X
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 25 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 240,333 times.
Learn more...
This guide will show you how you can store your sessions securely in a mySQL database. We will also encrypt all session data that goes into the database, which means if anyone manages to hack into the database all session data is encrypted by 256-bit AES encryption.
Steps
Method 1
Method 1 of 3:
Configure mySQL Database
-
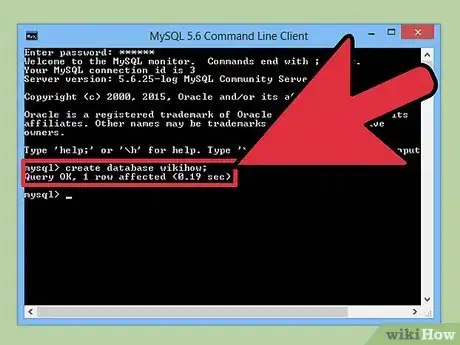
1Create a MySQL database.
In this guide we will create a database called "secure_sessions".
See how to Create-a-Database-in-phpMyAdmin.
Or you can use the SQL code below will create one for you.
Create Database Code:Note: Some hosting services don't allow you to create a database through phpMyAdmin, Learn how to do it in cPanel.CREATE DATABASE `secure_sessions` ;
-
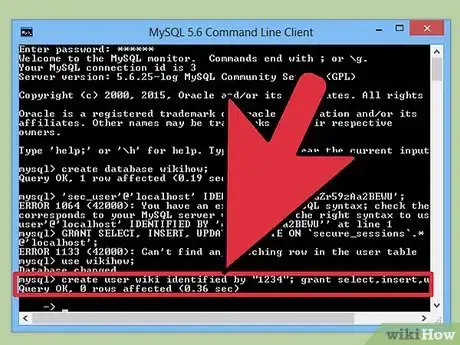
2Create a user with only SELECT, INSERT and DELETE privileges.
This means that if there was ever a breach of security in our script the hacker couldn't drop tables from our database. If you're really paranoid, create a different user for each function.- User: "sec_user"
- Password: "eKcGZr59zAa2BEWU"
Create User Code:CREATE USER 'sec_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'eKcGZr59zAa2BEWU'; GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON `secure_sessions`.* TO 'sec_user'@'localhost';
Note: It is a good idea to change the password in the code above when running on your own server. (Make sure you change your PHP code also.) Remember it doesn't need to be a password that you can remember so make is as complicated as possible. Here's a random password generator.Advertisement -
3Create a MySQL table named "sessions".
The code below creates a table with 4 fields (id, set_time, data, session_key).
Create the "sessions" table:We use the CHAR datatype for fields we know the length of, as the fields "id" and "session_key" will always be 128 characters long. Using CHAR here saves on processing power.CREATE TABLE `sessions` ( `id` char(128) NOT NULL, `set_time` char(10) NOT NULL, `data` text NOT NULL, `session_key` char(128) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
Advertisement
Method 2
Method 2 of 3:
Create session.class.php file
-
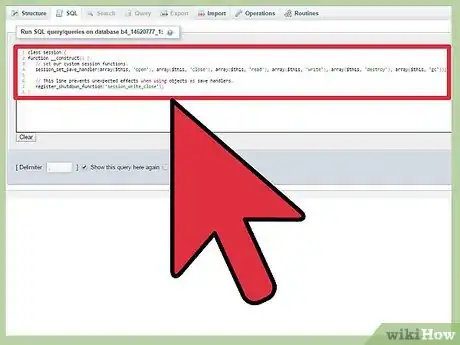
1Create Class.
To start a new class you will need to enter the code below:
New Class:class session {
-
2Create __construct function.
This function will be called every time we create a new instance of an object using the 'session' class. You can read up on the PHP __construct function here.
This function sets our custom session handler so it is available for use as soon as the class is instantiated (i.e., made/built/constructed).
__construct function:function __construct() { // set our custom session functions. session_set_save_handler(array($this, 'open'), array($this, 'close'), array($this, 'read'), array($this, 'write'), array($this, 'destroy'), array($this, 'gc')); // This line prevents unexpected effects when using objects as save handlers. register_shutdown_function('session_write_close'); }
-
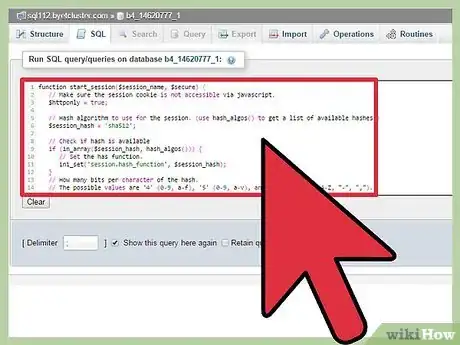
3Create start_session function.
