X
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 17 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 249,071 times.
Learn more...
Microsoft's Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is the standard language for writing programs to automate functions and tasks in Microsoft Office. Understand how to protect VBA code so others can't sabotage or steal your macros.
For unprotection and removal of VBA passwords, see this article.
Steps
Method 1
Method 1 of 3:
Secure VBA Code with a Password
-
1
-
2Go to the "Protection" tab.Advertisement
-
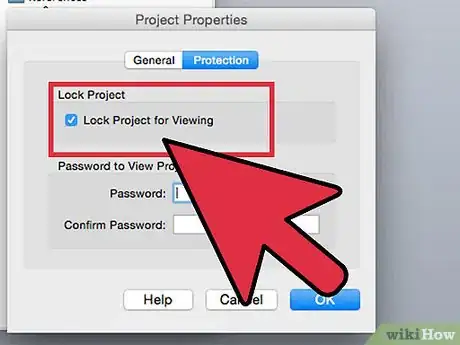
3Select the "Lock Project for Viewing" check box. If you don't check this box, you won't hide your code.
-
4Create and confirm your desired password in the indicated boxes.
-
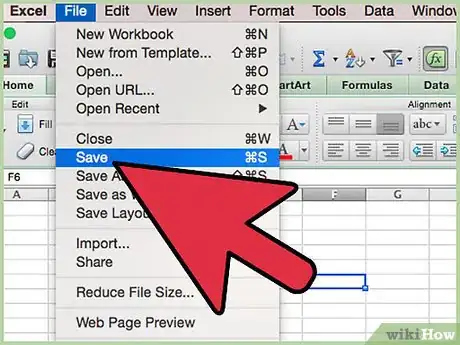
5Save, close, and reopen your workbook for the protection to take effect. (In Microsoft Excel 2007 and later, you may need to save as an XLSM file for your code to work.)
Advertisement
Method 2
Method 2 of 3:
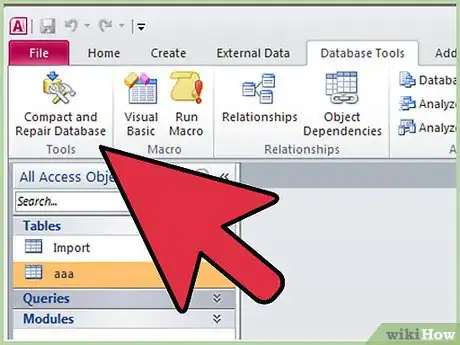
Hide VBA Code in a Read-Only File with Access 2007
Method 3
Method 3 of 3:
Protect Your VBA Code by Making an Add-In
-
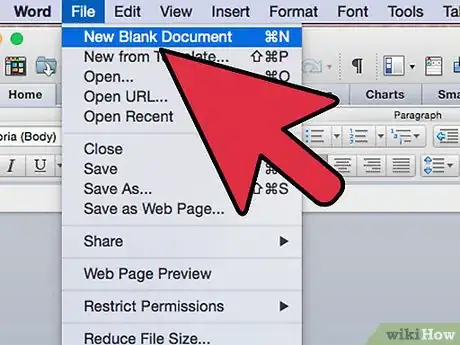
1Create an empty Office file of the type that will use your code. (For example, if your code works with MS Excel, create an Excel file.)
-
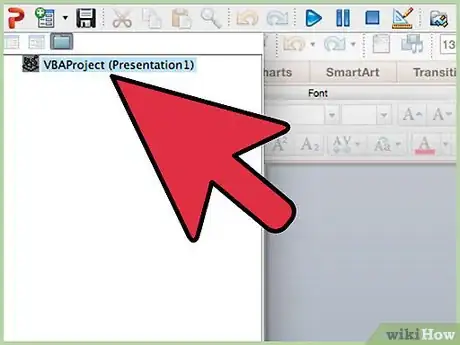
2Copy your VBA code into the Visual Basic Editor of that empty file.
