Section 2
Functions of Antimicrobial Drugs
Book
Version 6
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Microbiology
Microbiology
by Boundless
5 concepts

Inhibiting Cell Wall Synthesis
β-Lactam (beta-lactam) and glycopeptide antibiotics work by inhibiting or interfering with cell wall synthesis of the target bacteria.
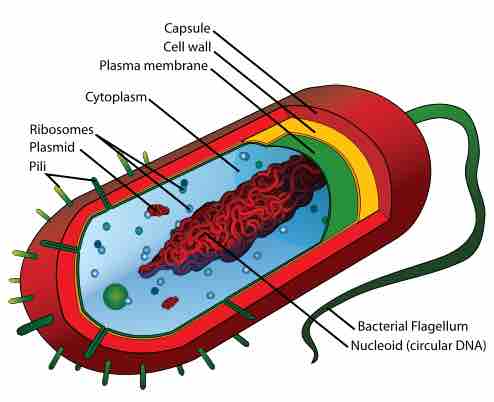
Injuring the Plasma Membrane
Several types of antimicrobial drugs function by disrupting or injuring the plasma membrane.
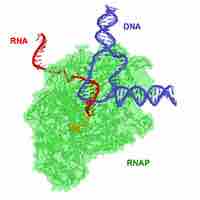
Inhibiting Nucleic Acid Synthesis
Antimicrobial drugs inhibit nucleic acid synthesis through differences in prokaryotic and eukaryotic enzymes.
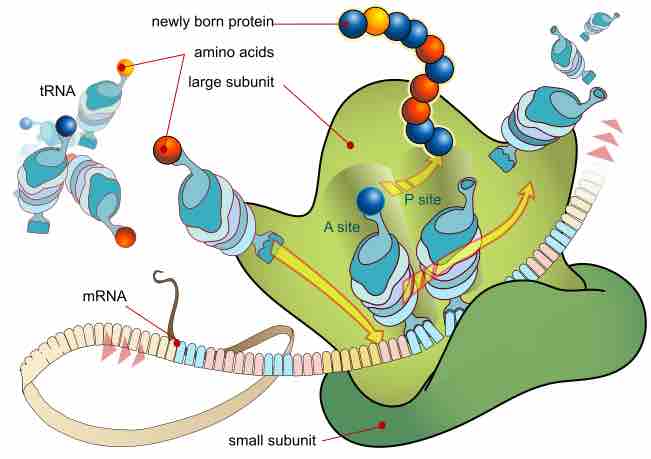
Inhibiting Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis inhibitors are substances that disrupt the processes that lead directly to the generation of new proteins in cells.

Inhibiting Essential Metabolite Synthesis
An antimetabolite is a chemical that inhibits the use of a metabolite, a chemical that is part of normal metabolism.