X
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 22 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 652,117 times.
Learn more...
One of the biggest difficulties migrating to Ubuntu is losing access to your windows files. Fortunately, it is not too difficult to overcome this...but read the warnings before trying this out. All that is needed is to mount the windows partition after you boot into Ubuntu. Of course, the first problem is determining which partition contains the windows files.
Steps
-
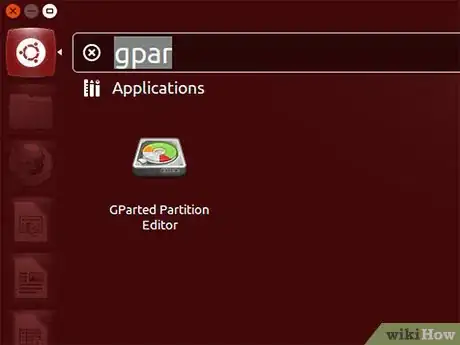
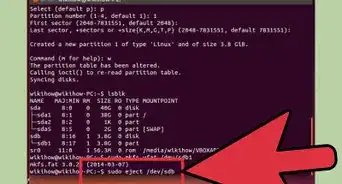
1Install gparted (System → Administration → Synaptics Package Manager → search for gparted, mark it for installation and, when it installs, run it from System → Partition Editor). Look for an NTFS partition – it is likely to be the one windows is on.
-
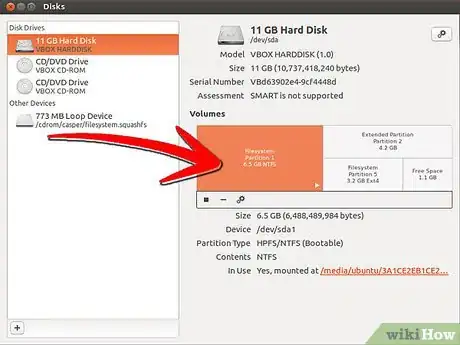
2Having located the partition, write down the name – it will look something like /dev/hda2 or /dev/sda2, depending if your drives are PATA, SCSI or SATA. Do this carefully – Now check to see if this is the partition by manually mounting it and looking at the files.Advertisement
-
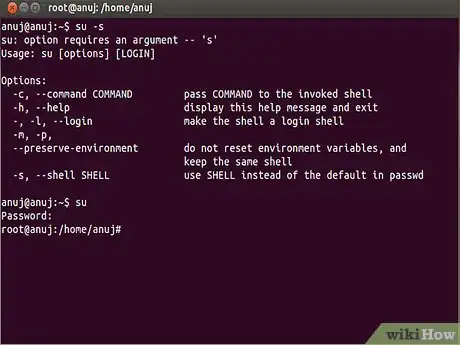
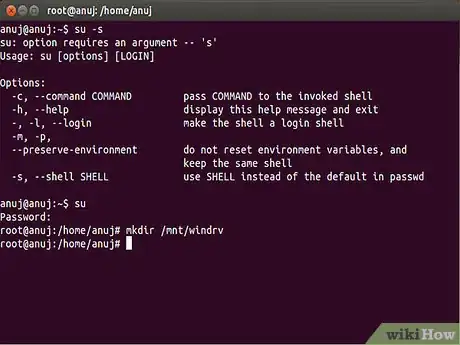
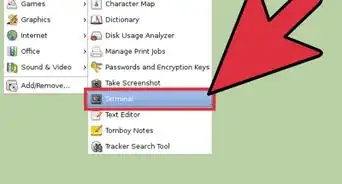
3Open a terminal (Application → Accessories → Terminal) and make yourself root by typing sudo -s and pressing enter. You will be prompted for the root password and will then become root. Being root assumes that you know what you are doing – you could easily cause disaster if you make a mistake, so concentrate. Carefully type this line at the prompt and press enter
-
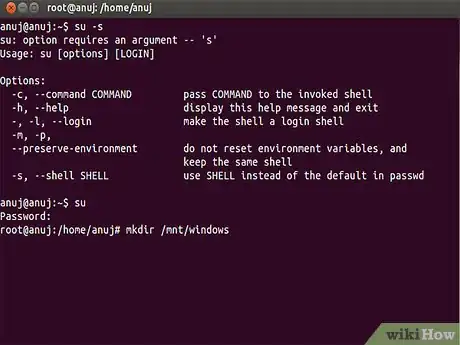
4Type the prompt. mkdir /mnt/windows
-
5Replace the name. You may replace /mnt/windows with /mnt/windrv or any other name you prefer. Having created the directory that is going to hold your windows files, type the following command carefully at the prompt and press enter
-
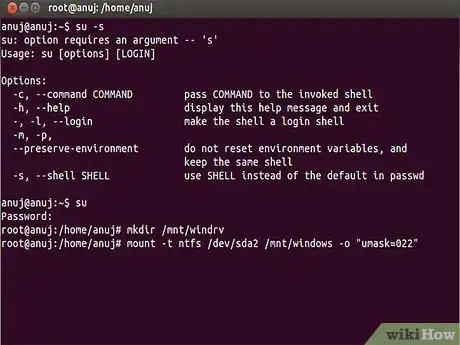
6Type the command. mount -t ntfs /dev/sda2 /mnt/windows -o "umask=022"
-
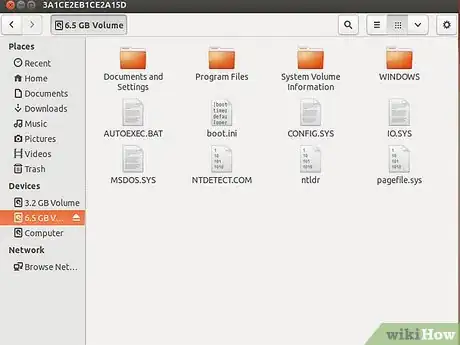
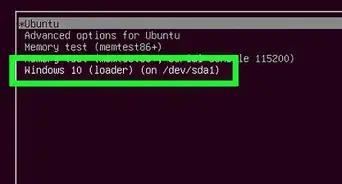
7Make sure you replace /dev/sda2 with the name of the windows partition you wrote down. Now access the mounted drive and ensure that you can read the files by going to Places → Computer and navigating to /mnt/windows. If you can see your files, you are all set. If not, you've mounted the wrong drive, unmount it using umount /dev/sda2, making sure that you use the correct name for your drive.
Advertisement
Community Q&A
-
QuestionIt says that it can't find /dev/sda/2 in /etc/fstab. What does that mean?The location will not always be /dev/sda2. It may be something else on your system. You will need to look at GPartEd in order to figure out what you need to type in for the mount command. Also, you put an extra '/' in /dev/sda2 right before the 2. This may have affected your mount command as well.
-
QuestionWhat does it mean when it says Mount is denied because the NTFS volume is already exclusively opened?
 SomoneCommunity AnswerIt means something else is already accessing the volume. Make sure that no other programs are using the volume and try again.
SomoneCommunity AnswerIt means something else is already accessing the volume. Make sure that no other programs are using the volume and try again. -
QuestionMy root password is wrong. What can I do?
 SomoneCommunity AnswerYou will have to change your root password. The root password is typically the administrator's login password. But if it's not, you will have to change it by editing boot commands.
SomoneCommunity AnswerYou will have to change your root password. The root password is typically the administrator's login password. But if it's not, you will have to change it by editing boot commands.
Advertisement
Warnings
- Always back your important files up before making changes to your system.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Leave yourself plenty of time to recover - never do this before a deadline.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Always verify your backup before trusting it.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Advertisement
About This Article
Advertisement