Chapter 21
The Functions of Money and Banking
By Boundless

The main functions of money are as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value.

Nearly all contemporary money systems are based on fiat money, which is modern currency that has value only by government order.
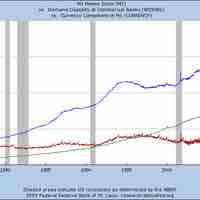
In economics, the money supply or money stock, is the total amount of money available in an economy at a specific time.

A nation's money supply is determined by the monetary policy actions of its central bank.

The foreign exchange market is a form of exchange for international currencies that determines the relative values of different currencies.

Credit is a term used to denote transactions involving the transfer of money or other property on promise of repayment.

Capacity to repay, capital, collateral, conditions, and character, are referred to as the "Five Cs of Credit".

A credit rating evaluates the credit worthiness of a debtor, specifically a business (company), individual, or a government.
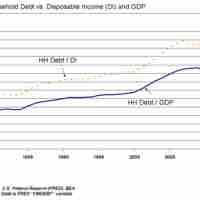
Debt compliance describes various legal measures taken to ensure that debtors honor their debts.
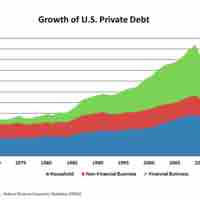
The economic collapse of 2008 had substantial impacts on the banking industry and the availability of credit for borrowers.

A non-bank financial institution offers customers bank-related services such as payday lending, cashier's checks, and check cashing.
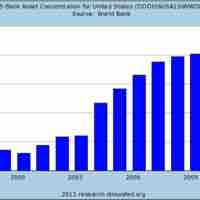
Commercial banks enable business by providing access to resources and risk-mitigating exchanges.

A savings and loan association is a special kind of deposit institution that only participates in a subsection of financial activities.
Credit unions offer local communities unique banking benefits by empowering local ownership and reinvesting in the community.

Electronic banking includes such services as ATMs, direct deposits, electronic fund transfers, and online banking.
An online direct bank has no physical branches, relying only on internet, phone, and mail services and often delivering better rates to customers.
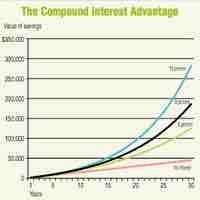
Personal finance is the application of the principles of finance to the monetary decisions of an individual or family.

The Federal Reserve System is the central banking system of the United States, which conducts the nation's monetary policy.

One of the Federal Reserve's duties is to regulate financial institutions, such as bank-holding companies and state member banks.

The U.S. Federal Reserve as the "lender of last resort" extends credit to financial institutions unable to obtain credit elsewhere.
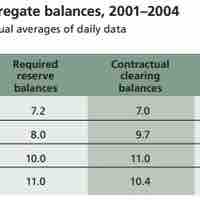
The Fed created a nationwide check-clearing system that provided an efficient and stable way of transferring funds between institutions.
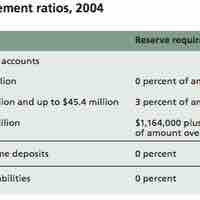
The Federal Reserve is in charge of setting reserve requirements for all depository institutions in the country.
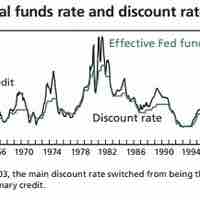
The Fed makes loans to depository institutions and charges different discount rates for each of discount windows.
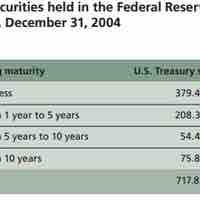
Open market operations (OMO) refer to a central bank's selling or buying of government bonds on the open market.

The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation is an independent agency whose mandate is to maintain stability and public confidence in financial system.
The NCUA is the independent federal agency created by the U.S. Congress to regulate, charter, and supervise federal credit unions.
Between 1989 and 2006, there were two separate FDIC funds–Bank Insurance Fund (BIF), and Savings Association Insurance Fund (SAIF).