This article was co-authored by MacKenzie Cain. MacKenzie Cain is an Interior Designer and a LEED-certified Green Associate for Habitar Design based in Chicago, Illinois. She has over seven years of experience in interior design and architectural design. She received a BA in Interior Design from Purdue University in 2013 and received her LEED Green Associate certification from the Green Building Certification Institute in 2013.
There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 86% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 126,138 times.
Standing for "Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, LEED certification designated buildings that take exceptional steps towards sustainable architecture. LEED was created by the U.S. Green Building Council and provides a set of standards to help building owners or builders decrease their environmental impact and utilize resources effectively. Whether you want to become a LEED certified professional or you want to certify your building with LEED, read on to learn how to navigate the LEED process.
Steps
Becoming a LEED Green Associate
-
1Understand the LEED credentialing progression. The LEED v3 credentialing process has three tiers for individual certification. No matter what path you plan to take in green building, you must become a LEED Green Associate (GA) before proceeding with certification. The GA exam covers the basics of the LEED Green Building Rating Systems.[1]
-
2Know the qualifications to become LEED certified. At minimum, you must be 18 years old. The Green Buildings Council also highly recommends that you have experience with LEED design and green building practices, found through any combination of the following:
- Educational background in environmental design.
- Work/Internship experience on green building projects.
- Volunteer work with LEED or similar green building certifications.[2]
Advertisement -
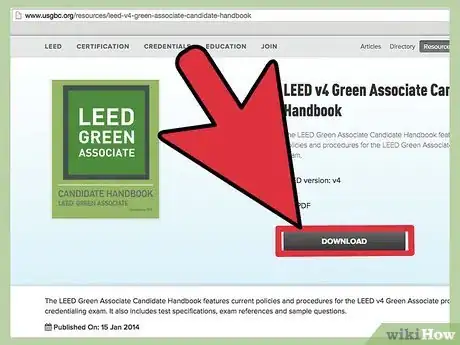
3Download the LEED Green Associates Handbook. Available for free on the LEED website, this comprehensive book covers testing, registration, certification, and frequently asked questions in specific detail, and should be read completely.
-
4Apply for the LEED Green Associate Exam. The test is administered at specific testing sites throughout the country. To register for the test, you must apply online here. You will be asked to locate an exam center near your and schedule an appointment to take the test.
- The LEED GA exam costs $250. There is a $50 rebate for previous members of LEED.[3]
-
5Study for the exam. You can attend a class, purchase the official LEED exam book, or take the online course through the Building Council. The GA test requires specific knowledge of building codes, LEED requirements, and Minimum Project Requirements (MPR) of every type of building, and you'll need to memorize a lot of standards and facts to keep them all straight.[4]
- The Green Building Council has created a simple primer for the test, complete with practice problems and links to suggested study materials, on their website.[5]
- You can find tutoring opportunities near you by searching online for "LEED Green Associates Tutoring" plus your zip code. They start around $300 for a 5-hour course.
-
6Know the types of questions on the test. The test consists of 100 randomly chosen multiple chose questions, and is taken electronically at your testing site. No matter how you choose to study, you should know the types of questions the test will ask:
- Recall: This is simply remembering and reciting facts and building codes taken straight from the exam prep book.
- Application: You will be given a problem or scenario and asked to solve it using familiar theories and practices of green buildings and LEED codes.
- Analysis: The most complicated questions, these require that you break down complex problems and determine a solution that accounts for multiple relationships, theories, and interactions within a building.[6]
-
7Take the test. Make sure that you bring a valid, non-expired photo ID or you will not be allowed to take the test. At your testing center, you will be seated at a personal workstation and given 100 questions to answer within a two hour window. You must answer all of them, though you can "flag" questions to return to later if you wish. When you are done, you will be given your score instantly.
- You must score 170 points or higher to pass.[7]
- You will be given a 10 minute break midway through the test.
