxis.
- Oral or injected antihistamines for hives and/or itching.
- Hospital stay for cardiovascular reactions or loss of consciousness.
-
4Monitor your symptoms closely. In many cases, bad reactions to the flu vaccine will go away without treatment. However, it’s important to pay attention to any symptoms you may experience following the injection or treatment for an adverse reaction. If your symptoms don’t go away or get worse, contact your doctor or seek prompt medical attention. This can minimize the risk of adverse reactions and serious complications.[9]
- Contact your doctor if you are unsure of any of your side effects or how you’re feeling. It’s better to be safe than sorry with an adverse reaction.
Relieving Less Adverse Side Effects at Home
-
1Recognize common adverse reactions. Serious reactions to the flu vaccine are uncommon. However, you may still have an adverse reaction to the injection or nasal spray vaccine (The nasal flu vaccine is not currently recommended). Recognizing the common side effects of the flu vaccine can help you figure out the best way to treat them. Adverse reactions include:[10]
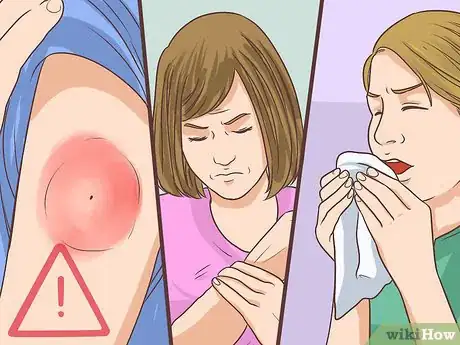
- Soreness, swelling, or redness at the injection site.
- Headache.
- Low grade fever (below 101 degrees Fahrenheit/ 38 Celsius).
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Muscle aches.
- Cough or sore throat.[11]
- Runny nose.
-
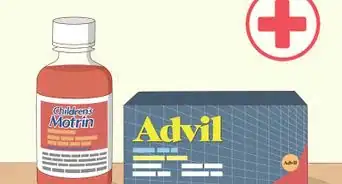
2Take ibuprofen for pain or swelling. Most side effects from the flu vaccine go away in two days. The most common adverse reactions happen at the injection site. These usually include redness, soreness, or slight swelling. Taking a pain reliever such as ibuprofen can ease any discomfort and decrease swelling.[12]
- Take an NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) such as aspirin, ibuprofen or naproxen sodium. These can relieve pain and reduce swelling or inflammation.
- Follow dosing instructions as directed on the product packaging or by your doctor.
-
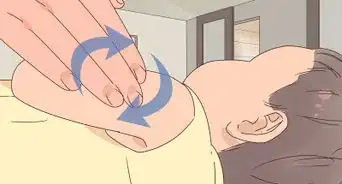
3Apply a cool compress. You may have itching, soreness, or discomfort at the injection site. You may even experience some lightheadedness or weakness. Putting a cool compress either on the injection site or your face can relieve these adverse reactions to your flu vaccine.[13]
- Place a cool washcloth or ice pack on the injection site if you have any swelling, discomfort, or redness. Use as often as necessary for 20 minutes at a time until your symptoms go away.
- Put a cool, damp washcloth on your face or neck if you have any dizziness, lightheadedness, or sweating.[14]
- Remove the compress if your skin gets too cold or numb.[15]
-
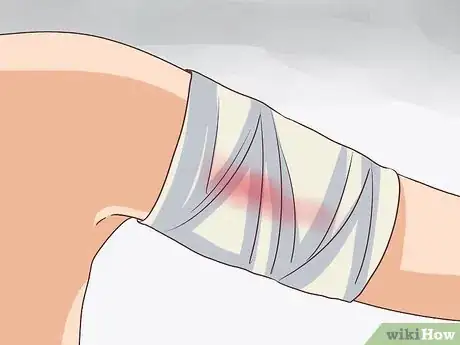
4Compress slight bleeding with a bandage. The injection site may bleed a bit following your vaccination. In some cases, it may continue to bleed slightly for a couple of days after the injection. If this happens, put an adhesive compress over the site until it stops bleeding.[16]
- Contact your doctor if the bleeding doesn’t stop within a day or two or gets worse.