This function will be called every time you want to start a new session, use it instead of session_start();. See the comments in the code to see what each line does.
start_session function:function start_session($session_name, $secure) { // Make sure the session cookie is not accessible via javascript. $httponly = true; // Hash algorithm to use for the session. (use hash_algos() to get a list of available hashes.) $session_hash = 'sha512'; // Check if hash is available if (in_array($session_hash, hash_algos())) { // Set the has function. ini_set('session.hash_function', $session_hash); } // How many bits per character of the hash. // The possible values are '4' (0-9, a-f), '5' (0-9, a-v), and '6' (0-9, a-z, A-Z, "-", ","). ini_set('session.hash_bits_per_character', 5); // Force the session to only use cookies, not URL variables. ini_set('session.use_only_cookies', 1); // Get session cookie parameters $cookieParams = session_get_cookie_params(); // Set the parameters session_set_cookie_params($cookieParams["lifetime"], $cookieParams["path"], $cookieParams["domain"], $secure, $httponly); // Change the session name session_name($session_name); // Now we cat start the session session_start(); // This line regenerates the session and delete the old one. // It also generates a new encryption key in the database. session_regenerate_id(true); }
-
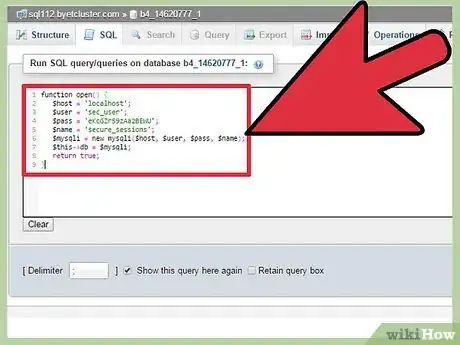
4Create open function.
This function will be called by the PHP sessions when we start a new session, we use it to start a new database connection.
open function:function open() { $host = 'localhost'; $user = 'sec_user'; $pass = 'eKcGZr59zAa2BEWU'; $name = 'secure_sessions'; $mysqli = new mysqli($host, $user, $pass, $name); $this->db = $mysqli; return true; }
-
5Create close function.
This function will be called when the sessions want to be closed.
close function:function close() { $this->db->close(); return true; }
-
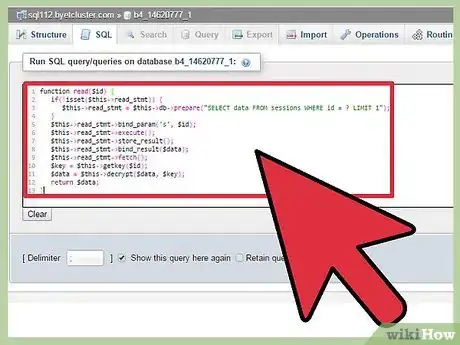
6Create read function.
This function will be called by PHP when we try to access a session for example when we use echo $_SESSION['something'];. Because there might be many calls to this function on a single page, we take advantage of prepared statements, not only for security but for performance also. We only prepare the statement once then we can execute it many times.
We also decrypt the session data that is encrypted in the database. We are using 256-bit AES encryption in our sessions.
read function:function read($id) { if(!isset($this->read_stmt)) { $this->read_stmt = $this->db->prepare("SELECT data FROM sessions WHERE id = ? LIMIT 1"); } $this->read_stmt->bind_param('s', $id); $this->read_stmt->execute(); $this->read_stmt->store_result(); $this->read_stmt->bind_result($data); $this->read_stmt->fetch(); $key = $this->getkey($id); $data = $this->decrypt($data, $key); return $data; }
-
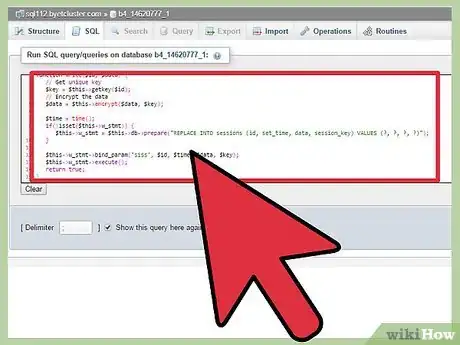
7Create write function.
This function is used when we assign a value to a session, for example $_SESSION['something'] = 'something else';. The function encrypts all the data which gets inserted into the database.
write function:function write($id, $data) { // Get unique key $key = $this->getkey($id); // Encrypt the data $data = $this->encrypt($data, $key); $time = time(); if(!isset($this->w_stmt)) { $this->w_stmt = $this->db->prepare("REPLACE INTO sessions (id, set_time, data, session_key) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)"); } $this->w_stmt->bind_param('siss', $id, $time, $data, $key); $this->w_stmt->execute(); return true; }
-
8Create destroy function.
This function deletes the session from the database, it is used by php when we call functions like session__destroy();.
destroy function:function destroy($id) { if(!isset($this->delete_stmt)) { $this->delete_stmt = $this->db->prepare("DELETE FROM sessions WHERE id = ?"); } $this->delete_stmt->bind_param('s', $id); $this->delete_stmt->execute(); return true; }
-
9Create gc (garbage collector) function.
