Section 1
Introduction to Linear Functions
By Boundless
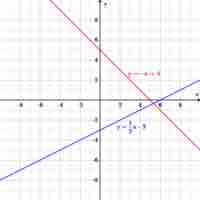
Linear functions are algebraic equations whose graphs are straight lines with unique values for their slope and y-intercepts.
Slope describes the direction and steepness of a line, and can be calculated given two points on the line.
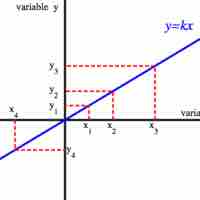
Two variables in direct variation have a linear relationship, while variables in inverse variation do not.
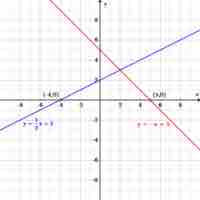
A zero, or
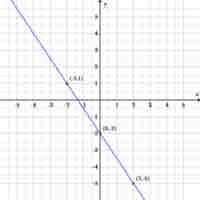
The slope-intercept form of a line summarizes the information necessary to quickly construct its graph.
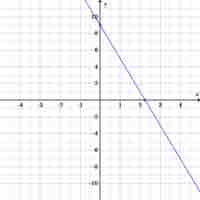
The point-slope equation is another way to represent a line; only the slope and a single point are needed.
Any linear equation can be written in standard form, which makes it easy to calculate the zero, or