wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 17 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 85,979 times.
Learn more...
This instruction will explain how to write a Java program with two classes, using Eclipse. It will highlight some of the features of the Eclipse IDE, including the automatic Class generator and the built in debugger. The Eclipse Foundation is an open source collaborative development community with many specific groups and interests. The article assumes you have correctly installed Eclipse on your computer. While this tutorial does not focus on writing Java code, the sample program is broken into steps that should be easy enough to follow.
Steps
-
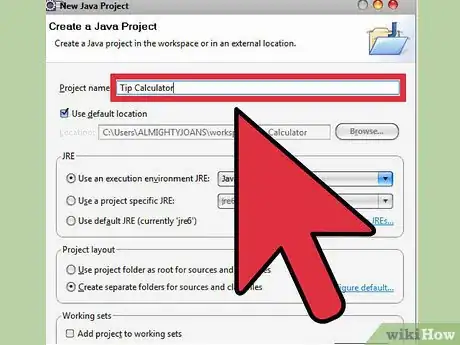
1Create a Java project. Click the drop down arrow beside the first icon at the top left of the screen called “new.” Select “Java Project."
- Give your new project a name and click finish. I will call my project "Tip Calculator." You can see that a new folder with your project name appears in the left hand column.
-
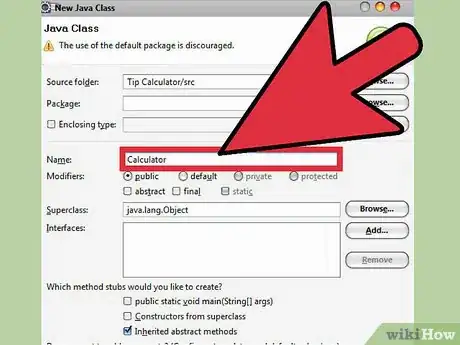
2Highlight the folder you have just created. Now click the “new” drop down menu once again. This time, pick "Class."
- Give your new class a name. For this class, we can simply use the default settings. Click finish and Eclipse will open a new Java class in the program window. I called my class "Calculator.”
Advertisement -
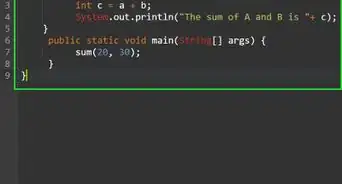
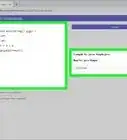
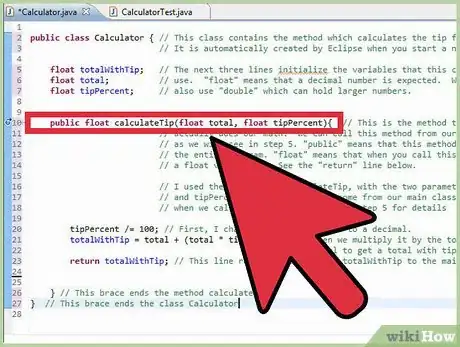
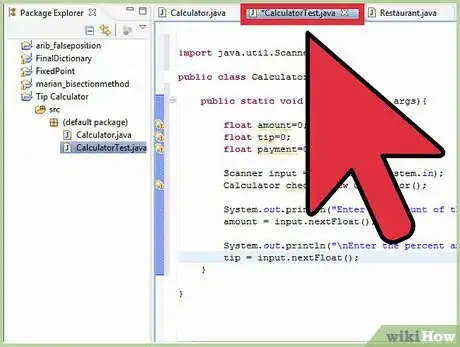
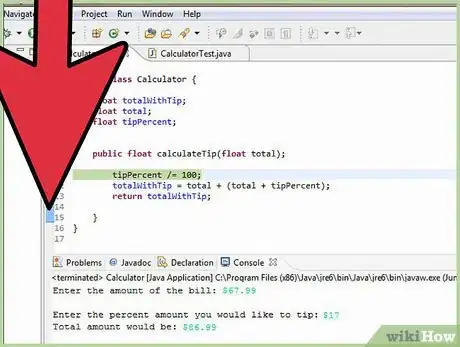
3Eclipse automatically creates a class in the program window. My class uses a method called calculate tip to calculate the tip on a restaurant check. For those who are interested, I have included the code in the image to the right. Each line is explained using line comments. Line comments start with “//” and are ignored by the java compiler.
