Chapter 5
Organizational Behavior
By Boundless
Perception is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information to represent and understand the environment.

Perceptual distortions, such as cognitive bias, can result in poor judgement and irrational courses of action.
Impression management is a goal-directed conscious or unconscious process in which people attempt to influence the perceptions of others.

The Big Five personality traits are openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism.
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator is a commonly used personality test exploring 16 personality types.

The disposition theory, three fundamental traits, and HEXACO model of personality structure are applicable to the work place.

Stress is defined in terms of its physical and physiological effects on a person, and can be a mental, physical, or emotional strain.
Work stress is caused by demands and pressure from both within and outside of the workplace.
Stress can impact an individual mentally and physically and so can decrease employee efficiency and job satisfaction.
A combination of organizational change and stress management is a productive approach to preventing stress at work.

An attitude is generally defined as the way a person responds to his or her environment, either positively or negatively.
Attitudes can positively or negatively affect a person's behavior, regardless of whether the individual is aware of the effects.

Values are guiding principles that determine individual morality and conduct.
Values influence behavior because people emulate the conduct they hold valuable.
Job satisfaction is the level of contentment employees feel about their work, which can affect performance.

Job satisfaction can affect a person's level of commitment to the organization, absenteeism, and job turnover.

Emotion and mood can affect temperament, personality, disposition, motivation, and initial perspectives and reactions.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs helps managers understand employees' needs in order to further employees' motivation.
Alderfer's ERG theory, based on Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, outlines three core needs: existence, relatedness, and growth.

David McClelland describes three central motivational paradigms: achievement, affiliation and power.
Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory states that certain factors cause job satisfaction and other factors cause dissatisfaction.
Equity theory explains the relational satisfaction in terms of fair or unfair distribution of resources within interpersonal relationships.
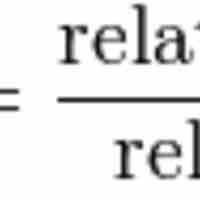
The assessment and restoration of equity helps improve employee performance and organizational behavior.
Expectancy theory deals with mental processes regarding choices and behaviors.

People perform better when they are committed to achieving certain goals, enabling businesses to benefit from employing goal-setting theory.

People perform better when they are committed to achieving certain goals, emphasizing the importance of strategic goal setting.

Reinforcement is a process of strengthening desirable behaviors, often through the use of rewards.

Punishment is the imposition of a negative consequence with the goal of reducing or stopping someone's undesirable behavior.
Managers can employ motivational theory and reinforcement tools to motivate employees and increase efficiency.
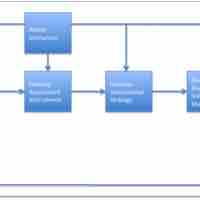
Job design is the systematic and purposeful allocation of tasks to individuals and groups within an organization.

The Job Characteristics Theory is a framework for identifying how job characteristics affect job outcomes.

Ways of improving job fit include assessing employee activities through various tools to increase employee satisfaction and efficiency.
Monetary compensation can be either guaranteed (base) pay or variable pay and positively correlates with job satisfaction.
Non-monetary compensations (e.g., benefits) are essential in recruiting skilled employees and maintaining a satisfied workforce.
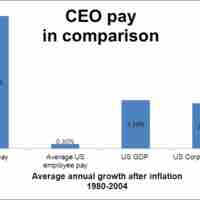
Financial rewards are often used as a tool to motivate managers to perform better.