Chapter 21
Metals
By Boundless

Most pure metals are either too soft, brittle, or chemically reactive for practical use, and few pure metals occur naturally.

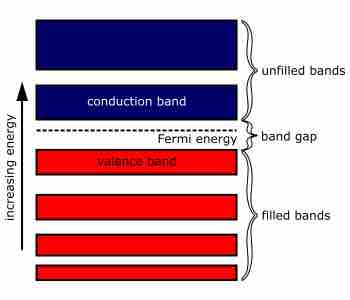
A metal can refer to an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat.
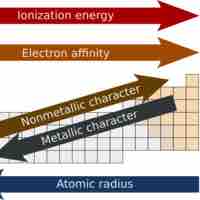
Metallic properties tend to decrease across a period and increase down a periodic group.

Alkali metals are chemical elements from the s-block of the periodic table. They have homologous physical and chemical properties.

The alkaline earth metals are chemical elements in the s-block of the periodic table with very similar physical and chemical properties.

Aluminum is a soft, silvery metal in the boron group of the periodic table.

Titanium, chromium and manganese are 3d transition metals notably used to add corrosion-resistance, durability, and lightness to steel.

Cobalt, nickel, copper, and zinc are 3d orbital transition metals with a variety of properties.