-
8Print your certification if you have passed. When you pass, your Green Building Council account will update to reflect your new certification and provide you with a link to print a copy. You may now also legally refer to yourself as a LEED Green Associate on any official documents or resumes.[8]
Becoming a LEED Associated Professional
-
1Attain your LEED Green Associate certification. You must be a LEED GA to certify as an Associated Professional. LEED AP's have specific, detailed knowledge of one area of LEED certification, from building to interior design to home construction, allowing them to work on complicated projects and systems.[9]
-
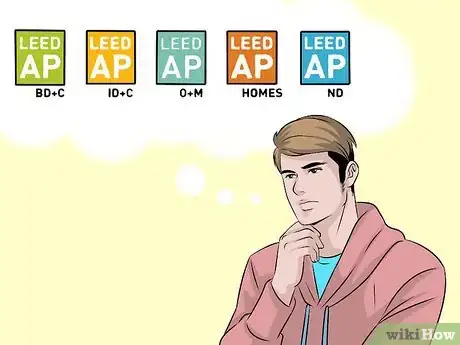
2Determine which LEED AP certificate you need. There are five specific LEED AP certifications, each with their own test, eligibility, and requirements:
- BD+C: Building Design and Construction. Plans and builds green structures in any sector-- commercial, home, healthcare, educational, etc.
- O+M: Operations and Management. LEED O+Ms update existing structures to be more sustainable, resourceful, and efficient.
- ID+C: Interior Design and Construction. Design and build indoor home and commercial spaces to make them more healthy, efficient and productive.
- ND: Neighborhood Development. Designs, plans, and develops large living spaces as walkable, comfortable neighborhoods.
- Homes: Specializes in designing healthy, durable homes with minimal waste and efficient energy consumption.[10]
-
3Register for your test. The test is administered at specific testing sites throughout the country. To register for the test, you must apply online here. You will be asked to locate an exam center near your and schedule an appointment to take the test.
- To save money and time, you can take both the GA test and your specific AP test together.[11]
-
4Study for your specific test. Each test has different questions and requirements to pass. Be sure to buy the correct study materials for you test a few months in advance and take a class if you need. Exam prep guides for each test can be found on the LEED website here.
-
5Take the test. Make sure that you bring a valid, non-expired photo ID or you will not be allowed to take the test. You will be seated at a personal computer and given 100 questions to answer within a two hour window. You must answer all of them, though you can "flag" questions to return to later if you wish. When you are done, you will be given your score instantly.
- Like the GA test, you must score 170 points or higher to pass.
- You will be given a 10 minute break midway through the test.
-
6Continue your education to maintain certification. AP's must prove they have earned 30 continuing education (CE) hours (six must be LEED-specific) every 2 years to maintain their credential. This can include building projects, classes, or internships.[12]
- If you do not document your CE hours, you will have to retake the test after two years.
Certifying a Building Project with LEED
-
1Know the Minimum Program Requirements for LEED certification. Before requesting a member of LEED comes to certify your building, you need know if your building or project is eligible. In general any new building -- commercial or residential -- is eligible to be certified if it is a permanent structure, meets local building codes, and fits the LEED size requirements.
- New Neighborhoods, building upgrades, and complete remodeling projects can all be LEED certified.
-
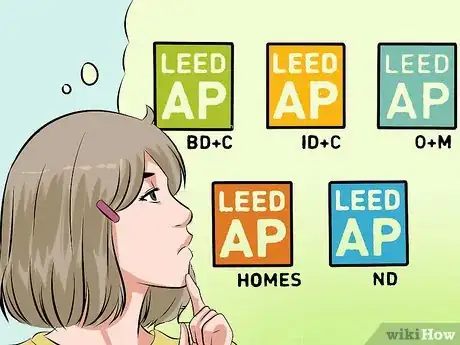
2Determine what type of project you need certified. There are different processes for all types buildings, including neighborhoods, renovations, and homes. Each certification is done by a different set of professionals:[13]
- BD+C: Building Design and Construction. This certifies any newly constructed building that meets LEED requirements.
- O+M: Operations and Management. Certifies improvements to existing buildings that makes them more efficient or green.
- ID+C: Interior Design and Construction. Certifies interior designs as healthy and efficient work spaces.
- ND: Neighborhood Development. Certifies neighborhood construction, design, and planning.
- Homes: Certifies individual homes as efficient in energy consumption and wast management.
-
3Understand the LEED credit system. LEED credits add up to form your building's "LEED Score," and includes everything from solar panels to light pollution reduction. A complete list of potential credits can be found in the LEED Credit Library. As you plan your building, discuss potential LEED credits with your architect and designers to maximize your project's green efficiency. To become certified, you need a minimum of 40 credits.
- Several credits, like "building water metering" are required to become LEED certified.
- Buildings can also reach for higher certifications, such as Silver (50-59 points), Gold, (60-79 points) or Platinum (80+ points) certifications.[14]
-
4Consult LEED certified professionals. LEED certified Associate Professionals (APs) are trained to help you plan, design, and build LEED specific projects. They are required to pass rigorous exams and continue their education even after their test. When starting a project, look for the title "LEED AP" next to any builder or designer you hire.
