Chapter 13
Oligopoly
By Boundless

An oligopoly - a market dominated by a few sellers - is often able to maintain market power through increasing returns to scale.

Oligopolies can form when product differentiation causes decreased competition within an industry.

One important source of oligopoly power are barriers to entry: obstacles that make it difficult to enter a given market.

Price leadership is a form of tacit collusion that oligopolies may use to achieve a monopoly-like market outcome.

Firms in an oligopoly can increase their profits through collusion, but collusive arrangements are inherently unstable.
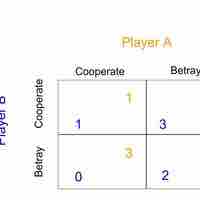
Game theory provides a framework for understanding how firms behave in an oligopoly.
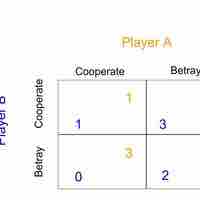
The prisoner's dilemma shows why two individuals might not cooperate, even if it is collectively in their best interest to do so.
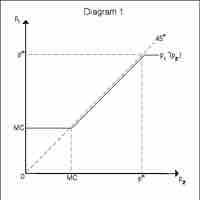
The Cournot model, in which firms compete on output, and the Bertrand model, in which firms compete on price, describe duopoly dynamics.
A cartel is a formal collusive arrangement among firms with the goal of increasing profits.
- Monopolistic Competition