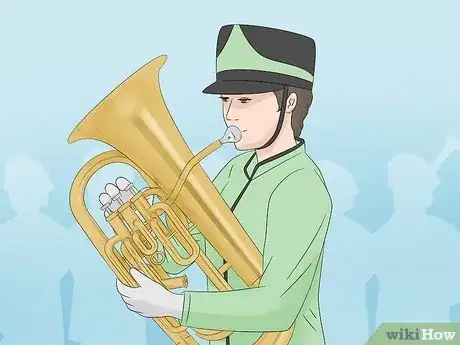This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Aly Rusciano. Aly Rusciano is a Creative Writer based outside of Nashville, Tennessee. She has over ten years of experience in creative, academic, and professional writing. Aly’s writing has been nationally recognized in the Sigma Tau Delta Rectangle and featured in Blue Marble Review, The Sunshine Review, PopMatters, and Cathartic Literary Magazine. She graduated from The University of Tennessee at Martin with a BA in English, focusing in Creative Writing and minoring in Theatre.
There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
Learn more...
An orchestra is playing a beautiful ballad when you notice something: there are two instruments that look almost exactly the same. They have large bells and curved tubing. They’re not tubas or trumpets, so what are they? Those are euphoniums and baritones, and these brass instruments have quite a few differences (and similarities). So, what makes them different? Keep reading to find out!
Things You Should Know
- Euphoniums and baritones are both brass instruments, but euphoniums are in the tuba family, while baritones are part saxhorn.
- Baritones have cylindrical tubing and narrow bells, whereas euphoniums have conical tubing and wide bells.
- A euphonium and baritone are both low-pitched instruments that mainly produce B♭ notes.
Steps
References
- ↑ https://primesound.org/euphonium-vs-tuba/
- ↑ https://www.britannica.com/art/serpent-musical-instrument
- ↑ https://www.oxfordreference.com/display/10.1093/oi/authority.20110803100443811;jsessionid=EC1A1D6CBB5B295CA4866D16433BD060
- ↑ https://www.britannica.com/art/transposing-musical-instrument
- ↑ https://omeka-s.grinnell.edu/s/MusicalInstruments/item/1255
- ↑ https://www.orsymphony.org/learning-community/instruments/brass/
- ↑ https://www.britannica.com/art/euphonium
- ↑ https://www.britannica.com/art/baritone-saxhorn