This article was co-authored by Claudia Carberry, RD, MS. Claudia Carberry is a Registered Dietitian specializing in kidney transplants and counseling patients for weight loss at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. She is a member of the Arkansas Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. Claudia received her MS in Nutrition from the University of Tennessee Knoxville in 2010.
There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 96% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 194,215 times.
If you go by the multitude of books, websites, programs, celebrity endorsements, prepackaged foods, and varying rules about what’s “in” and what’s “out,” starting on a low-carb diet may seem like an impossibly complicated task. By sticking to a few basic principles, planning out your menu, and drinking lots of water (yes, really), you too may discover that low-carb dieting can be simple, easy, enjoyable, effective, and delicious.
Steps
Keeping It Simple
-
1Simplify your definition of low-carb dieting. Start with the basics. When present in the body, carbohydrates, converted into simple sugars (known as glucose in your bloodstream), are your main fuel source. Low-carb dieting is based on the premise that, without sufficient carbs available as fuel, your body will burn its fat stores to keep you moving.[1]
- There’s no official definition for a low-carb diet, but the range limit is usually somewhere between 50-100g of carbs per day. This range will vary with each person's body weight. Anything below 50g per day would typically cause the individual to go into ketosis. In comparison, typical American dietary guidelines recommend between 225-325 grams of carbs (900-1300 calories) daily.[2]
- Medical opinions vary on the efficacy of low-carb diets as well. They do seem to offer weight-loss benefits, at least in the short term, and may have benefits for diabetics by decreasing blood glucose levels.[3] [4] Long-term health impacts are less clear. Consult your physician before beginning a low-carb diet.
-
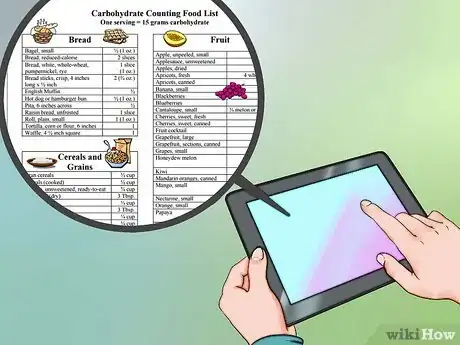
2Learn to identify carb amounts in foods. Once on a low-carb diet, you'll likely be able to spot carb-heavy foods with ease before too long. It may be helpful, however, to keep a guide handy, at least early on, that identifies carb amounts in various foods.
- Such a guide can be especially useful when eating out.
- For example, each of the following has approximately 15 grams of carbs:
- 1 slice bread; ½ bagel
- 1 banana, orange, or apple; ¾ c. blueberries; 1 ¼ c. strawberries
- ½ c. apple or orange juice
- 1 c. milk (skim, full fat, or in between)
- ½ c. cooked beans, lentils, corn, or peas
- 1 small baked potato
- ½ packet of instant oatmeal
- 15 chips or pretzels; 1 cookie; ½ donut
- ⅓ c. mac & cheese; ½ breaded chicken sandwich
- ½ c. ice cream
- 1 ½ c. cooked or 3 c. raw of most non-starchy vegetables
- meats, fish, eggs, and many flavorings, dressings, and toppings have fewer than 5 carbs per serving
Advertisement -
3Simplify what’s “in” and what’s “out.” This is where it can start to get confusing. Different low-carb diet plans will tell you different things about what you should and should not eat.
- Some plans tell you to eat high-fat proteins (like meats and dairy) and skip almost all grains (especially containing gluten), while others emphasize low-fat proteins and a more moderate amount of whole grains.
- Vegetables are a staple of low-carb dieting. All vegetables contain carbohydrates but some contain even more. The ones to focus on consuming are 'non-starchy' vegetables. In addition, some low-carb dieters do not count green non-starchy vegetables into their overall carbohydrate count. This is due to the high fiber count in these vegetables and many believe that this fiber content 'counteracts' any carbohydrates within these vegetables.
- To make your low-carb diet simple, make your criteria simple: more protein and vegetables, less refined starches and sugars, and much less processed food.
- One simple suggestion would be do eat lots of lean proteins and vegetables, prepared simply; add in supplementary helpings of whole grains, legumes, lowfat dairy, and fruits, and skip processed foods.#Don’t buy what you don’t need. If guidebooks or diet plans will help your stick to your low-carb diet, then it may be a worthwhile expenditure for you. However, you can begin and sustain a low-carb diet without buying any of those things. Just repeat to yourself, “more protein, more vegetables, less starches and sugars.”
