Section 2
The Early Atom
By Boundless
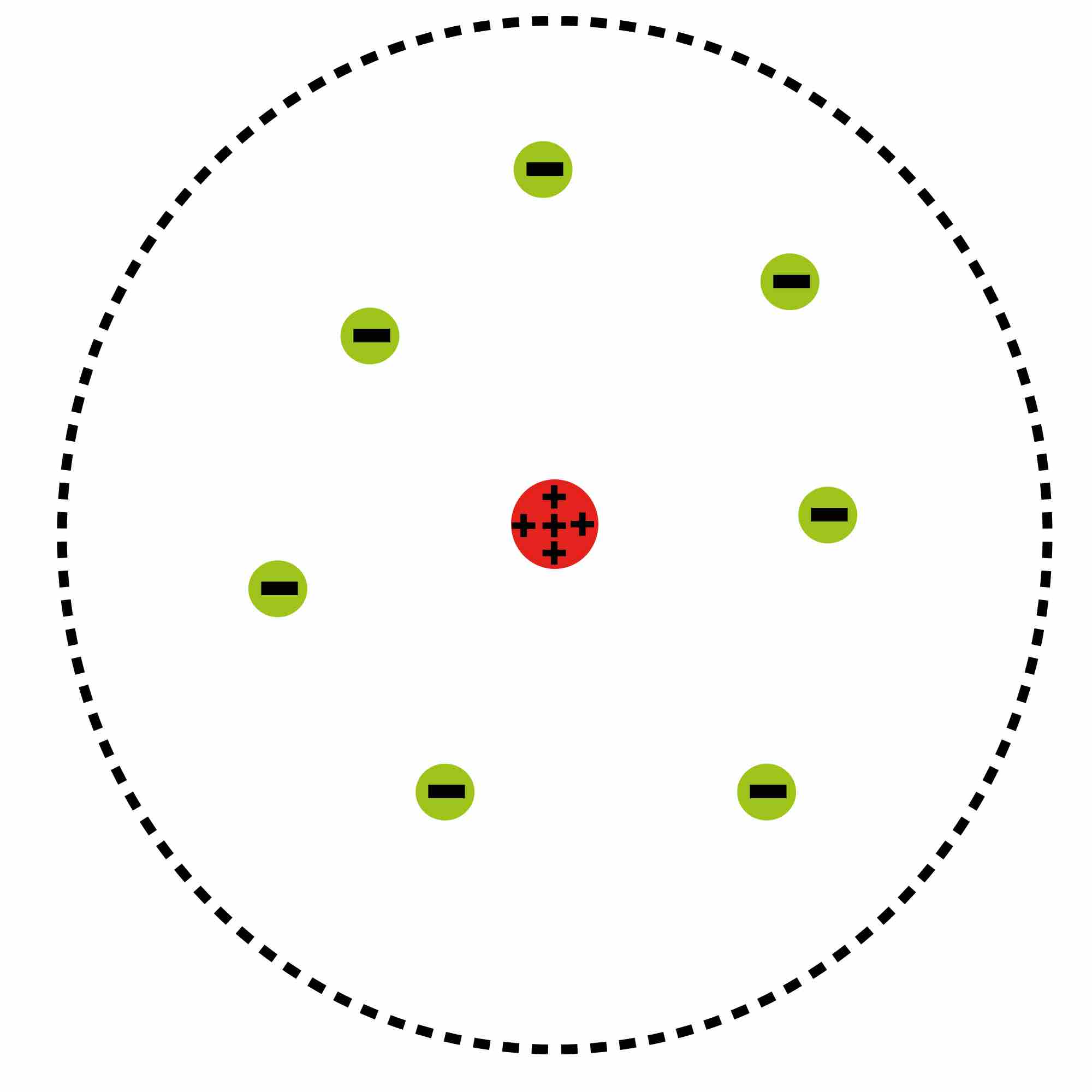
Modern scientific usage denotes the atom as composed of constituent particles: the electron, the proton and the neutron.

Dalton believed that that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms -- indivisible, ultimate particles of matter.

Thomson proposed that the atom is composed of electrons surrounded by a soup of positive charge to balance the electrons' negative charges.
Rutherford confirmed that the atom had a concentrated center of positive charge and relatively large mass.

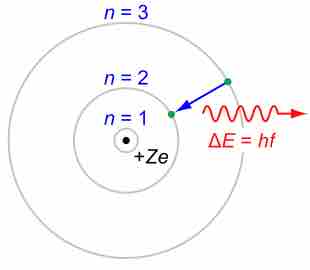
Bohr suggested that electrons in hydrogen could have certain classical motions only when restricted by a quantum rule.
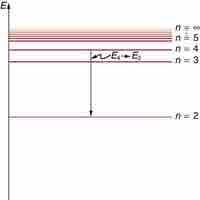
Bohr explained hydrogen's spectrum successfully by adopting a quantization condition and by introducing the Planck constant in his model.
According to Bohr, electrons can only orbit stably, in certain orbits, at a certain discrete set of distances from the nucleus.
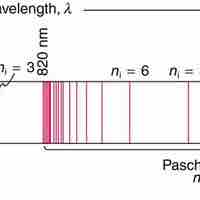
Based on his assumptions, Bohr derived several important properties of the hydrogen atom from the classical physics.
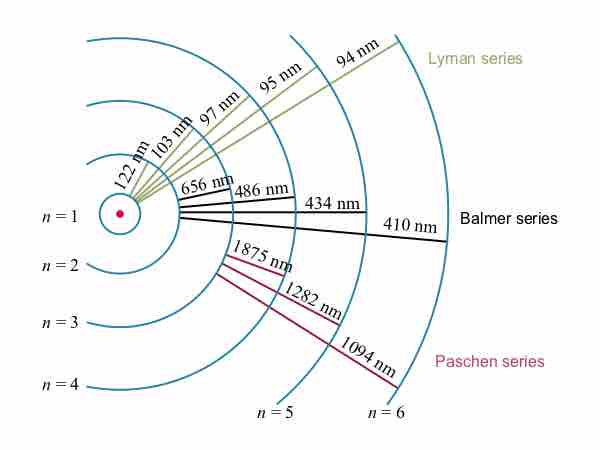
The observed hydrogen-spectrum wavelengths can be calculated using the following formula:
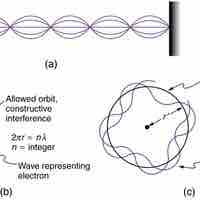
By assuming that the electron is described by a wave and a whole number of wavelengths must fit, we derive Bohr's quantization assumption.
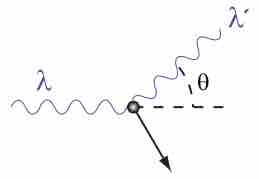
Compton explained the X-ray frequency shift during the X-ray/electron scattering by attributing particle-like momentum to "photons".

X-ray shows its wave nature when radiated upon atomic/molecular structures and can be used to study them.
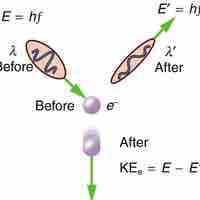
The Compton Effect is the phenomenon of the decrease in energy of photon when scattered by a free charged particle.