This article was co-authored by Laura Marusinec, MD. Dr. Marusinec is a board certified Pediatrician at the Children's Hospital of Wisconsin, where she is on the Clinical Practice Council. She received her M.D. from the Medical College of Wisconsin School of Medicine in 1995 and completed her residency at the Medical College of Wisconsin in Pediatrics in 1998. She is a member of the American Medical Writers Association and the Society for Pediatric Urgent Care.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, several readers have written to tell us that this article was helpful to them, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 231,640 times.
A fever can result from a variety of sources — viruses, bacterial infection, or even the common cold — causing discomfort for your baby. Fevers are a natural reaction by the body to fight off an infection or illness. It is characterized by a temporary increase in body temperature, which can be concerning and uncomfortable after it reaches 103°F (39.4°C) or higher. For babies, a fever can sometimes indicate something more serious, so you should observe your baby closely. As a parent or caregiver, you will want to take the necessary steps to relieve baby's discomfort.
Steps
Treating the Fever at Home
-
1Drink plenty of fluids. Keep your baby hydrated by providing plenty of fluids. Fevers cause excessive sweating and, therefore, the loss of fluids is greater and could lead to dehydration.[1] Talk to your doctor about offering an electrolyte solution such as Pedialyte in addition to formula.
- Avoid feeding your baby fruit or apple juice or dilute it with fifty percent water.
- Popsicles or gelatin are also acceptable.
- Avoid caffeinated drinks because they force urination and the loss of fluids.
- Offer your baby his usual diet but realize that your baby may not want to eat as much when he has a fever. Try offering bland foods such as breads, crackers, pastas, and oatmeal.
- Infants who are breastfeeding should only drink breast milk. Keep them hydrated by giving them plenty of breast milk.
- Never force your baby to eat if food is refused.
-
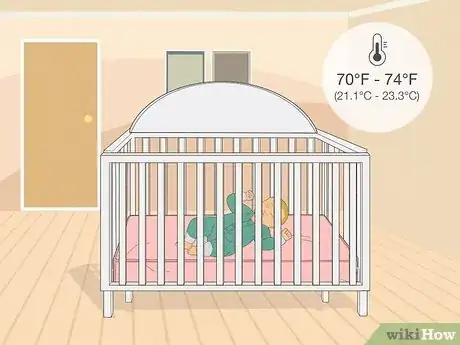
2Rest in a comfortable room. Do not overexert your baby or her temperature might rise. Instead, place your baby in a room with a comfortable temperature between 70°F to 74°F (21.1°C to 23.3°C).[2]
- Avoid running the heater nonstop so that your baby does not overheat.
- Same with the air conditioner. Keep it off so your baby doesn't shiver and raise her temperature.
Advertisement -
3Dress your baby in light clothing. Even heavy clothing on a baby can raise his temperature. Overdressing your baby can trap heat making your baby more miserable.[3]
- Keep your baby comfortably dressed and cover him with a light blanket if the temperature is too cold in the room or you notice your baby shivering. Adjust the room temperature as needed to keep your baby comfortable.
-
4Provide a lukewarm bath. Not too hot and not too cold, a lukewarm bath could alleviate a fever.[4]
- If you plan to give your baby a lukewarm bath, give her some medicine to make sure her temperature does not rise after getting out of the bath.
- Avoid cold baths, ice, or alcohol rubs. These will cause your baby to shiver and make the situation even worse.
-
5Give medicine. Be cautious giving your baby Tylenol, Advil, or Motrin. Read the label carefully to make sure you are giving the right dosage for the right age. It might even be a good idea to consult a healthcare professional before giving your baby a fever medication.[5]
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) is usually what the doctor or nurse recommends for fevers in babies.
- If your baby is under three months old, call the doctor before administering medication.
- Do not go over the recommended dosage or there is a potential it could cause liver or kidney damage, or worse, it could be fatal.
- Acetaminophen can be taken every four to six hours and Ibuprofen can be taken every six to eight hours as long as the baby is older than six months old.
- Keep track of what medicine you give, how much, and when you gave it, so as not to overdose your child.
- For temperatures under 102°F (38.9°C), try to refrain from using medication unless the doctor or nurse suggests it.
- Never give aspirin to babies it could trigger a rare, but fatal, disorder called Reye's syndrome.
Seeking Medical Attention
-
1Check for a rise in temperature. Even a low-grade fever could indicate a serious infection in babies. Therefore, depending on the age of your baby, a significant rise in temperature demands a call to the pediatrician.[6]
- For newborn babies up to three months old that have a temperature of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, you should contact a pediatrician for instructions.
- If your baby is older than three months old with a 102°F (38.9°C) and the fever lasts longer than a day, call your pediatrician.
- If you are ever in doubt, make a call to the pediatrician just to be safe.
-
2Call your pediatrician. If your baby has a fever but continues to play and eat normally, then there is usually no major concern at that time. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends calling a pediatrician if your infant is under three months old and has a temperature of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher. If your baby is older than three months and has a fever longer than 24 hours and has other symptoms such as coughing, earache, loss of appetite, vomiting, or diarrhea, call your pediatrician or visit an urgent care clinic.[7]
- If your baby is not alert or comfortable when the fever subsides, is very irritable, has a stiff neck, or no tears appear when baby cries, contact your doctor right away.
