Chapter 16
Sound
By Boundless

Sound is a longitudinal wave of pressure that travels through compressible medias, which can be solid, liquid, gaseous, or made of plasma.
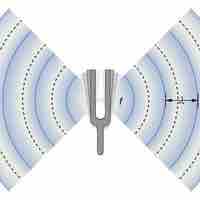
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. The perception of frequency is called pitch.
Sound can be produced by many different devices. A vibrating string or air column can both create music and have unique properties.
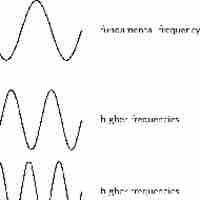
Sound quality is an assessment of accuracy or enjoyability of how a sound is perceived.

The speed of sound is is the distance traveled in a unit of time by a sound wave through an elastic medium, and is usually given as 344 m/s.
Sound Intensity is the power per unit area carried by a wave. Power is the rate that energy is transferred by a wave.

The study of human perception of sound is called psychoacoustics.
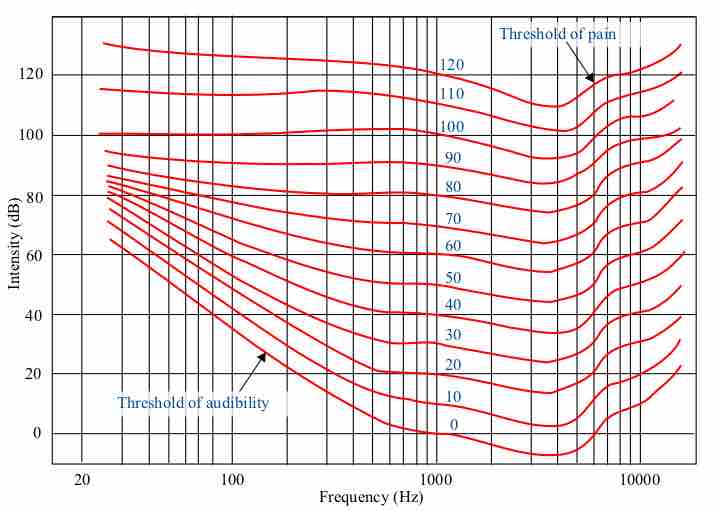
The decibel is a logarithmic unit used to quantify sound levels, by comparing a physical quantity to a reference level.
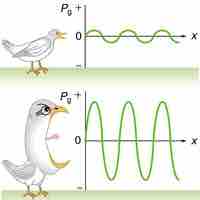
The Doppler effect is the apparent change in frequency of a wave when the observer and the source of the wave move relative to each other.
The Doppler effect is the apparent change in frequency of a wave when the observer and the source of the wave move relative to each other.
The Doppler effect is the apparent change in frequency of a wave when the observer and the source of the wave move relative to each other.
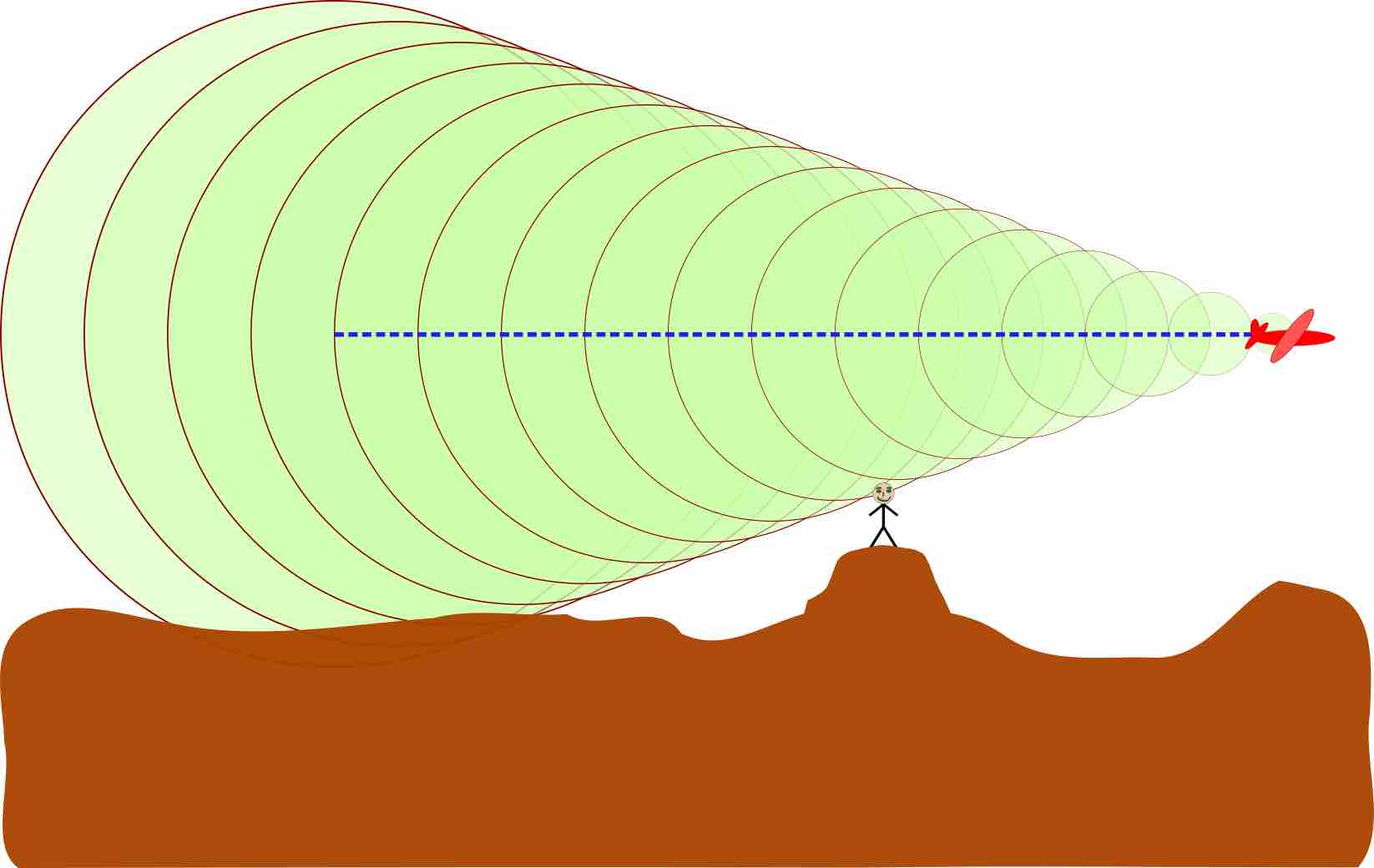
A sonic boom is the sound associated with the shock waves created by an object traveling through the air faster than the speed of sound.
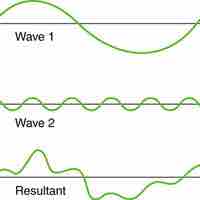
Superposition occurs when two waves occupy the same point (the wave at this point is found by adding the two amplitudes of the waves).
Interference occurs when multiple waves interact with each other, and is a change in amplitude caused by several waves meeting.
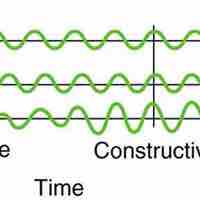
The superposition of two waves of similar but not identical frequencies produces a pulsing known as a beat.
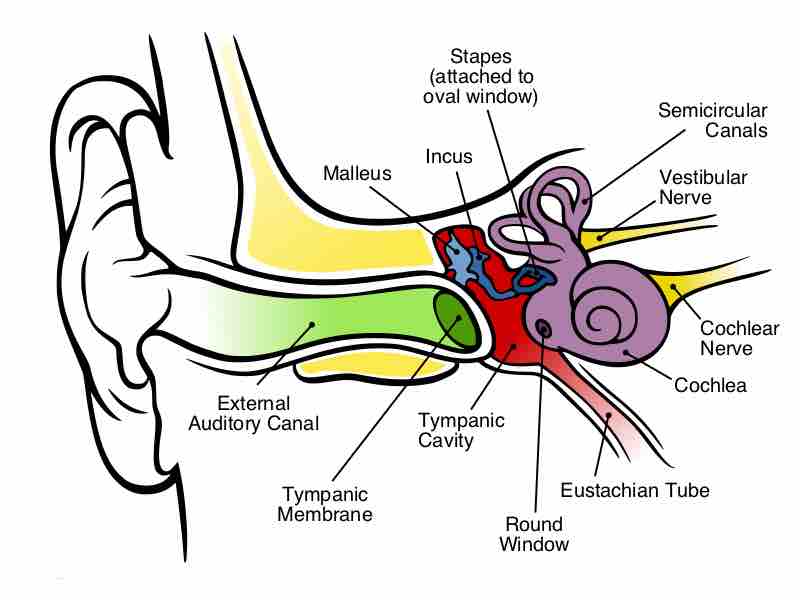
The ear is the sensory organ that picks up sound waves from the air and turns them into nerve impulses that can be sent to the brain.

