Element Symbols
The periodic table is structured as an 18 X 7 grid, positioned above a smaller double row of elements. The periodic table only lists chemical elements, and includes each isotope of each element within one cell. In the typical periodic table, each element is listed by its element symbol and atomic number. For example, "H" denotes hydrogen, "Li" denotes lithium, and so on. Most elements are represented by the first letter or first two letters of their English name, but there are some exceptions. Two notable exceptions include silver and mercury. The symbol for silver is "Ag" from Latin argentum, which means "gray" or "shining." The symbol for mercury is "Hg" from the Latinized Greek hydrargyrum, which means "water-silver." Many periodic tables include the full name of element as well and color-code the elements based on their phase at room temperature (solid, liquid, or gas).
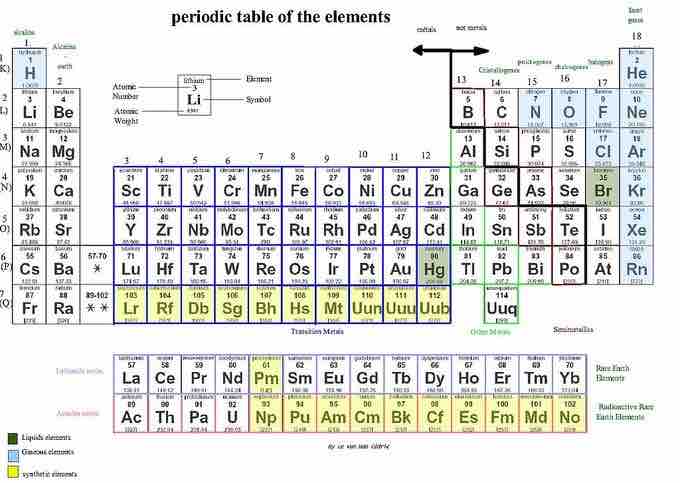
The periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular display of all the chemical elements. The atoms are grouped in order of increasing atomic number.
Rows and Periods
The element symbol is always almost accompanied by other information such as atomic number and atomic weight. Atomic number describes the number of protons in one atom of that element. For example, an atom of oxygen contains 8 protons. Elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number from left to right. Each row of the periodic table is called a period and each column of the periodic table is called a group (or family). Some groups have specific names like the halogens or noble gases. Elements within the same period or group have similar properties.
Determining Chemical Properties using the Periodic Table
Chemical properties of each element are determined by the element's electronic configuration, and particularly by its outermost valence electrons. An element's location in the periodic table is largely dependent on its electrons; the number of valence shell electrons determines its group, and the type of orbital in which the valence electrons lie in determines the element's block. In addition, the total number of electron shells an atom determines which period it belongs to. Because of its structure, the periodic table has become an extremely useful tool for assessing and predicting elemental and chemical trends.