This function is the garbage collector function it is called to delete old sessions. The frequency in which this function is called is determined by two configuration directives, session.gc_probability and session.gc_divisor.
gc() function:function gc($max) { if(!isset($this->gc_stmt)) { $this->gc_stmt = $this->db->prepare("DELETE FROM sessions WHERE set_time < ?"); } $old = time() - $max; $this->gc_stmt->bind_param('s', $old); $this->gc_stmt->execute(); return true; }
-
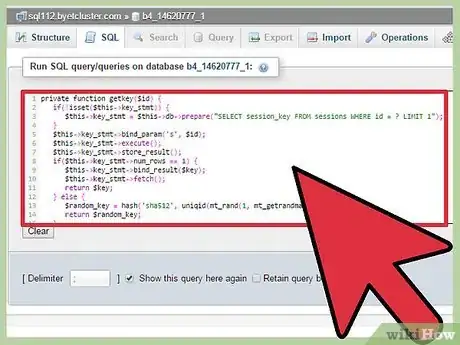
10Create getKey function.
This function is used to get the unique key for encryption from the sessions table. If there is no session it just returns a new random key for encryption.
getkey() Function:private function getkey($id) { if(!isset($this->key_stmt)) { $this->key_stmt = $this->db->prepare("SELECT session_key FROM sessions WHERE id = ? LIMIT 1"); } $this->key_stmt->bind_param('s', $id); $this->key_stmt->execute(); $this->key_stmt->store_result(); if($this->key_stmt->num_rows == 1) { $this->key_stmt->bind_result($key); $this->key_stmt->fetch(); return $key; } else { $random_key = hash('sha512', uniqid(mt_rand(1, mt_getrandmax()), true)); return $random_key; } }
-
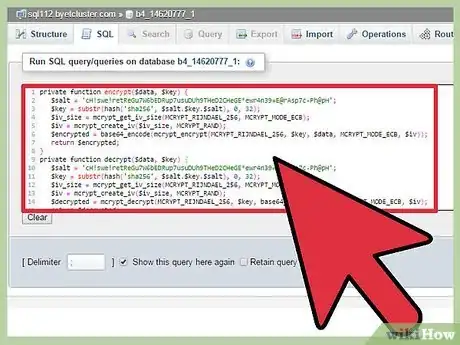
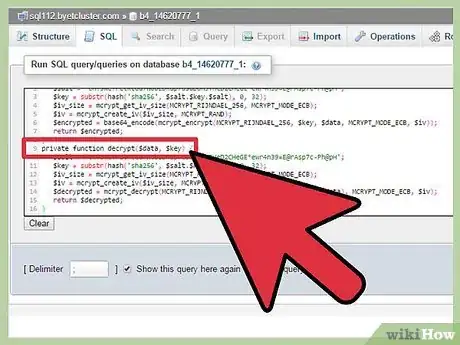
11Create encrypt and decrypt functions.
These functions encrypt the data of the sessions, they use an encryption key from the database which is different for each session. We don't directly use that key in the encryption but we use it to make the key hash even more random.
encrypt() and decrypt() functions:private function encrypt($data, $key) { $salt = 'cH!swe!retReGu7W6bEDRup7usuDUh9THeD2CHeGE*ewr4n39=E@rAsp7c-Ph@pH'; $key = substr(hash('sha256', $salt.$key.$salt), 0, 32); $iv_size = mcrypt_get_iv_size(MCRYPT_RIJNDAEL_256, MCRYPT_MODE_ECB); $iv = mcrypt_create_iv($iv_size, MCRYPT_RAND); $encrypted = base64_encode(mcrypt_encrypt(MCRYPT_RIJNDAEL_256, $key, $data, MCRYPT_MODE_ECB, $iv)); return $encrypted; } private function decrypt($data, $key) { $salt = 'cH!swe!retReGu7W6bEDRup7usuDUh9THeD2CHeGE*ewr4n39=E@rAsp7c-Ph@pH'; $key = substr(hash('sha256', $salt.$key.$salt), 0, 32); $iv_size = mcrypt_get_iv_size(MCRYPT_RIJNDAEL_256, MCRYPT_MODE_ECB); $iv = mcrypt_create_iv($iv_size, MCRYPT_RAND); $decrypted = mcrypt_decrypt(MCRYPT_RIJNDAEL_256, $key, base64_decode($data), MCRYPT_MODE_ECB, $iv); $decrypted = rtrim($decrypted, "\0"); return $decrypted; }
-
12End Class.
Here we just end the classes curly brackets:
End Class:}
Advertisement
Community Q&A
-
QuestionWhen and where do I call the open(), encrypt() and decrypt() functions?
 Community AnswerYou do not call these functions. These functions are for PHP to call itself.
Community AnswerYou do not call these functions. These functions are for PHP to call itself. -
QuestionWhat do I do if I get an "Unable to use session__destroy(); getting Uncaught Error: Call to undefined function session__destroy() error?"
 Community AnswerTake a look at step 8. Make sure that the function exists before the your script uses it.
Community AnswerTake a look at step 8. Make sure that the function exists before the your script uses it.
Advertisement
About This Article
Advertisement