- Each AP specializes in a specific field related to your project (ie. AP O+Ms are trained to work on improvement projects).
-
5Apply online for LEED certification. This process will take several months and requires you to build up LEED credits -- specific projects that contribute to your building's overall efficiency score. To apply:
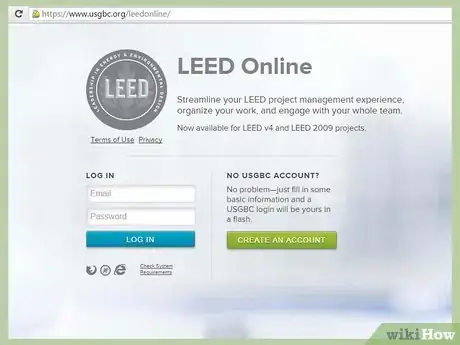
- Create a U.S. Green Business Council account.
- Register your building project. If you are certifying multiple buildings at once (for a campus or large project) be sure to apply for "group" certification.[15]
- Provide documentation of LEED credits you apply for.
-
6Know the LEED certification deadline. While this changes every year, the Green Building Council publishes the deadlines online as well.
-
7Work with the US Green Building Council during the review process. Within 20-25 days you will get a review of you application detailing the credits you will receive and any issues with your project. You will be asked to either accept the review or make any changes to your proposal. If you do not resubmit the proposal will be reviewed again before it is accepted or denied.
- If you are denied, you may appeal by adding new credits, documentation, or testimony to your application.[16]
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionWhat can I do with a LEED certification?
 MacKenzie CainMacKenzie Cain is an Interior Designer and a LEED-certified Green Associate for Habitar Design based in Chicago, Illinois. She has over seven years of experience in interior design and architectural design. She received a BA in Interior Design from Purdue University in 2013 and received her LEED Green Associate certification from the Green Building Certification Institute in 2013.
MacKenzie CainMacKenzie Cain is an Interior Designer and a LEED-certified Green Associate for Habitar Design based in Chicago, Illinois. She has over seven years of experience in interior design and architectural design. She received a BA in Interior Design from Purdue University in 2013 and received her LEED Green Associate certification from the Green Building Certification Institute in 2013.
Interior Designer & LEED Green Associate
Warnings
- The LEED Green Associate Exam is not easy. Do not procrastinate during your studies. Plan to study 20-30 hours unless you decide to attend a live class.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://support.usgbc.org/hc/en-us/articles/4404406912403-What-is-LEED-certification-
- ↑ http://www.usgbc.org/articles/interested-becoming-leed-green-associate-or-leed-ap-what-you-need-know
- ↑ http://www.usgbc.org/articles/interested-becoming-leed-green-associate-or-leed-ap-what-you-need-know
- ↑ https://www.usgbc.org/articles/3-tips-studying-leed-green-associate-exam
- ↑ http://www.usgbc.org/articles/prepare-your-leed-green-associate-exam
- ↑ https://kapost-files-prod.s3.amazonaws.com/published/53fce56c083261362000052b/leed-v4-green-associate-candidate-handbook.pdf
- ↑ https://www.usgbc.org/credentials/leed-green-associate
- ↑ https://kapost-files-prod.s3.amazonaws.com/published/53fce56c083261362000052b/leed-v4-green-associate-candidate-handbook.pdf
- ↑ http://www.usgbc.org/articles/interested-becoming-leed-green-associate-or-leed-ap-what-you-need-know
- ↑ http://www.usgbc.org/credentials#preparing
- ↑ http://www.usgbc.org/articles/interested-becoming-leed-green-associate-or-leed-ap-what-you-need-know
- ↑ https://support.usgbc.org/hc/en-us/articles/4404381867411-Earning-and-reporting-continuing-education-CE-hours
- ↑ https://www.usgbc.org/leed
- ↑ http://www.usgbc.org/leed#certification
- ↑ http://www.usgbc.org/cert-guide/commercial
- ↑ http://www.usgbc.org/cert-guide/commercial
- http://www.everbluetraining.com
- http://www.usgbc.org
- http://www.gbci.org
About This Article
To become LEED certified, download the LEED Green Associates Handbook for free on the LEED website and apply for the LEED Green Associate Exam. Next, study for the exam, focusing specifically on knowledge of building codes, LEED requirements, and Minimum Project Requirements. Then, take the exam electronically at your testing site. When you pass, you are a certified LEED Green Associate. You can also go on to become a certified LEED Associated Professional. For tips on higher certifications you can attain, read on!