Chapter 7
Polynomials and Rational Functions
By Boundless
A polynomial is a finite expression containing constants and variables connected only through basic operations of algebra.
Polynomials can be added or subtracted by combining like terms.
To multiply two polynomials together, multiply every term of one polynomial by every term of the other polynomial.
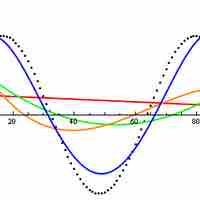
Functions are commonly used in fitting data to a trend line. Polynomial and rational functions are both relatively accurate and easy to use.
Factoring by grouping divides the terms in a polynomial into groups, which can be factored using the greatest common factor.
Polynomial long division functions similarly to long division, and if the division leaves no remainder, then the divisor is called a factor.
Synthetic division is a technique for dividing a polynomial and finding the quotient and remainder.
Finding factors of polynomials is important, since it is always best to work with the simplest version of a polynomial.
The fundamental theorem states that every non-constant single-variable polynomial with complex coefficients has at least one complex root.
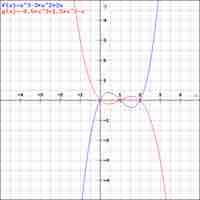
To construct a polynomial from given zeros, set
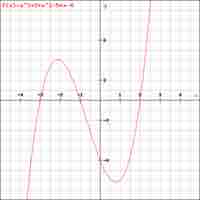
The factored form of a polynomial reveals its zeros, which are defined as points where the function touches the
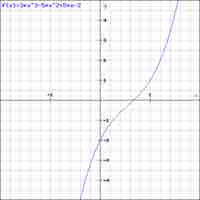
Each solution to a polynomial, expressed as
The rule of signs gives an upper bound number of positive or negative roots of a polynomial.
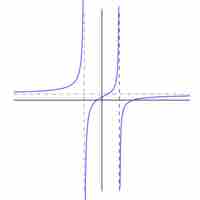
A rational function is one such that
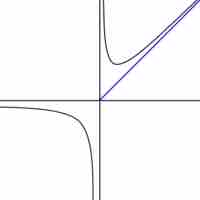
A rational function can have at most one horizontal or oblique asymptote, and many possible vertical asymptotes; these can be calculated.
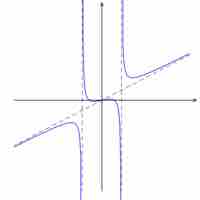
The
A rational expression can be treated like a fraction, and can be manipulated via multiplication and division.
Partial fraction decomposition is a procedure used to reduce the degree of either the numerator or the denominator of a rational function.