Chapter 13
Antimicrobial Drugs
By Boundless

The era of antimicrobials begins when Pasteur and Joubert discover that one type of bacteria could prevent the growth of another.

Observations of antibiosis between micro-organisms led to the discovery of natural antibacterials produced by microorganisms.
Antibiotics are able to selectively target specific types of bacteria without harming the infected host.
An antibiotic's spectrum can be broad or narrow.
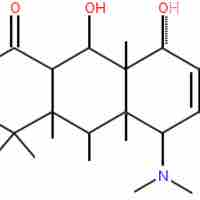
Bactericidal antibiotics kill bacteria; bacteriostatic antibiotics slow their growth or reproduction.

β-Lactam (beta-lactam) and glycopeptide antibiotics work by inhibiting or interfering with cell wall synthesis of the target bacteria.
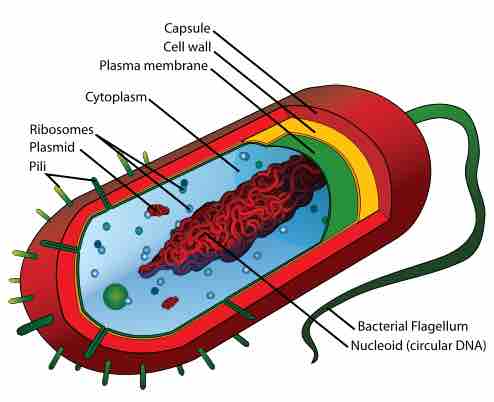
Several types of antimicrobial drugs function by disrupting or injuring the plasma membrane.
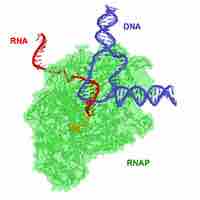
Antimicrobial drugs inhibit nucleic acid synthesis through differences in prokaryotic and eukaryotic enzymes.
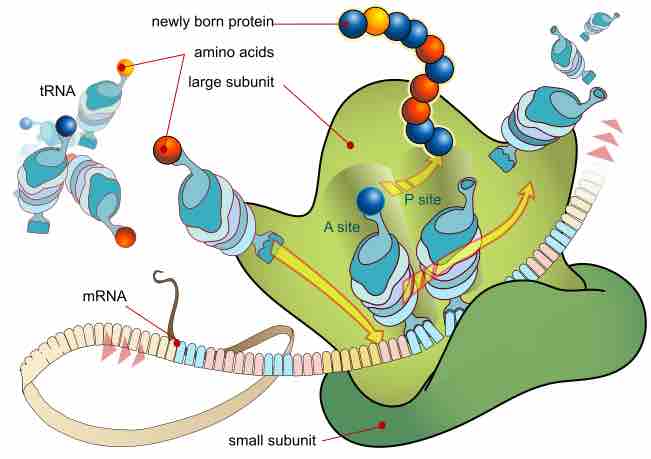
Protein synthesis inhibitors are substances that disrupt the processes that lead directly to the generation of new proteins in cells.

An antimetabolite is a chemical that inhibits the use of a metabolite, a chemical that is part of normal metabolism.
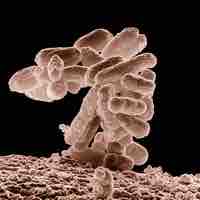
An antimicrobial is a substance that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or protozoans.
An antimicrobial is a substance that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or protozoans.
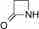
The β-lactam ring is part of the core structure of several antibiotic families.

Most of the currently available antibiotics are produced by prokaryotes mainly by bacteria from the genus Streptomyces.
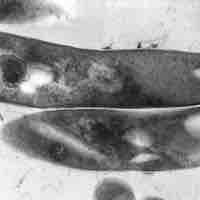
Antimycobacterial antibiotics target microbes classified as mycobacterium.
The accumulation of antimicrobial drugs and their metabolic byproducts in organs can be toxic, leading to organ damage.
Antimicrobrial drugs can cause immune responses which can be fatal.
Our bodies depend upon, and host, a vast number of complex microbial flora that can be affected negatively by antimicrobial treatments.
Antimicrobial drugs can interact with other drugs in deleterious ways or can be used in combination to combat microbial infections.
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration is the lowest drug concentration that prevents visible microorganism growth after overnight incubation.

Kirby-Bauer testing measures sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics by culturing bacteria on solid growth media surrounding sources of drug.
Development of microbial resistance to antimicrobial agents requires alterations in the microbe's cell physiology and structure.

Antibiotic misuse is one factor responsible for the emergence of antimicrobial resistant bacterial strains.

Antimicrobial resistance is a major public health and economic burden on patients, affected communities, and healthcare providers.
Biofilms and persisters are bacterial communities responsible for chronic diseases and antibiotic tolerance.
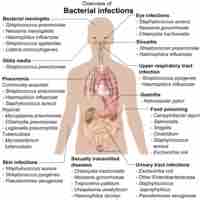
Antimicrobial resistance has created a public health crisis in the treatment of infectious diseases and necessitates the discovery of new drugs.
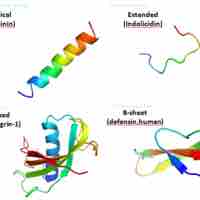
Antimicrobial peptides exhibit cytotoxic activity against all microbes.

Antisense agents are short oligonucleotides that bind to target messenger RNA and inhibit protein synthesis.
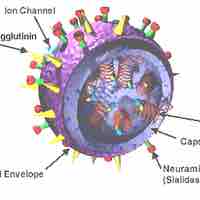
Different approches are used to target the initial and final steps of a virus life cycle.
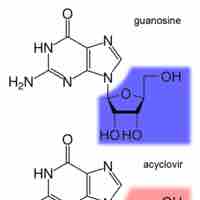
Inhibiting DNA synthesis during viral replication is another key approach in battling viral infections.
Reverse transcriptase in viruses is inhibited by nucleoside (nucleotide) analogues or drugs that change the conformation of the enzyme.
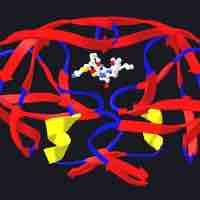
Protease inhibitors target viral proteases which are key enzymes for the completion of viral maturation.

The development of antifungal drugs focuses on the classes of mycotic diseases for which fungi are responsible.

Antiprotozoan and antihelminthic drugs are characterized based on structure and the mechanism of action by which they target the organism.