Chapter 8
Control
By Boundless
A company's standards define its practices, while its objectives define what actions the company needs to take.
Managers must consistently update performance reports to monitor progress and measure operational success.
When comparing results it is important for an organization to look inward against historical trends and outward against competitive trends.
Taking corrective action requires identifying the problem and implementing a potential solution.
Organizational control involves using strategy, tactics, and operational oversight to monitor and improve company processes.
Bureaucratic control uses formal systems to influence employee behavior and help an organization achieve its goals.
Control uses information from the past and present and projections for the future to create effective control processes.
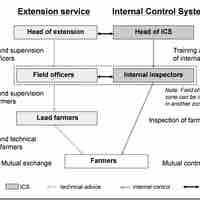
The control process can be hindered by internal and external constraints that require contingency thinking.

The quality control cycle improves processes through a continuous cycle of planning, doing, checking, and acting.
Quality control is used to evaluate and address the quality of the goods a business provides.
Total quality management (TQM) is the continuous management of quality in all aspects of an organization.
RATER is a service quality framework that highlights five important business areas customers use to analyze strength or weaknesses.

Six sigma, JIT, Pareto analysis, and the Five Whys technique are all approaches that can be used to improve overall quality.
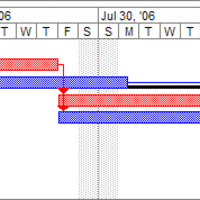
Gantt charts display the duration of steps in a project and are used by project managers to track the time and sequence of each step.

CPM and PERT are charts used to determine the sequence and maximum and minimum timing of activities in a project.
Financial and budget controls help ensure project success by controlling (and giving visibility to) input resources and output returns.

Project management audits are used to determine and control the quality, completion, and timing of a project.
A key component of project management is controlling inventory trajectories and quantities to reduce costs and maximize returns.
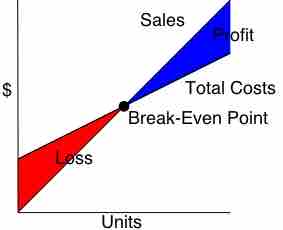
Break-even analysis can determine the minimum amount a company needs to sell in order to cover its costs with no gains or losses.
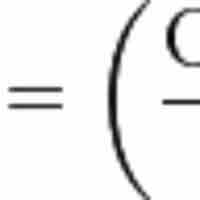
Ratio analysis is a useful tool for benchmarking the financial and operational efficiency of a project compared with other projects.
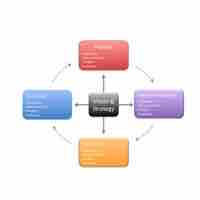
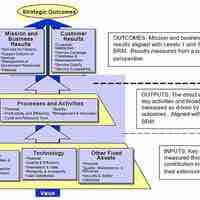
A balanced scorecard is a device that managers use to convey performance across a range of relevant strategic criteria.
The visual scorecard is a graphic analogy of the balanced scorecard framework and a key visual link between performance and strategy.

Balanced scorecard measurements require extensive data collection and are essential in validating scorecard outputs.
The key elements of a control process include a characteristic to be tested, sensors, comparative standards, and implementation.
Barriers to managing control include lack of resources, inaccurate measurements, improper information flow, and incorrect analyses.