-
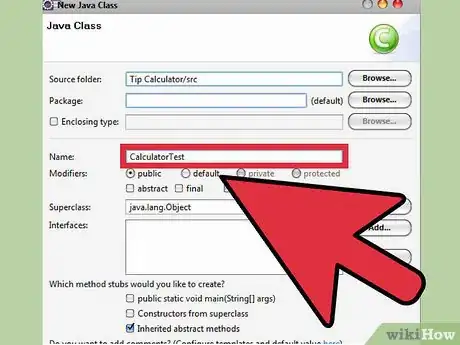
4It is time to create our main method. Go back to the drop down menu called “new” and, once again, pick “Class.” This time, check the box that says “public static void main(String[]args).” This indicates to Eclipse that you want to create a main method. Give your main class a name and click finish. I will call mine CalculatorTest. Eclipse now opens a new tab with your main class.
-
5We can now write the main method that calls the method calculateTip from the Calculator class. This main class will take input from the user for the amount of the bill and the % that they would like to tip. It then passes this information to the Calculator class and gets the calculation. Then the program displays the total. Once again, click on the image to the right to see the code I used.
-
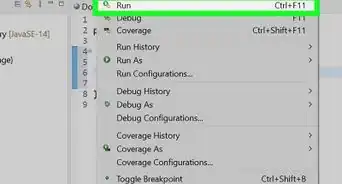
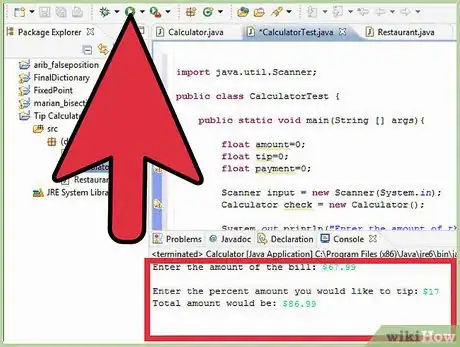
6Click the "run" button (which looks like a "play" icon) that is located just above your program window. This action will automatically save and compile your code. Your program will run in the console window just below the program window. Check to see if your program works correctly.
-
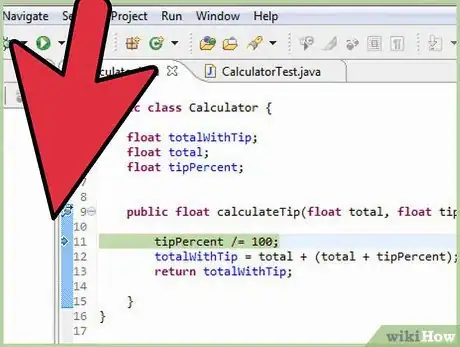
7Eclipse includes an excellent debug feature. I have changed my code so it now has a few mistakes. First, we will add a break point by double clicking the left margin of the line where we expect to encounter problems. You can see the break point at line 9.
-
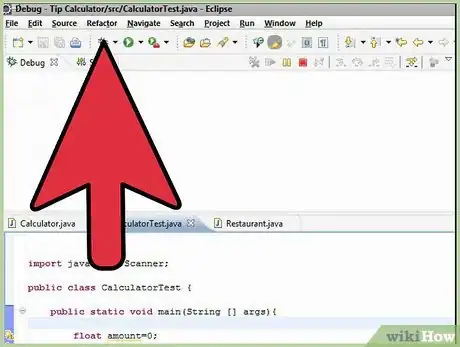
8Now click the "debug" icon at the top of the window, right beside the "run" button. It looks like a bug. Debugging mode will open some new windows that show you exactly what is happening when your program runs.
-
9The program will stop at the break point that you have set up. From there, you can navigate using the “step over” arrow, just above your main display or by hitting F6. The “step over” command takes you line by line through your program.
-
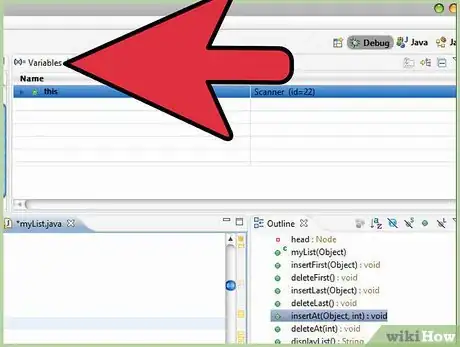
10As you "step" through your program, you can "mouse" over your variables in your program window to see what values they contain during each step. Alternatively, you can open the variable window located at the top right of Eclipse. With this window open, you can see what a list of your variables, and what numbers they are holding.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow can I find out where my Java programs are going wrong? I am a beginner at Java.
 Community AnswerYou can use the debug feature in Eclipse to find where your program goes wrong. Place breakpoints in places where you get an exception thrown, and debug to find the error in your code.
Community AnswerYou can use the debug feature in Eclipse to find where your program goes wrong. Place breakpoints in places where you get an exception thrown, and debug to find the error in your code.
-Step-42.webp)