-
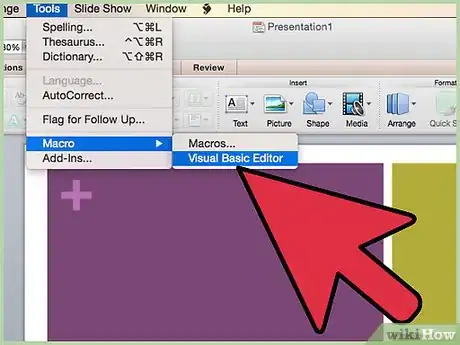
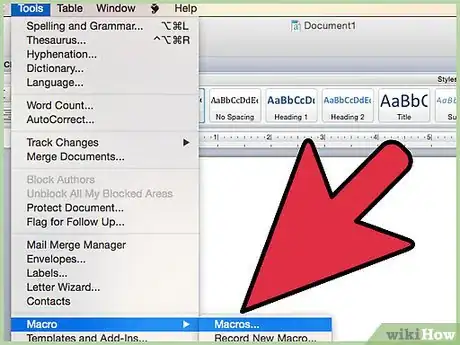
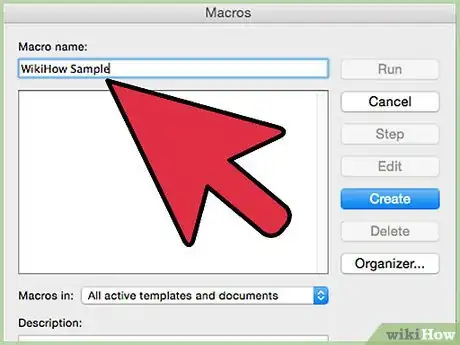
3Open the "Macros" window, usually stored under "Tools."
-
4Test your code again, which debugs it.
-
5Remove anything added to the empty file by your test.
-
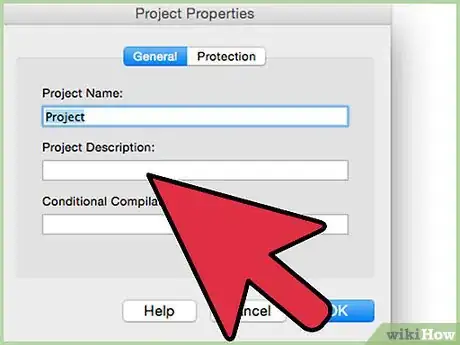
6Add a description to the macro that will run in your add-in. (You may need to select macro "Options" to be able to insert the description.)
-
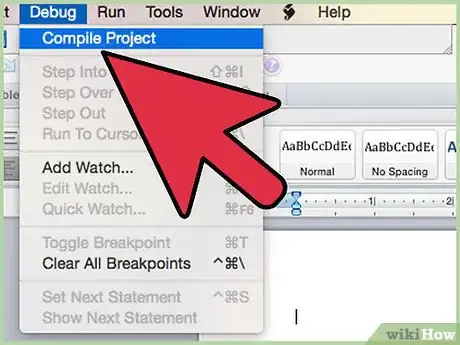
7Compile your code. (In the Visual Basic Editor, look under the "Debug" menu and select "Compile VBA Project.")
-
8Save a copy of the file in a standard file type.
-
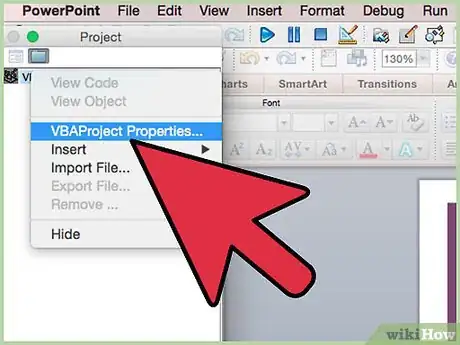
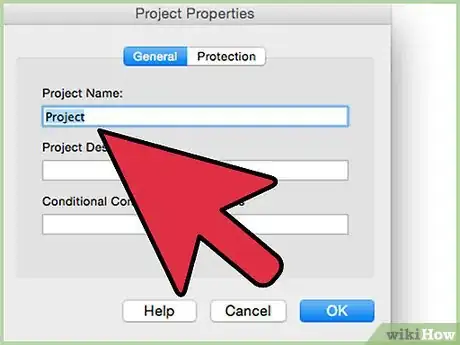
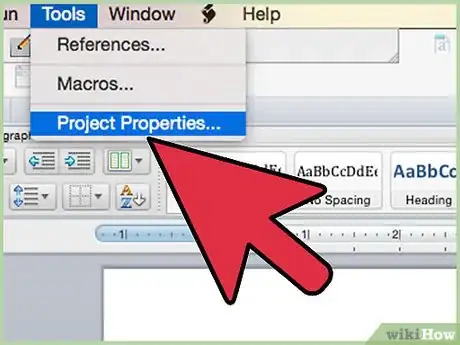
9Go to "Tools" in the Visual Basic Editor, then select "Project Properties."
-
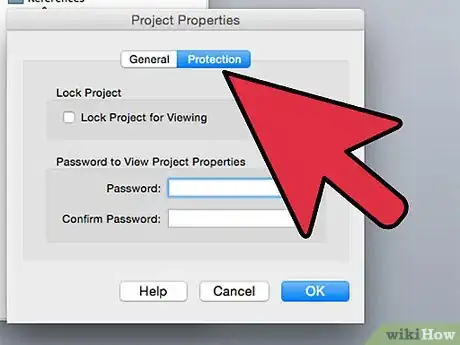
10Select the "Protection" tab.