-
5Sit and snack for dizziness. Some people may get dizzy or even faint with a flu shot. In general, these adverse reactions won’t last longer than a day or two. The best way to treat dizziness and prevent fainting is rest. Having a snack while you rest can boost your blood sugar and help you feel better.[17]
- Sit or even lie on the floor for a few minutes if you’re feeling dizzy. Loosening any clothing or sitting with your head between your knees may help the dizziness go away.[18]
- Eat a small snack to boost your blood sugar and help minimize any dizziness you may feel.[19] Aim to eat a healthy snack such as a piece of string cheese, toast with peanut butter, or apple slices.
-
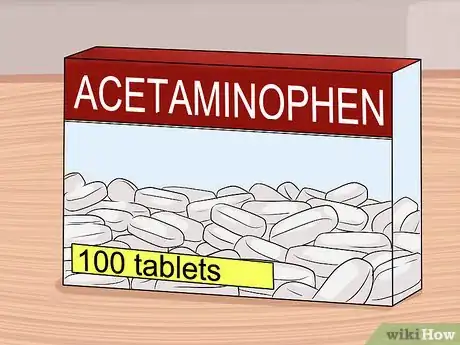
6Kill a fever with acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Many people experience a low-grade fever (below 101 degrees Fahrenheit or 38 degrees Celsius) following the flu vaccine. This is a common reaction and usually goes away within one to two days. If the fever bothers you, taking ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help decrease the your temperature as well as any discomfort you may have from it such as muscle aches.[20]
- Follow packaging instructions or your doctor’s orders for treating your fever with ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Contact your doctor right away if your fever doesn’t go away after two days or increases above 101 degrees Fahrenheit or 38 degrees Celsius.
-
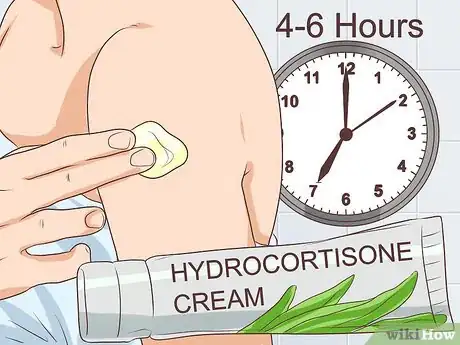
7Use an anti-itch medication. Itching at the injection site is also a common adverse reaction to a flu vaccine. In most cases, this will also go away within a day or two. However, you might find the itchiness uncomfortable. You can use an antipruritic, or anti-itch, medication to relieve any itching sensations at the injection site.
- Apply a hydrocortisone cream every four to six hours to relieve itching. If the itching is severe, your doctor may prescribe oral prednisone or methylprednisolone.
- Take an antihistamine such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or hydroxyzine (Atarax) every four to six hours to control injection site itching.
Warnings
- Do not have a child younger than 6 months vaccinated.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Do not avoid getting a flu shot if you have had a mild reaction to it in the past. Keep in mind that you can still get a flu shot even if you get sick after getting one because the formula changes every year.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Contact your doctor if you are unsure of any reactions. It’s always better to be safe than sorry.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/flu/basics/definition/con-20035101
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/general.htm
- ↑ https://www.medicinenet.com/flu_shot_side_effects/views.htm
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/general.htm
- ↑ https://www.medicinenet.com/flu_shot_side_effects/views.htm
- ↑ https://www.medicinenet.com/flu_shot_side_effects/views.htm
- ↑ http://www.immunize.org/catg.d/p3082.pdf
- ↑ http://www.immunize.org/catg.d/p3082.pdf
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/keyfacts.htm
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/general.htm
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/keyfacts.htm
- ↑ https://corporatecare.com.au/flu-vaccination/flu-vaccine/flu-vaccine-side-effects/
- ↑ http://www.immunize.org/catg.d/p3082.pdf
- ↑ http://www.immunize.org/catg.d/p3082.pdf
- ↑ https://www.randeye.com/cold-compresses/
- ↑ http://www.immunize.org/catg.d/p3082.pdf
- ↑ https://www.immunize.org/catg.d/p3082.pdf
- ↑ http://www.immunize.org/catg.d/p3082.pdf
- ↑ https://www.immunize.org/catg.d/p3082.pdf
- ↑ https://corporatecare.com.au/flu-vaccination/flu-vaccine/flu-vaccine-side-effects/
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/egg-allergies.htm


























































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...