Chapter 30
Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
By Boundless

Nuclear size is defined by nuclear radius; nuclear density can be calculated from nuclear size.
The stability of an atom depends on the ratio and number of protons and neutrons, which may represent closed and filled quantum shells.
Nuclear force is the force that is responsible for binding of protons and neutrons into atomic nuclei.
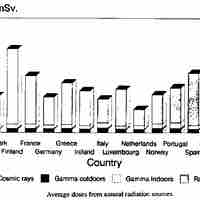
Detectable amounts of radioactive material occurs naturally in soil, rocks, water, air, and vegetation.
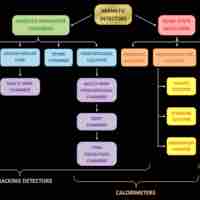
A radiation detector is a device used to detect, track, or identify high-energy particles.

Radioactive decay series describe the decay of different discrete radioactive decay products as a chained series of transformations.
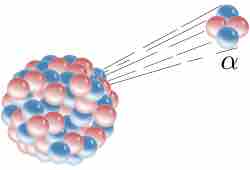
In alpha decay an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle and transforms into an atom with smaller mass (by four) and atomic number (by two).
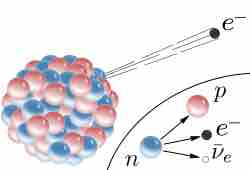
Beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (an electron or a positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus.
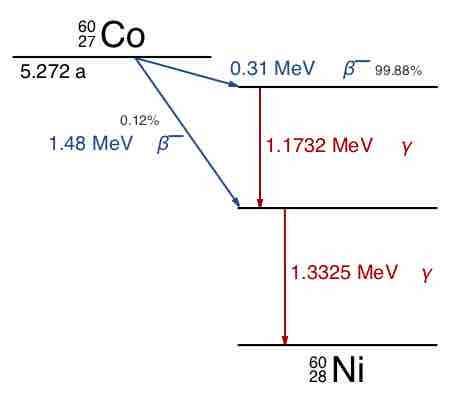
Gamma decay is a process of emission of gamma rays that accompanies other forms of radioactive decay, such as alpha and beta decay.
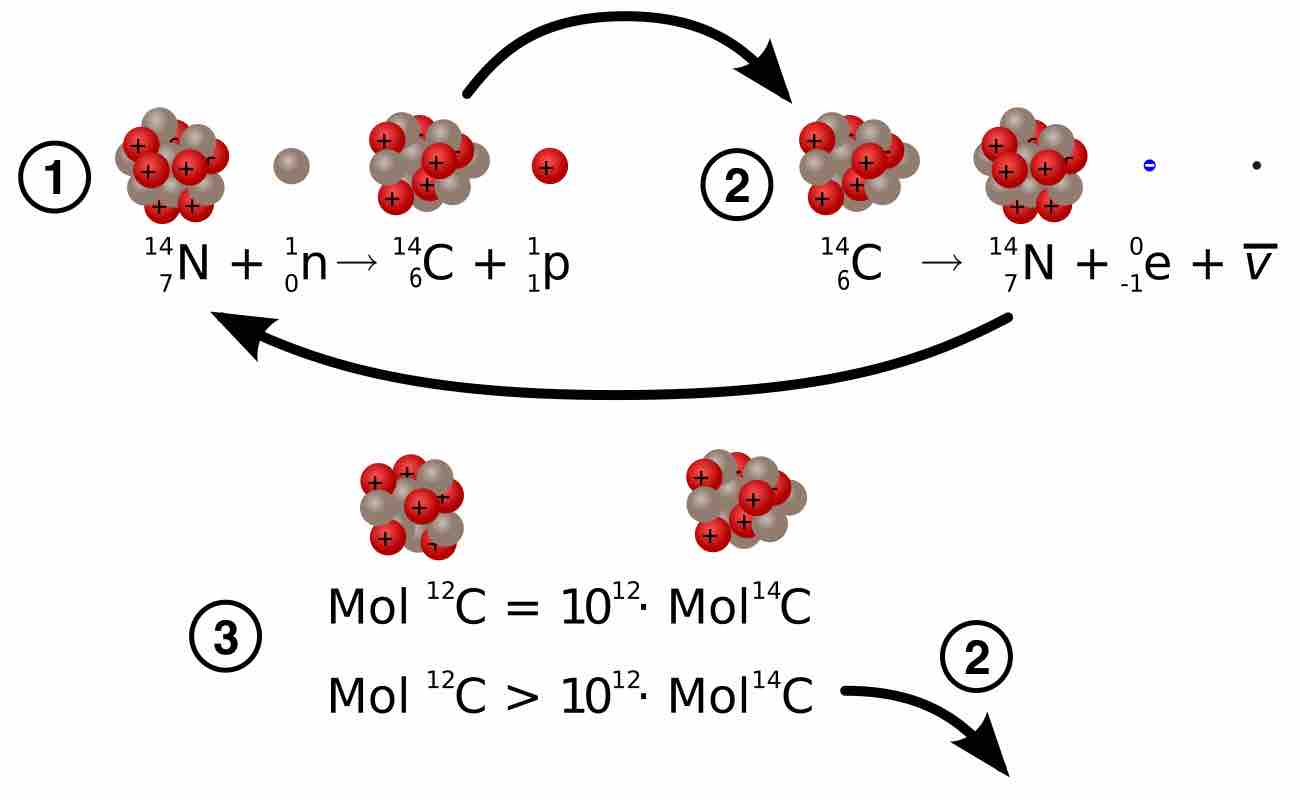
Carbon-14 dating is a radiometric dating method that uses the radioisotope carbon-14 (14C) to estimate the age of object.