-
11Activate the "Lock Project for Viewing" check box. (You may also need to set a password, depending on the specific file type you're working with and your settings for MS Office and your computer.)
-
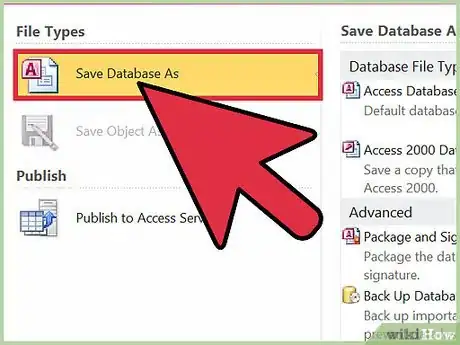
12Open the "Save As�" or "Save a Copy" dialog box.
-
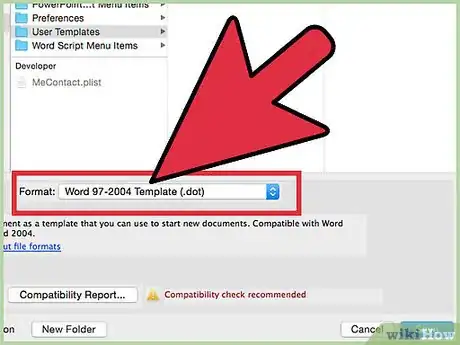
13Access the drop-down menu and change the file type to the appropriate type of add-in.
- Save a Microsoft Word add-in as a DOT file, a document template. (If you want the add-in to run when you start Word, save it in the Word Startup folder.)
- Save a Microsoft Excel add-in as an XLA file.
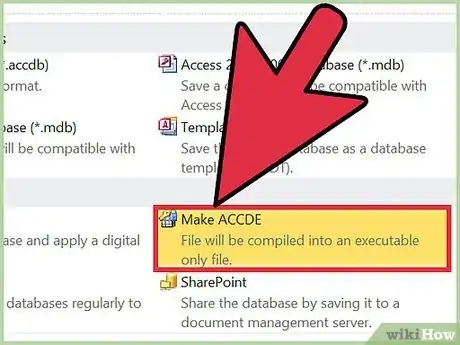
- Save a Microsoft Access add-in as a MDE file, which will protect the VBA code. (Microsoft Access add-ins can also be saved as MDA files, but this doesn't hide the code.)
- Save a Microsoft PowerPoint add-in as a PPA file which will hide the VBA code and leave it unable for anyone other than you to access it or edit it.
-
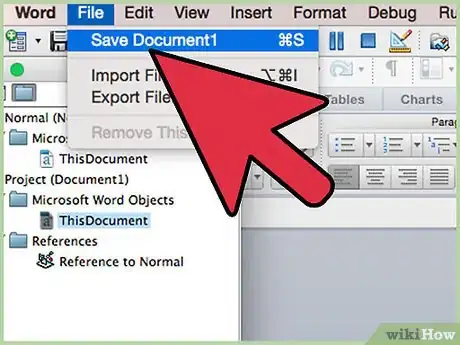
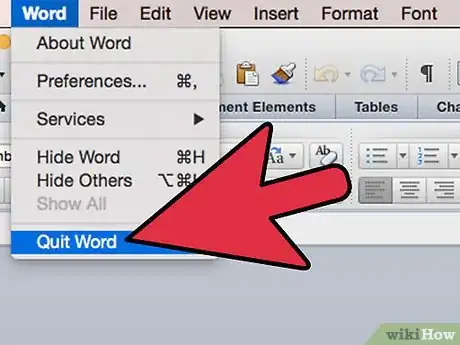
14Quit and reopen Microsoft Office. Your add-ins should now be usable.
Advertisement
Community Q&A
-
QuestionWhat if I forgot my password to open the VBA project? Will it become unrecoverable?
 Sylvia SaltaformajoCommunity AnswerUnfortunately yes, you won't be able to recover it using VBA editor you used to set the password. However, VBA passwords are easily removed by password recovery software such as Password-Find, Password Lastic, Rixler, etc, you can find it online.
Sylvia SaltaformajoCommunity AnswerUnfortunately yes, you won't be able to recover it using VBA editor you used to set the password. However, VBA passwords are easily removed by password recovery software such as Password-Find, Password Lastic, Rixler, etc, you can find it online.
Advertisement
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Visual_Basic_for_Applications
- http://www.ozgrid.com/VBA/protect-vba-code.htm
- http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/access-help/hide-vba-code-from-users-HA010239557.aspx?CTT=1
- https://www.stl-training.co.uk/article-371-vba-excel-2007.html
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/Aa140937
- http://www.fontstuff.com/vba/vbatut03.htm
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa141032
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa140944
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa141283
About This Article
Advertisement