Chapter 2
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
By Boundless
The concept of the atom as an indivisible building block of matter was recorded as early as the 5th century BCE.

The law of conservation of mass states that mass in an isolated system is neither created nor destroyed.

The law of definite composition states that chemical compounds are composed of a fixed ratio of elements as determined by mass.
The law of multiple proportions states that elements combine in small whole number ratios to form compounds.
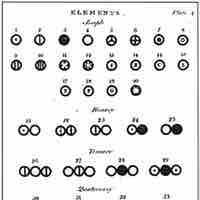
Dalton introduced a theory that proposed that elements differed due to the mass of their atoms.
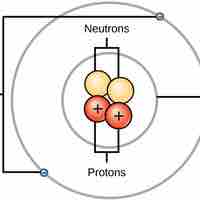
Atoms are made up of particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, which are responsible for the mass and charge of atoms.
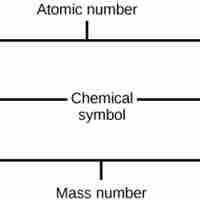
The atomic number is the number of protons in an element, while the mass number is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons.

Isotopes are various forms of an element that have the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons.

The periodic table shows all the elements and their physical properties; it is arranged based on atomic numbers and electron configurations.
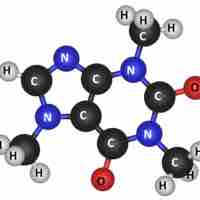
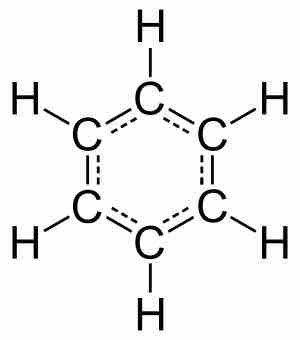
Molecules are electrically neutral compounds made of multiple atoms bound together by chemical bonds.
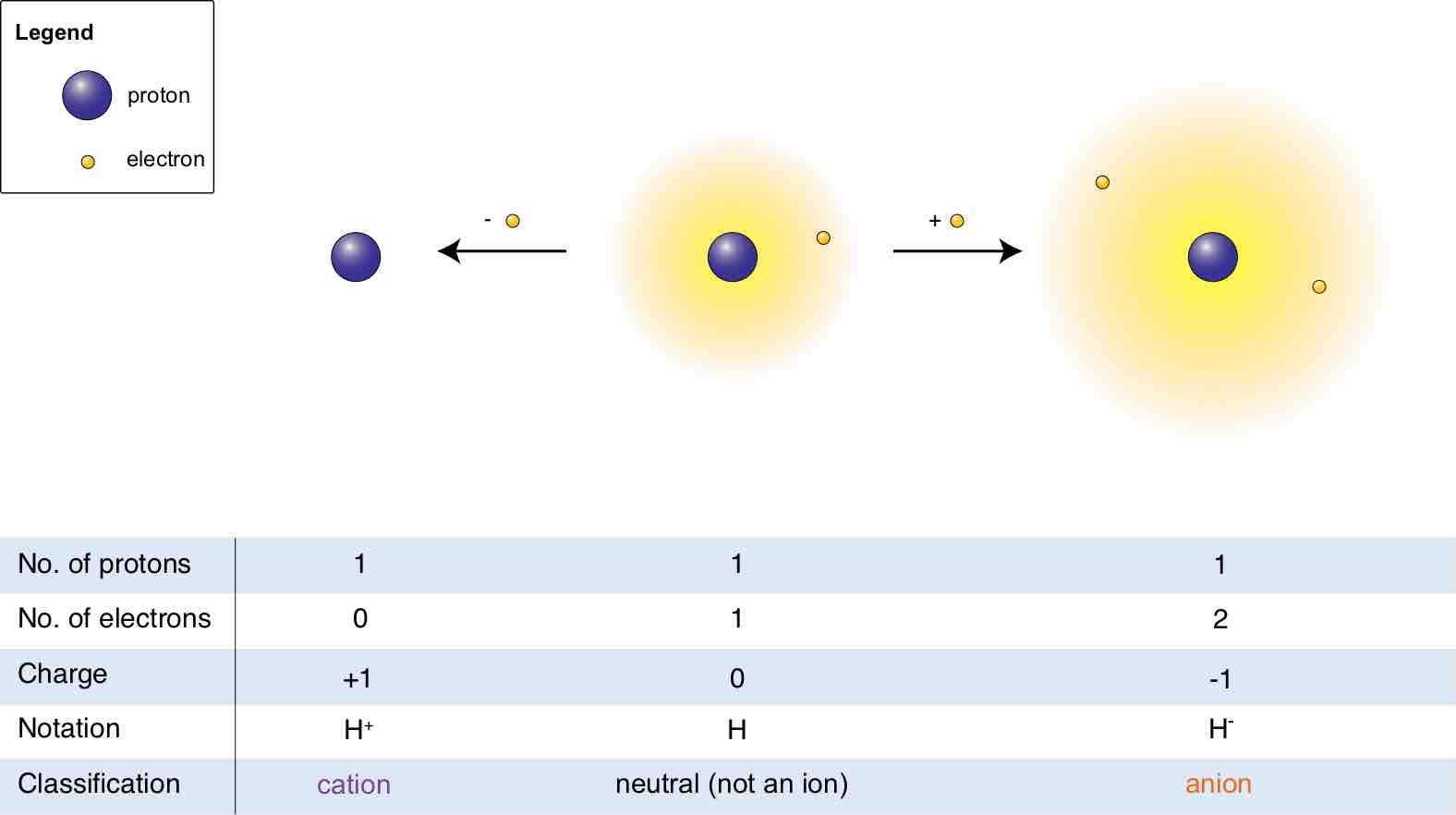
An ion is an atom or molecule that has a net electrical charge because its total number of electrons is not equal to its number of protons.

Chemical bonding describes a variety of interactions that hold atoms together in chemical compounds.
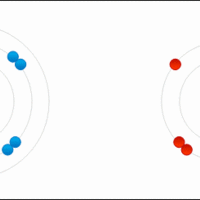
Ionic bonds are a subset of chemical bonds that result from the transfer of valence electrons, typically between a metal and a nonmetal.
Covalent bonding involves two atoms, typically nonmetals, sharing valence electrons.
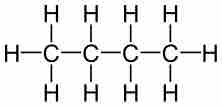
Molecular formulas are a compact chemical notation that describe the type and number of atoms in a single molecule of a compound.
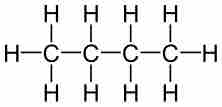
Empirical formulas describe the simplest whole-number ratio of the elements in a compound.
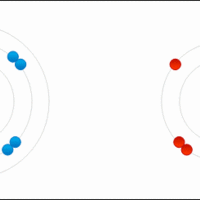
An ionic formula must satisfy the octet rule for the constituent atoms and electric neutrality for the whole compound.

An ionic compound is named first by its cation and then by its anion.
Molecular compounds are named using a systematic approach of prefixes to indicate the number of each element present in the compound.
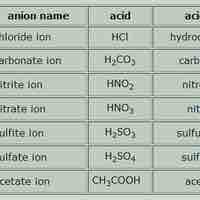
Acid names are based on the anion they form when dissolved in water; base names follow the rules for ionic, organic, or molecular compounds.

The name of a hydrate follows a set pattern: the name of the ionic compound followed by a numerical prefix and the suffix -hydrate.
Familiar inorganic and organic compounds are often known by their common, or "trivial," names.