- Don’t bother with prepackaged low-carb foods if possible. Eating fresh, minimally-processed foods is always preferable.
-
4Realize that you won’t be hungry all the time. This might be your first worry when you think about giving up bread, pasta, potatoes, and other foods you think of as filling (and tasty). Your body can and will adjust and can be just as easily satisfied by a low-carb diet.
- For a low-carb diet, you don’t eat less, just differently. Stick to eating 3-4 meals per day with small, healthy snacks as needed.[5] You also experience less hunger due to your blood sugar being better regulated. With less carbohydrates, fewer blood sugar spikes (and falls) occur. This keeps you from getting too hungry or experiencing cravings.
-
5Make water your friend. You may not believe it at first, but water can be filling and can help make your low-carb transition easier.
- You want to drink at least 8 (8 oz) glasses of water per day, but even more will help.[6]
- Carry a water bottle with you all day. Take regular drinks, before you’re thirsty. When you feel a craving coming on (especially for a cookie, donut, etc.), drink water first and see if that calms it.
- Slice fresh lemons and add them to your water pitcher if you need some flavor.
-
6Stock your pantry right. If you live in a household of carb-eaters, you won’t be able to pitch the potatoes and bread, but you can make sure you are well-stocked with staples of low-carb cooking.
- A sampling from of low-carb pantry staples includes:
- canned tuna / salmon / sardines
- canned vegetables / fruit (in light syrup)
- chicken / beef stock
- canned tomatoes / tomato paste
- low-sugar peanut butter
- jarred roasted peppers
- olives, pickles, and capers
- whole grain pasta, rice, and flour
- oatmeal and high-fiber, no-sugar cereal
- sugar substitute
- olive oil
- As you develop your personalized low-carb menu, stock your pantry to suit.
Planning Your Meals
-
1Pack your breakfast with protein. If a good old-fashioned bacon and eggs breakfast sounds good to you (minus any toast, home fries, or pancakes), you’re in luck.
- A poached or fried egg, with bacon or sausage on the side if desired, can become your standard daily breakfast.
- For more variety, make omelets with a variety of vegetables (spinach, bell peppers, sun-dried tomatoes, zucchini, etc.), meats, and a little cheese.[7]
- You can even try your hand at low-carb blueberry or zucchini muffins.
- Drink water, plus some coffee or tea (minus sugar, plus sugar substitute if necessary) if you need a caffeine boost.
-
2Switch out your sandwich for lunch. Take the good stuff sandwiched inside a sandwich, skip the bread, and you’re on your way to a low-carb lunch.
- Roll some deli meat up in a lettuce leaf. Add mustard, a bit of cheese, a pickle spear, or other flavor additions. Pair with fresh veggies -- carrots, celery, pepper slices, etc.
- Mix up some chicken or shrimp salad and skip putting it in bread. Just use your fork and add some veggies on the side.[8]
- Low-carb pizza could be dinner one night and lunch the next day.[9]
- Drink -- you guessed it -- water. Will an occasional iced tea or diet soda ruin your diet? No. But get used to making water your standard mealtime (and other times) beverage.
-
3Have meat-and-no-potatoes dinners. Steak, meatballs, pork chops, grilled chicken or fish (no frying, no breading) -- these will likely become dinnertime staples. Roasted or grilled vegetables and a side salad can become a standard accompaniment.[10]
- Rely on spices and other seasonings -- capers or olives, for instance -- to change the flavor profile of your meals.
- A roasted pork tenderloin,[11] perhaps with roasted asparagus and a salad, will make even a family of carb-lovers happy at dinnertime.
- Let’s all say it together -- Drink water!
-
4Slip in low-carb snacks. Starving yourself between meals will only make it easier for you to “cheat” on high-carb guilty pleasures, so prepare yourself by pre-packaging your own low-carb snacks to see you through the end of the workday (or any other time you need it).
- Something as simple as a handful of almonds or blueberries (both of which are generally seen as all right in moderation in low-carb diets) can provide a quick boost.
- Standard options include cut veggies with low-carb dressing; mozzarella cheese strings; or unsweetened yogurt, to name a few. Fruit intake will need to be a bit more limited, but having an apple, orange, raisins or grapes, dried apricots, or an unsweetened applesauce / peach / mixed fruit cup is far better than a bag of chips or a snack cake.
- Have we mentioned drinking water?
