This article was co-authored by Soren Rosier, PhD. Soren Rosier is a PhD candidate at Stanford's Graduate School of Education. He studies how children teach each other and how to train effective peer teachers. Before beginning his PhD, he was a middle school teacher in Oakland, California, and a researcher at SRI International. He received his undergraduate degree from Harvard University in 2010.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 93% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 86,033 times.
Teaching first graders to read is a rewarding task that's very important to their education. Reading is a step-by-step process, beginning with learning phonemic awareness and eventually ending with children being able to not only read words but comprehend their meaning. Practicing things like sight words and phonics rules will give your first graders the skills they need to read in groups and independently.
Steps
Teaching Important Skills
-
1Strengthen phonemic awareness skills by going over letters and sounds. It’s important for kids to recognize their letters and know which sounds each letter makes before they’re able to form words. Go over each letter of the alphabet, saying its name and which sound it makes. While you can do this as a class, it’s also a good idea to do it individually with each student so you know which letters and sounds they need help with.[1]
- Letter sounds include consonants, short vowels, long vowels, and digraphs.
- For example, when going over the letter “R,” you might say, “R makes the ‘rrrrrr’ sound, like “rat.””
-
2Help students learn to decode words by sounding them out. Once your first graders know their sounds, teach them to string these sounds together when they see them to form a word. Show them how to start from the left and sound out each sound until they get to the right, completing the word.[2]
- Some great early decodable words include “sun,” “mom,” “has,” or “shut.”
- If your first graders are having trouble stringing each sound together to form the full word, encourage them to sing each sound. This helps prevent long pauses between each one.
Advertisement -
3Practice phonics to teach your first graders important spelling patterns. There are plenty of special rules when it comes to reading where simply sounding out a word won’t work. Encourage your first graders to look at groups of letters, not just individual sounds. to Teach them special phonics rules so that they are able to recognize a written word like “bake” and know how to pronounce it.[3]
- ”Bake” would be an example of how a silent “e” often turns a short vowel into a long vowel.
- Another example of an important phonics rule might be when a syllable has 2 vowels in it, the first vowel is often long and the second is silent, such as in “rain” or “meat.”
EXPERT TIPSoren Rosier is a PhD candidate at Stanford's Graduate School of Education. He studies how children teach each other and how to train effective peer teachers. Before beginning his PhD, he was a middle school teacher in Oakland, California, and a researcher at SRI International. He received his undergraduate degree from Harvard University in 2010.PhD in Education Candidate, Stanford University
 Soren Rosier, PhD
Soren Rosier, PhD
PhD in Education Candidate, Stanford UniversityExperiment to find which approach works best for each child. Phonics certainly helps children learn to read, especially if they're struggling. However, some children do better with the whole word approach, where they focus on the word and its meaning, rather than breaking it down into its subparts.
-
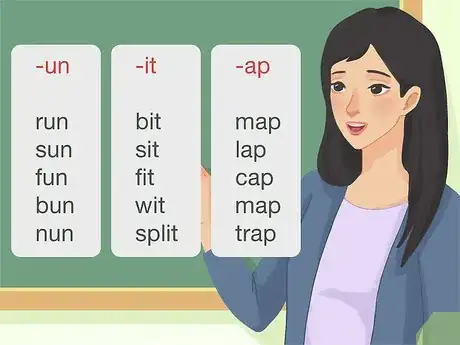
4Teach word families to help them learn rhyming words. Not only does this help them learn word endings much more quickly, but it teaches them that there are patterns in words and that beginning sounds can be changed to alter the meaning of words. Go over words with endings like “-un,” “-it,” or “-ap.”
- For example, words that end in “-un” might be run, sun, fun, bun, nun, or spun.
- Other word families to teach are “-ip,” “-ing,” “-ack,” and “-op.”
-
5Go over sight words to encourage memorization. Sight words, or high frequency words, are words that your first graders will encounter often. Many of them aren’t easy to sound out because they don’t follow traditional phonics rules. Make flashcards or write sight words on the board to help first graders begin to memorize these words.[4]
- Look for first grade sight word lists online, including words like "learn," "any," or "because."
- Your first grader knows a sight word once they’re able to immediately say the word without hesitating or having to sound it out.
- Encourage your students to write these words and say them out loud when they’re learning them to help them remember the words more easily.
-
6Incorporate spelling into reading lessons whenever possible. While spelling may not seem like the most important tool to teach reading, spelling words correctly will help your first graders read the word correctly faster. Write out words that coincide with phonics rules you’re learning, or have your first grader write down words they’re having trouble reading as extra reading and writing practice.[5]
- Have your first graders write out each word in a word family to practice spelling and saying them.
- Once your first grader is able to read a sight word, instead of showing it to them, say it out loud and ask them to write it down.
-
7Use hands-on activities to make learning to read more interactive. While simply reading texts and going over words in print can work, getting kids more physically involved in reading will get them more excited to learn. Use foam phonics dice to create words with your first graders or pull out letter magnets to use when you’re teaching sounds. Any sort of activity that gets them moving or that they can manipulate will improve their reading skills.
- Give each child a handful of letter magnets and ask them to say each letter and its sound.
- Sing songs about phonics to help reinforce special rules that they might be struggling to remember.
- Write different sight words on flashcards and place them along the floor, encouraging students to hop from one word to the next once they say them correctly.
Choosing Texts and Reading Aloud
-
1Give first graders reading level assessments so you can choose texts for them. Before you pick out books for your first graders to read, it’s important to know which level they’re on so you’re not choosing books that are too difficult or too easy for each reader. Use a reading level assessment like Reading A-Z and then give each student texts based on their discovered reading level.[6]
- If you’re working with students in small groups, place students with similar reading levels in the same groups.
