This article was co-authored by Marshall Stephens. Marshall Stephens is an Aquarium Expert at Private Oceans Aquariums in West Palm Beach, Florida. Marshall has over 20 years of experience in the aquarium industry and focuses on captive-bred animals. They specialize in tropical and marine aquariums and are a contributor to the Loggerhead Marine life center in Jupiter Florida.
There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 14 testimonials and 85% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 297,431 times.
Ammonia is a chemical compound that can infiltrate your aquarium. Ammonia can enter your tank through outside water or decomposition of fish or other natural matter in your tank. Ammonia can be very harmful to your fish. That is why it is important to keep your ammonia levels as close to zero as possible. You can take several steps to monitor your ammonia levels and to lower them as necessary.
Steps
Lowering Ammonia Levels
-
1Purchase a test kit. A test kit is the fastest and most reliable way to determine if you have ammonia in your tank. There are many effective test kits that you can purchase. Ask the employees at your local pet store to help you choose the best one for your needs.[1]
- Ammonia test kits are very affordable. Most cost between $5-$10.
- A test kit can tell you whether you have elevated ammonia levels. Keep one on hand in case you notice any symptoms.
- Follow the directions on the packaging. If the test indicates any level of ammonia, that is too much.
-
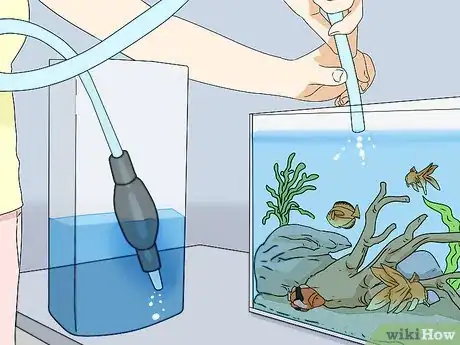
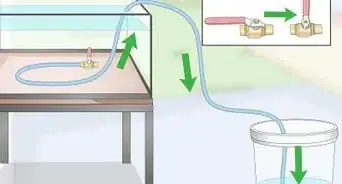
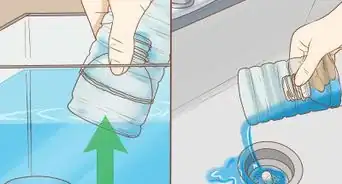
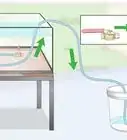
2Change your water. The only safe level of ammonia is zero. If your test kit detects any amount of ammonia, you need to perform a water change. This process can take several days.[2]
- Changing the water is the only safe way to lower ammonia levels. Products that promise to remove ammonia might have negative side effects, so they should be avoided.
- A water change means that you will remove 20% of the water in the tank. Use a clean bucket or jug to remove the water.
- If your fish are very stressed, check the pH. If it’s no more than a point difference of what the new water is, you can change half of the water.
- Replace the water with fresh water. Use dechlorinated tap water.
- Continue changing the water over the next 2-3 days until there is no trace of ammonia. You do not need to remove your fish or any plants that are in your tank.
Advertisement -
3Cycle your aquarium. The process by which you keep the water in your aquarium healthy for your fish is known as "cycling". The primary reason to cycle your aquarium is to ensure that the levels of ammonia and nitrates are at the proper level. You can cycle a new tank or an already established tank.
- A full cycle will take 4-6 weeks to complete. Begin by placing all new water in your tank.
- With a new aquarium, start slowly. Let the aquarium run for at least a day before adding fish.
- Add fish slowly. Do not add more than 3 new fish per week to any tank.
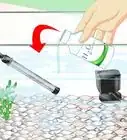
- Purchase a cycling aid product. You can ask for these at your local pet or fish supply store. There are several brands that will contain bacteria to supplement your tank.
- These products will help promote healthy bacteria in your tank. Follow the instructions on the product packaging.
-
4Keep track of water conditions. When you are preparing and cycling an aquarium, it is important to keep a log of the components of your tank water. Closely monitor the levels of ammonia, nitrate, and pH. Keeping careful records can help you notice changes and correct the levels as fast as possible.
- You can write down all of the chemical levels in your water. You can also note factors such as temperature level and population statistics.
- There are many websites and apps that can help you monitor your tank. Some sites offer basic memberships for free.[3]
- Other sites are more sophisticated. You can purchase memberships if you need to monitor several aquariums.
