The atomic composition of chemical compounds can be described using a variety of notations including molecular, empirical, and structural formulas. Another convenient way to describe atomic composition is to examine the percent composition of a compound by mass.
Percent Composition by Mass
Percent composition is calculated from a molecular formula by dividing the mass of a single element in one mole of a compound by the mass of one mole of the entire compound. This value is presented as a percentage.
For example, butane has a molecular formula of C4H10. Butane's percent composition can be calculated as follows:
- Mass of H per mol butane:
$10\:mol\:H \cdot \frac{1.00794\:g}{1\:mol\: H} = 10.079\:g\:H$ - Mass of C per mol butane:
$4\:mol\:C\cdot\frac{12.011\:g\:C}{1\:mol\:C}=48.044\:g\:C$ - Mass percent H in butane:
$\frac{10.079\:g\:H}{58.123\:g\:butane} \cdot 100$ = 17.3% H - Mass percent C in butane:
$\frac {48.044\:g \:C}{ 58.123 \:g \:butane} \cdot 100$ = 82.7% C
Therefore, the atomic composition of butane can also be described as 17.3% hydrogen and 82.7% carbon, and, as expected, these values sum to 100%.
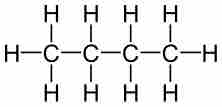
Butane
The structural formula of butane.
In practice, this calculation is often reversed. Mass percents can be determined experimentally via elemental analysis, and these values can be used to calculate the empirical formula of unknown compounds. However, this information is insufficient to determine the molecular formula without additional information on the compound's molecular weight.