Chapter 3
Mass Relationships and Chemical Equations
By Boundless

The average atomic mass of an element is the sum of the masses of its isotopes, each multiplied by its natural abundance.
Mass spectrometry is a powerful characterization method that identifies elements, isotopes, and compounds based on mass-to-charge ratios.

The mole is represented by Avogadro's number, which is 6.02×1023 mol-1.
By understanding the relationship between moles and Avogadro's number, scientists can convert between number of moles and number of atoms.
The molar mass of a particular substance is the mass of one mole of that substance.
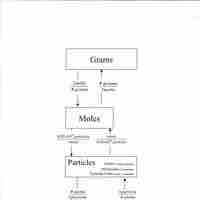
A substance's molar mass can be used to convert between the mass of the substance and the number of moles in that substance.
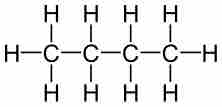
The percent composition (by mass) of a compound can be calculated by dividing the mass of each element by the total mass of the compound.

Combustion analysis is commonly used to determine the relative ratios of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in organic compounds.
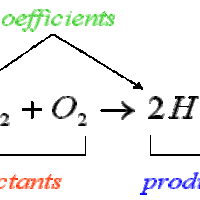
Stoichiometry is the study of the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions and how to calculate those quantities.
Molar ratios, or conversion factors, identify the number of moles of each reactant needed to form a certain number of moles of each product.
Mole-to-mole conversions can be facilitated by using conversion factors found in the balanced equation for the reaction of interest.
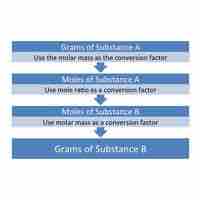
Mass-to-mass conversions cannot be done directly; instead, mole values must serve as intermediaries in these conversions.
Mass-to-mole conversions can be facilitated by employing the molar mass as a conversion ratio.
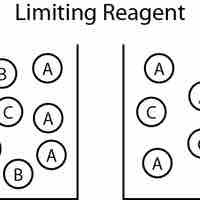
The reagent that limits how much product is produced (the reactant that runs out first) is known as the limiting reagent.
The percent yield of a reaction measures the reaction's efficiency. It is the ratio between the actual yield and the theoretical yield.