-
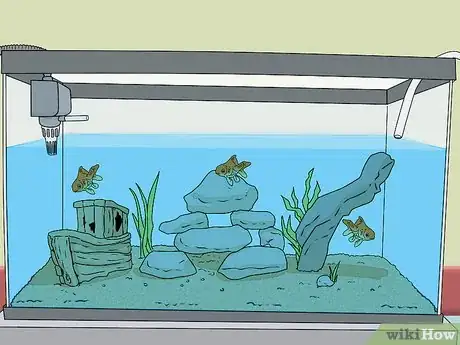
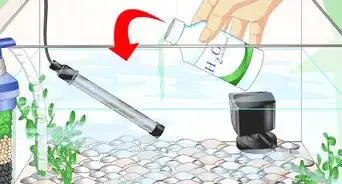
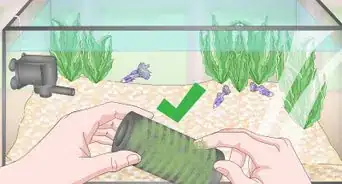
5Choose the right filter. A filtration system is key to lowering and regulating ammonia levels. A good filter will regulate and neutralize ammonia and nitrates. It will also remove floating debris from your tank.
- Purchase the best filter for your tank. Filters come in many sizes and price ranges, so do your research.
- Read reviews online. You should also talk to experienced employees at your local pet store.
- Power filters are commonly used for tanks up to 55 gallons. They are used to increase biological filtration, which means you can keep more fish in your tank.
- If your tank is larger than 55 gallons, consider getting a Canister filter. They are the most powerful and effective for large tanks.
Maintaining A Zero Ammonia Level
-
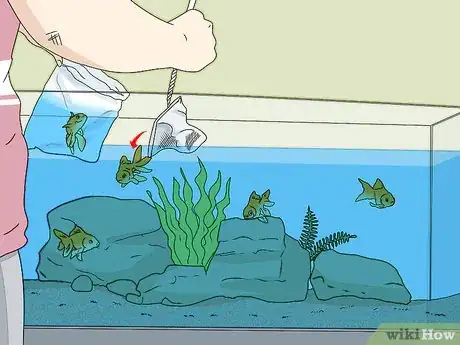
1Introduce new fish slowly. Ammonia can be toxic to tropical fish. For this reason, it is important to regularly monitor the water quality of your tank. You should also only add new fish gradually to your tank.[4]
- Fish are responsible for some of the ammonia output that inevitably ends up in your tank. When you are setting up a new tank, introduce fish slowly.
- Add tropical fish to your tank in small groups. Monitor the water to make sure that the ammonia levels are remaining steady.
- Ammonia is lethal, so try to keep your levels as close to zero as possible. 0 is the ideal level of ammonia in a fish tank.
-
2Know the signs of a problem. In addition to checking your water, you can look for other symptoms that your ammonia levels are too high. The primary symptom is the death of a new fish. If you add a new fish to a previously healthy tank, that fish might be reacting to unexpected ammonia.[5]
- Fish who are suffering from ammonia poisoning have trouble getting oxygen they need from the water. Ammonia causes fish gills to stick together and fish can't breathe.
- On many tropical fish, you can visually see their gills moving. If you can't see the gills moving anymore, your fish might be in distress.
- Non-lethal levels of ammonia can still be a problem. Fish exposed to ammonia will experience stress and might behave differently than usual. They may swim faster than usual or appear erratic in their movements.
-
3Protect your fish. Remember to always take care to keep your fish safe and healthy. If you discover that ammonia levels are too high, take steps to lower them immediately. You should also take precautions to try to prevent levels from rising.[6]
- Protect your fish by carefully monitoring your population. If a fish dies, it's a sign there might be a problem with your water.
- Make sure to relocate your fish if your filter breaks. Consider having a back up tank so that your fish will have a safe place to go.
Taking Care of Your Aquarium
-
1Set up a water care schedule. In addition to monitoring and regulating ammonia levels, there are several things you can do to keep your aquarium healthy. Make it a habit to care for your tank water regularly. For example, you should check the water temperature every day.
- On a weekly basis, replace 10% of the water with dechlorinated water.You should also test your water for nitrates and ammonia weekly.