Knowing Risks and Rewards
-
1Look for benefits beyond just weight loss. There is some debate whether it is the "low-carb" or "diet" portion that deserves more credit, but evidence exists that people on low-carb diets may prevent or improve health problems like metabolic syndrome, diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease.[12]
- Low-carb diets do seem to have an advantage in comparison to moderate-carb diets in regards to reducing LDL ("bad") cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
-
2Know the risks of insufficient carb intake. Our body needs carbohydrates to produce the energy it needs to operate. Properly-followed low-carb diets should not cause major medical issues, but severely restricting carbohydrate intake does carry risks.[13]
- If you go to the extreme and consume less than 50 grams of carbs a day, you risk developing ketosis. This occurs when ketones build up in your body as a result of excessive break-down of stored fat for energy, and can cause nausea, fatigue, headaches, and bad breath.
- During the first week or two of a low-carb diet, you may experience symptoms akin to ketosis -- nausea, headache, bad breath, etc. -- as your body adjusts to the significant reduction in carbs. This should pass, however, and you should move on to feeling perhaps better than ever.
- Some medical professionals believe low-carb diets may increase long-term risks of cardiovascular disease and cancers because of the significant amounts of animal fats and proteins consumed, but the long-term risks of low-carb dieting, like the rewards, are more speculative than definitive.
-
3Don't miss out on nutrients. Especially if you are on a low-carb diet for an extended period of time, there is a risk of vitamin and mineral deficiencies that can cause a host of problems including bone loss, gastrointestinal disorders, and increased risk for various chronic conditions[14]
- Fruits may be full of sugars, but they are also full of vitamins and minerals. Don't completely exclude them from your low-carb diet. Make them a supporting player, not the star of the show that is your daily menu.
- You may want to consider taking a multivitamin, or other supplements, but it is best to discuss this with a medical professional first.
-
4Involve a medical professional. Talk to your doctor or other healthcare professional about your desire to begin a low-carb diet. Discuss your medical history and relative risks and benefits of the diet for you.
- If you have a heart condition, reduced kidney function, or diabetes, among other conditions, it is especially important that you talk to your physician. You may well still be advised to begin the low-carb diet and it may benefit you greatly, but your doctor may also have specific advice and guidelines for you.[15]
Warnings
- Get as many temptations out of your house as you can. If you're living with carb eaters, this may not be possible so keep that water pitcher nearby. It can keep a lot of demons at bay.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Know that there are risks for a low carbohydrate diet. Remember, consult your medical professional first.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Carbohydrate-free diets may lead to low energy and unexplained headaches. Talk to a doctor if these symptoms occur.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- If you have doubts about your health, see your doctor and get testing done before and a few months after. Many doctors are supportive of low carb dieting now and realize that, when followed correctly, it is a healthy way to eat. Gauge how you are feeling. Generally you will go through an adjustment period in the first week, but it does pass.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Things You'll Need
- Water pitcher
- A good leak-proof sports water bottle you can carry with you everywhere
- A determined attitude
References
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537084/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537084/
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/low-carb-diet/art-20045831
- ↑ http://www.diabetes.co.uk/diet/low-carb-diabetes-diet.html
- ↑ https://www.dietdoctor.com/low-carb
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002471.htm
- ↑ https://nutrition.org/protein-its-whats-for-breakfast/
- ↑ http://authoritynutrition.com/low-carb-diet-meal-plan-and-menu/
- ↑ http://www.foodnetwork.com/topics/low-carb-recipes.html
- ↑ http://authoritynutrition.com/low-carb-diet-meal-plan-and-menu/
- ↑ http://www.foodnetwork.com/topics/low-carb-recipes.html
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/low-carb-diet/art-20045831?pg=2
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/low-carb-diet/art-20045831?pg=2
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/low-carb-diet/art-20045831?pg=2
- ↑ http://www.diabetes.co.uk/diet/low-carb-diabetes-diet.html
About This Article
To make low carb dieting simple and easy, try to focus on eating more protein and vegetables instead. You can stock up on low-carb staples, such as canned fish, canned fruit and vegetables, whole grain pasta, rice, flour, and canned tomatoes. For breakfast, try eating protein-rich foods like vegetable omelettes, fried or poached eggs, and bacon or sausage. At lunchtime, you can make a salad from your usual sandwich ingredients, just without the bread. For dinner, you can roast or grill vegetables to go with steak, meatballs, pork chops, or fish. For more tips form our Dietary co-author, including how to make low-carb snacks easy, read on!













-Step-3-Version-3.webp)






















-Step-3-Version-3.webp)

































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...