The half-life of a radionuclide is the time taken for half the radionuclide's atoms to decay.

If an object lacks enough energy to pass through a barrier, it is possible for it to "tunnel" through imaginary space to the other side.
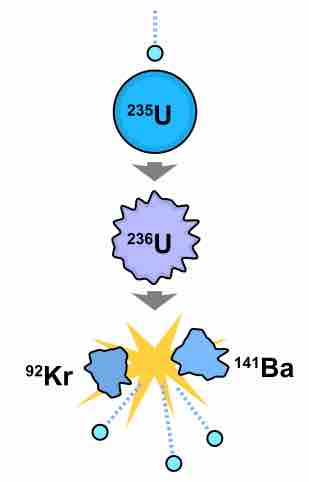
Through radioactive decay, nuclear fusion and nuclear fission, the number of nucleons (sum of protons and neutrons) is always held constant.
Radiation therapy uses ionizing radiation to treat conditions such as hyperthyroidism, cancer, and blood disorders.

Radiation dosimetry is the measurement and calculation of the absorbed dose resulting from the exposure to ionizing radiation.

Ionizing radiation is generally harmful, even potentially lethal, to living organisms.
Radiation therapy uses ionizing radiation to treat conditions such as hyperthyroidism, cancer, and blood disorders.

Food irradiation is a process of treating a food to a specific dosage of ionizing radiation for a predefined length of time.

A radioactive tracer is a chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radioisotope.
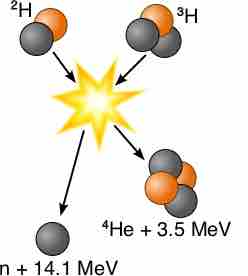
In nuclear fusion two or more atomic nuclei collide at very high speed and join, forming a new nucleus.

Nuclear reactors convert the thermal energy released from nuclear fission into electricity.
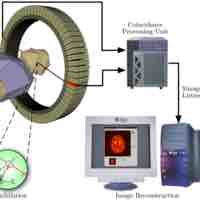
Positron emission tomography is a nuclear medical imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image of processes in the body.

A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions—either fission, fusion, or a combination.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize internal structures of the body in detail.