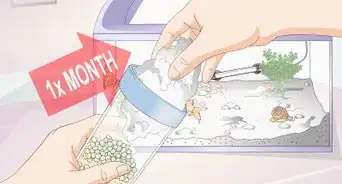
- Each month, change 25% of your water. You should also perform any necessary filter maintenance.
- On a monthly basis, scrub the algae from your tank. Prune live plants if you have them.
- Write down your maintenance schedule on your calendar so that you keep track of each of your steps.
-
2Perform regular maintenance. Part of maintaining a healthy aquarium is to provide the proper amount of lighting. Most fish need 8-10 hours per day. Make sure that they are getting the correct amount of light.[7]
- You can purchase lights with timers for your aquarium. This will ensure that you are not over or under lighting them.
- Practice precaution after a power failure. Even a brief loss of power can cause stress for your fish.
- After a power outage, check to make sure that all of your equipment is functioning properly.
-
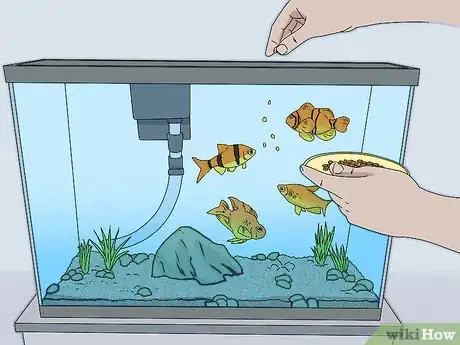
3Feed your fish properly. In order to have healthy and happy fish, you need to provide them with the proper diet on a proper schedule. What you feed them will depend on what type of fish you have. Make sure that you are purchasing the right food for your aquarium.[8]
- Make sure not to overfeed your fish. That can cause the tank to become contaminated.
- Experiment to find the right amount of food. Your fish should eat their fill in about 5 minutes.
- If it takes them longer than 5 minutes, reduce the amount. If they finish quickly, add more food.
- Try to feed the fish at the same time each day. Keeping to a schedule will help you keep track of feedings.
-
4Create a healthy home for your fish. An important part of keeping your fish healthy is to carefully control the population. When you are increasing the population, it is best to increase your number gradually. Do not add more than 3 fish at a time, and avoid overcrowding.[9]
- Purchase healthy fish. The best way to do this is to go to a reputable supplier. Read reviews from other customers.
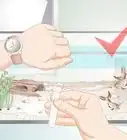
- Make sure to acclimate new fish. Keep them in their bag for the first 15-20 minutes that they are in the aquarium.
- If you have had to medicate your fish, take extra precautions to keep the others healthy. Perform water changes more frequently to make sure you get rid of traces of the medication.
Warnings
- A sign that you may want to treat the water is if the water smells bad and rotten. This can be a sign of ammonia from rotting food/waste!⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Some fish produce more waste than others, so it is especially important to cycle your tank, siphon it, and even use double filtration.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you'd like to learn more about fish tanks, check out our in-depth interview with Marshall Stephens.
References
- ↑ http://fins.actwin.com/mirror/begin-tests.html
- ↑ http://www.firsttankguide.net/ammonia-stress.php
- ↑ http://www.aquaticlog.com/
- ↑ http://www.fishchannel.com/fish-health/healthy-aquariums/controlling-ammonia.aspx
- ↑ http://www.petmd.com/fish/conditions/infectious-parasitic/c_fi_old_tank_syndrome
- ↑ http://www.peteducation.com/article.cfm?c=16+1276&aid=2751
- ↑ http://www.fish.com/fish-articles/10-steps-for-a-healthy-aquarium/697/
- ↑ http://www.petmd.com/fish/nutrition/evr_fi_fish_food
- ↑ http://www.fish.com/fish-articles/10-steps-for-a-healthy-aquarium/697/
About This Article
To lower ammonia levels in your fish tank, purchase a test kit to determine the current ammonia levels. If the kit detects any amount of ammonia in the tank, perform a water change by removing 10-15% of the water and replacing it with fresh water. Continue changing 10-15% of the water daily over the next 2-3 days until the test kit picks up no trace of ammonia. Don't worry, you don't need to remove your fish or plants from the tank! For tips on maintaining ammonia-free tank water, read on!