- If your child has any special medical problems such as heart problems, immune problems, or sickle cell disease, make sure to check with your doctor when he has a fever.
- Call your doctor if your child has a fever that lasts longer than 48 hours and a decreasing number of wet diapers, or excessive diarrhea or nausea, as this could indicate an illness that should be evaluated.
- Call your doctor if your child has a fever over 105°F (40.5°C) or has a fever for more than three days.
- Dial 9-1-1 if your baby has a fever and seems confused, cannot walk, difficulty breathing, or lips, tongue, or nails become blue.
-
3Prepare to go. If your baby needs medical attention make sure you take along all of the necessary information to ensure baby gets treated correctly and promptly. You should also be prepared to find out what to expect while you are at the doctor's office.[8]
- Record all of the necessary information about your baby's fever: when the fever started, how long ago you took your baby's temperature and informing the doctor of any other symptoms.
- Make a list of medications, vitamins, and supplements that your baby is taking and if your baby is allergic to anything.
- Think about questions to ask the doctor like what is causing the fever; what kind of tests need to be performed; what is the best approach for treatment; and will my baby need to take any medications?
- Be ready to answer the doctor's questions: when did the symptoms begin; did your baby take medication and if yes, when; what did you do to try and alleviate the fever?
- Prepare for the fact that your baby might have to be admitted to the hospital for observation or more testing if your baby is very ill or is younger than 3 months old.
Preventing Future Fevers
-
1Make sure your baby is up to date with all of her immunizations. Keeping on top of your child's immunizations — including her yearly flu shot — will help decrease the likelihood of her getting sick.
-
2Wash your hands. In nearly all situations, keep your hands clean since your hand is the direct part of your body that comes into contact with germs and transfers it to other parts of the body.[9]
- Wash hands, in particular, before eating, after using the toilet, petting or playing with an animal, using public transportation, or after visiting a sick person.
- Make sure to wash your hands thoroughly — front and back, between fingers, under your nails, and for at least twenty seconds with warm water and soap.
- Keep hand sanitizer with you when you travel or do not have access to soap and water.
-
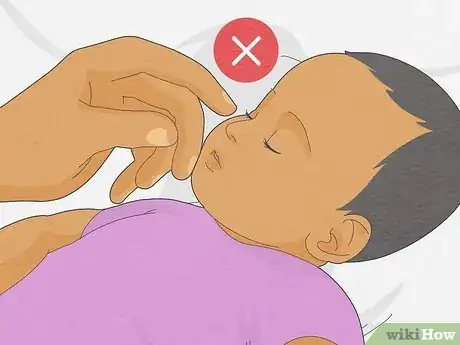
3Don't touch the “T” zone. The T zone consists of the forehead, nose, and chin that forms the letter “T” on the front of the face. The nose, mouth, and eyes that, located within the T, are the primary points of entry for viruses and bacteria to enter the body and cause infection.[10]
- Guard against all bodily fluids that exit the “T” zone as well: cover your mouth when you cough, your mouth and nose when you sneeze and wipe your nose when it is runny (then wash your hands!).
-
4Keep your baby home when he is sick. Keep your child home and out of daycare when he is ill or has a fever to prevent spreading it to others. If you know friends or family are sick, try to keep your baby away from these people until they are well again.
-
5Avoid sharing. Try not to share drinking cups, water bottles, or utensils with your baby since this is an easy way to transfer germs from one person to another, especially from parent to baby, who has not built an adequate immune system yet.[11]
- Avoid putting your baby's binky in your mouth as a way to clean it and then putting it back into your baby's mouth. Adult germs are powerful inside the baby's mouth and can easily cause illness. The same goes for toothbrushes.
References
- ↑ https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/patientinstructions/000319.htm
- ↑ https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/patientinstructions/000319.htm
- ↑ https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/patientinstructions/000319.htm
- ↑ https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/patientinstructions/000319.htm
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/fever/basics/treatment/con-20019229
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/fever/basics/symptoms/con-20019229
- ↑ https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/patientinstructions/000319.htm
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/fever/basics/preparing-for-your-appointment/con-20019229
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/fever/basics/prevention/con-20019229
About This Article
To make a baby with a fever feel better, make sure they're drinking plenty of fluids, since fevers can cause excessive sweating and dehydration. Help your baby rest comfortably by keeping the temperature of their room between 70 and 74 degrees Fahrenheit, so they don't overheat. Similarly, dress your baby in light clothing to keep them cool, but cover them with a light blanket if you notice them shivering. You can also give your baby a lukewarm bath to alleviate their fever, as long as you give them some pediatrician-approved medication as well, so their temperature doesn't rise after the bath. Because even a low-grade fever could indicate a serious infection in babies, call your pediatrician and schedule an appointment if you notice your baby's temperature is over 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit. For more tips from our Medical co-author, including how to prevent your baby from getting a fever, scroll down!

































































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...