- For example, if the reading assessment you used said Johnny was on a level C, you would choose books that are on this level for him to read.
- If you have specific books in mind and aren’t sure what their reading level is, type the name of the book and then “reading level” into an online search engine to find out.
-
2Choose texts below each student’s frustration level for independent reading. When your first grader is reading by themselves, it’s important that they feel confident and able to sound out each word independently. Choose books that won’t trip them up and include words or sounds that they’re able to figure out without assistance.[7]
- If students are reading independently in the classroom, you might ask them to whisper read so you can walk around and listen to them.
- If you're using a specific reading program, they will likely have texts for you to use that are all labeled with their reading levels.
- If you're not using a reading program, you might encourage your first grader to read "Go, Dog. Go!" by P.D. Eastman or "Clifford the Big Red Dog" by Norman Bridwell, though you'll want to check to ensure these books coincide with their specific reading level.
-
3Offer help when your first graders are reading more difficult texts. When you’re working 1-on-1 or in small groups, use texts that are a bit more challenging than the ones they would read by themselves. Go over tricky words they might encounter in the book before starting, and listen to them read these texts to help them whenever they’re struggling.[8]
- Choosing a book that’s one level above their independent reading level is often a good place to start when doing group work.
-
4Ask questions about the reading to help with their comprehension. As you’re reading a text aloud to students, or when they’re reading a text aloud to you, pause to ask questions about what’s happening. This teaches your first graders to pay attention to what they’re reading and understand the meaning behind each sentence, improving their comprehension skills.[9]
- You might ask, “Why did the fox hide in the shed?” or “How do you think that made the brother feel?”
- Encourage kids to ask questions throughout their reading whenever they don’t understand something.
-
5Read aloud to students to introduce them to new vocabulary. Children are never too old to be read to, and this is a simple way you can introduce new words and talk about comprehension with your first graders. Pick out a book that’s age appropriate and that talks about things you’re learning about as a class, such as certain phonics rules or even a holiday or event you’ve discussed.[10]
- Ask your first graders questions about events and characters throughout the book to keep them engaged, and explain the meaning of any tricky words.
- You might read books to your first graders like "Cloudy with a Chance of Meatballs" by Judi Barrett or "Stand Tall, Molly Lou Melon" by Patty Lovell.
-
6Have students read to you 1-on-1 to offer individualized help. This is a great time to listen to each of your students read to you, making note of any words they’re stumped by or how quickly or slowly they’re reading. Listen carefully as they’re reading and offer support when it’s needed.[11]
- Having them read to you individually is also how you’ll test their reading to see if they need to stay on the same reading level or move up.
-
7Select texts that are engaging to get them excited about reading. You’ll have a much harder time convincing your first graders that reading is fun when you’re reading texts that aren’t interesting to them. Choose books that are fun, silly, or related to a topic they find interesting to get them engaged and motivated to read.[12]
- Some days you might give your first graders a selection between 2 or 3 books that are their reading level and let them choose which one they’d like to read.
- Some engaging texts include books by Mo Willems or James Dean.
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionHow do you help students who are struggling with reading?
 Soren Rosier, PhDSoren Rosier is a PhD candidate at Stanford's Graduate School of Education. He studies how children teach each other and how to train effective peer teachers. Before beginning his PhD, he was a middle school teacher in Oakland, California, and a researcher at SRI International. He received his undergraduate degree from Harvard University in 2010.
Soren Rosier, PhDSoren Rosier is a PhD candidate at Stanford's Graduate School of Education. He studies how children teach each other and how to train effective peer teachers. Before beginning his PhD, he was a middle school teacher in Oakland, California, and a researcher at SRI International. He received his undergraduate degree from Harvard University in 2010.
PhD in Education Candidate, Stanford University Help them identify books that are within their independent reading level. If kids are reading texts that are above their independent reading level, they're going to be struggling through them, and they're going to hate reading, and they're not going to want to read. It is also very important is talking to kids about their interests, the kinds of books they like to read, help them find books that they'd be really interested in. Then, phonics certainly works, and it can be particularly useful for struggling readers and kids with dyslexia who tend to need a lot more time than other kids. With phonics you help them build associations between letters and sounds, and if they get a lot of that help early on, it can be a big difference maker. It does a lot of damage to a kids' learning trajectory if they have dyslexia and they don't get all that reading support early on.
Help them identify books that are within their independent reading level. If kids are reading texts that are above their independent reading level, they're going to be struggling through them, and they're going to hate reading, and they're not going to want to read. It is also very important is talking to kids about their interests, the kinds of books they like to read, help them find books that they'd be really interested in. Then, phonics certainly works, and it can be particularly useful for struggling readers and kids with dyslexia who tend to need a lot more time than other kids. With phonics you help them build associations between letters and sounds, and if they get a lot of that help early on, it can be a big difference maker. It does a lot of damage to a kids' learning trajectory if they have dyslexia and they don't get all that reading support early on.
References
- ↑ https://www.readingrockets.org/article/first-grade-instruction
- ↑ https://www.learnwithhomer.com/homer-blog/5796/sound-out-words/
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3UGSFKYDRyc
- ↑ https://brownbagteacher.com/guided-reading-1st-grade-style/
- ↑ https://www.theclassroom.com/teach-first-grade-reading-4450424.html
- ↑ https://brownbagteacher.com/guided-reading-1st-grade-style/
- ↑ https://www.readingrockets.org/article/first-grade-instruction
- ↑ https://www.readingrockets.org/article/first-grade-instruction
- ↑ https://www.theclassroom.com/teach-first-grade-reading-4450424.html