Balanced Scorecards Defined
A balanced scorecard is a semi-standardized strategic management tool used to track, monitor, update, and improve key performance indicators (KPI) within an organization. These variables are generally a mix of financial and non-financial indicators that allow managers to better control strategic operational and financial commercial outcomes. The balanced scorecard is currently one of the most popular management tools used for tracking organizational performance
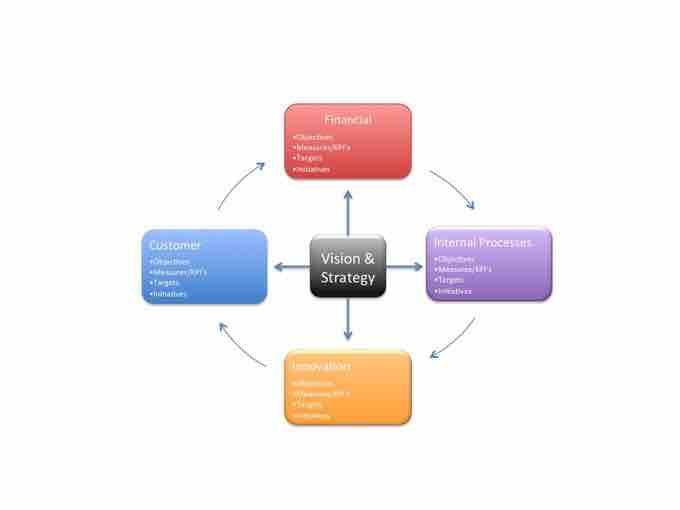
The balanced scorecard
On a standard balanced scorecard each"perspective" reminds the user to articulate attributes necessary for an effective scorecard: the financial perspective, the customer's perspective, innovation, and internal processes, all of which come together to form an organization's vision and strategy.
Originally created in 1987 by Art Schneiderman, an executive at the semiconductor firm Analog Devices, the balanced scorecard is an adaptation of early performance measurement techniques that were developed in complex post-industrial corporations in the U.S. and Europe.
Balanced Scorecard Perspectives
The balanced scorecard represents performance pictographically; its original design was a table broken up into sections, or perspectives, that generally included financial, customer, internal business processes, and learning and growth. Each perspective then included a set of five or six measures that could be compiled to inform the raw score for the corresponding perspective.
The four perspectives are:
- Financial: This section encourages the identification of a few relevant high-level financial measures that help companies to answer the question "How do we look to shareholders?"
- Customer: This section encourages the identification of measures that answer the question "How do customers perceive us?"
- Internal Business Processes: This section encourages the identification of measures that answer the question "What must we excel at?"
- Learning and Growth: This section encourages the identification of measures that answer the question "How can we continue to improve and create value?"
Managerial Use of the Scorecard
As organizational acceptance of performance management tools grew throughout the 1990s, the original design of the balanced scorecard evolved to include a host of other variables and considerations, most significantly at the intersection of performance and strategy.
Corporate strategic objectives were added to justify focusing on certain perspectives, effectively absorbing the original framework into a more comprehensive strategic planning exercise. Today, this second-generation balanced scorecard is often referred to as a "strategy map", but the vernacular "balanced scorecard" is still used to refer to anything consistent with a pictographic strategic management tool.
Managers generally use this tool to identify areas of the organization that need improved alignment and control with the broader organizational vision and strategy. The balanced scorecard gets each of the moving parts in an organization on the same page to ensure continuity and synergy between functional aspects.