Chapter 14
Inputs to Production: Labor, Natural Resources, and Technology
By Boundless

The marginal product of labor is the change in output that results from employing an added unit of labor.
The marginal revenue product of labor is the change in revenue that results from employing an additional unit of labor.
Firms will demand labor until the marginal revenue product of labor is equal to the wage rate.
Equilibrium in the labor market requires that the marginal revenue product of labor is equal to the wage rate, and that MPL/PL=MPK/PK.
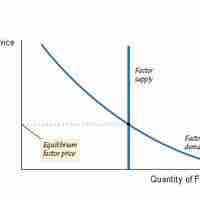
The wage rate is determined by the intersection of supply of and demand for labor.

Some differences in wage rates across places, occupations, and demographic groups can be explained by compensation differentials.
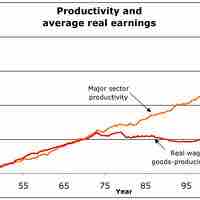
Theoretically there is a direct connection between job performance and pay, but in reality other factors often distort this relationship.
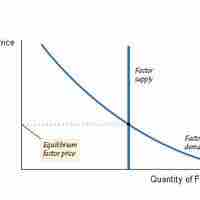
In a perfectly competitive market, the wage rate is equal to the marginal revenue product of labor.

A shift in the supply or demand of labor will cause a change in the market equilibrium.

Unions are organizations of workers that seek to improve working conditions and raise the equilibrium wage rate.
There are three factors of production that are required to produce economic output: land, labor, and capital.
The prices of different factors of production can help determine which products a country will produce.
Firms will demand more of a resource if the marginal product of the resource is greater than the marginal cost.
Demand for the type of workers that can provide positive marginal productivity over marginal cost will see an increase in their wages.
A capital market is a financial exchange for the buying and selling of long-term debt and equity-backed securities.

Commodity markets are exchanges that trade in primary rather than manufactured products.
Firms add capital to the point where the value of marginal product of capital is equal to the rental rate of capital.
Total factor productivity, which captures how efficiently inputs are utilized, is a key indicator of competitiveness.

Technological improvement improves the efficiency of production, which increases supply and lowers prices.