Sound waves reflect off different materials differently (when the reflections are collected, they can provide information and images).
Spherical waves come from point source in a spherical pattern; plane waves are infinite parallel planes normal to the phase velocity vector.

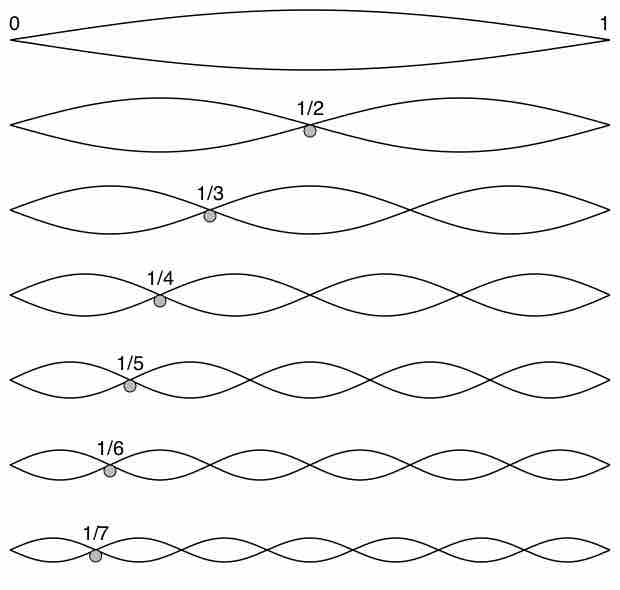
Standing wave occurs due to the interference when transverse waves in strings are reflected and the incident and reflected waves meet.
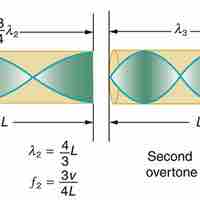
Standing waves in air columns is the physical phenomenon that gives wind instruments their resonance and, therefore, sound.
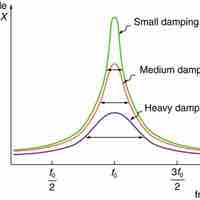
The phenomenon of driving a system with a frequency equal to its natural frequency is called resonance.