This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff. Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
The wikiHow Video Team also followed the article's instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 11,716 times.
Learn more...
Knowing the size of your pipe threads is essential for connecting pipes so they have a tight seal. While measuring pipe threads may seem confusing, it’s actually relatively easy to do because the size of the pipe and its thread size are measured according to the same scale. First, you need to identify whether you have a male or female pipe. A male pipe has the threads on the outside of it, while a female pipe has the threads inside of it. Take a few simple measurements so you compare them to find your pipe thread size.
Steps
Calculating Male Pipe Threads
-
1Wrap a string around the threaded end of the pipe. Take a piece of white or light-colored string longer than the circumference of the pipe and hold 1 end against the threading on the outside of the pipe. Wrap the string around the pipe evenly so it overlaps the end.[1]
- Use a thin piece of string so the diameter doesn’t affect your measurements.
-
2Mark the point where the strings overlap. Keep the string held against the exterior threading and take a dark marker and make a clear marking on the string right where it overlaps the end. Make sure the marking is clearly visible so you can easily measure it.[2]Advertisement
-
3Measure the distance between the end of the string and the mark. Remove the string from the pipe and place it on a flat surface so it’s lying straight. Take a ruler or tape measure and measure the distance from the end of the string to the marking that you made to find the circumference of the pipe. Write down the measurement for your calculations.[3]
- Make sure the string is flat and stretched straight for more accurate measurements.
-
4Divide the circumference by 3.14159 to find the decimal equivalent. Take the circumference measurement of your pipe and divide it by pi to reduce your measurement to a decimal value. Round to the nearest number so you have 3 decimal places. Write down the number after you divide it so you can use it to find the thread dimensions.[4]
- For example, if you have a circumference of 3.375 inches (85.7 mm), then dividing by 3.14159 would give you 1.07429.
-
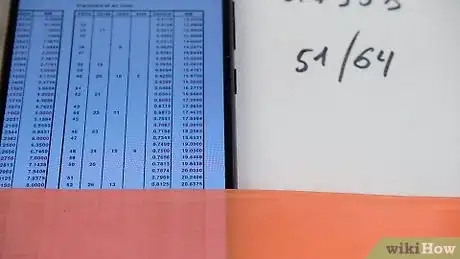
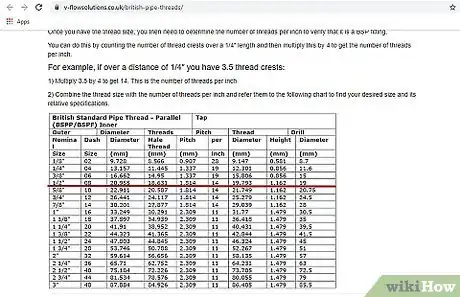
5Consult a conversion chart to find the thread dimensions. Search online or reference a paper chart that converts the decimal equivalents of the circumference of your pipe into a nominal diameter, which is the outside diameter of the pipe without the added wall thickness. Use the nominal diameter to find the thread dimension on the chart, which will be listed as “threads per inch” or “threads per millimeter.” Look for the number closest to your number to find your pipe thread measurements.[5]
Sample Conversion Chart (in Inches)
5/16 inch has a decimal equivalent of .313, which has 27 threads per inch.
13⁄32 inch (1.0 cm) has a decimal equivalent of .405, which has 27 threads per inch.
35/64 inch has a decimal equivalent of .540, which has 18 threads per inch.
43⁄64 inch (1.7 cm) has a decimal equivalent of .6.75, which has 18 threads per inch.
27⁄32 inch (2.1 cm) has a decimal equivalent of .840, which has 14 threads per inch.
Finding Female Pipe Thread Size
-
1Use a ruler or tape measure to measure the inner diameter of the pipe. Hold the pipe in 1 hand and take a ruler or tape measure in your other hand. Spread the ruler across the diameter of the pipe and measure from 1 interior wall to the other. Write down the number so you can use it for your calculations.[6]
- Write down your measurements on a piece of paper so you have space to add or subtract.
-
2Subtract 1⁄4 inch (0.64 cm) to find the nominal diameter of the pipe. Take the number you wrote down for the measurement of the inside diameter of the pipe and subtract 1⁄4 inch (0.64 cm) from it to reduce it down to its nominal diameter, which is its diameter without the added thickness of the wall of the pipe, so you can use it to reference the conversion chart. Write down the new number for easy reference.[7]
- For example, if the inside diameter of your pipe measured 1 inch (2.5 cm), then you need to subtract 1⁄4 inch (0.64 cm) to get a nominal diameter of 3⁄4 inch (1.9 cm).
Tip: Use a calculator or a calculator app on your smartphone to subtract small fractions of measurements so you can be sure they’re accurate.
-
3Match your measurement to a thread chart to find the dimensions. Look up a pipe conversion chart online or reference a paper one that lists the nominal diameters and the thread dimensions that correspond to them. Locate your diameter and see which thread dimensions match the measurement to find your pipe thread measurement.[8]
- Examples of common measurements include:
1⁄8 inch (3.2 mm) - 27 threads
1⁄4 inch (6.4 mm) - 18 threads
3⁄8 inch (9.5 mm) - 18 threads
1⁄2 inch (13 mm) - 14 threads
- Examples of common measurements include: