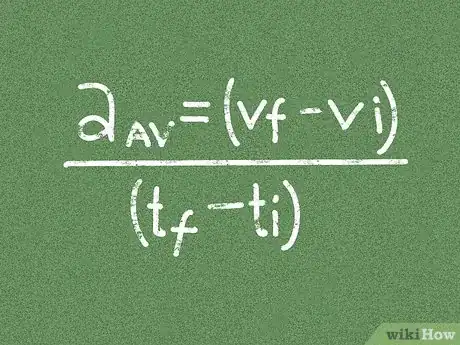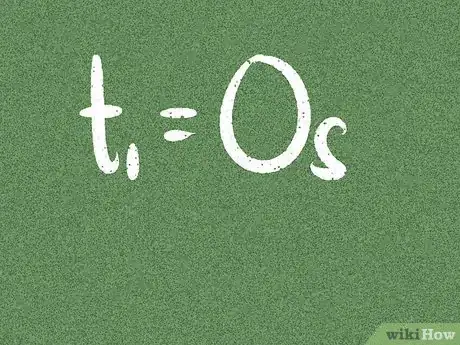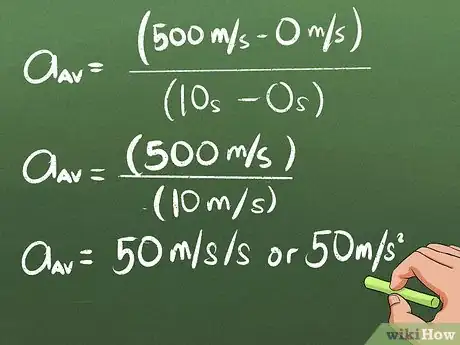This article was co-authored by Sean Alexander, MS. Sean Alexander is an Academic Tutor specializing in teaching mathematics and physics. Sean is the Owner of Alexander Tutoring, an academic tutoring business that provides personalized studying sessions focused on mathematics and physics. With over 15 years of experience, Sean has worked as a physics and math instructor and tutor for Stanford University, San Francisco State University, and Stanbridge Academy. He holds a BS in Physics from the University of California, Santa Barbara and an MS in Theoretical Physics from San Francisco State University.
There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 310,444 times.
Acceleration is a quantity that describes change in velocity, include both changes in speed and changes in direction. You can find the average acceleration to determine the average velocity of the object over a period of time. Because it's not something most people calculate in everyday life, acceleration problems can feel a little unfamiliar, but with the right approach, you'll be understanding them in no time.
Steps
Calculating Average Acceleration
-
1Understand acceleration. Acceleration describes how quickly something is speeding up or slowing down.[1] The concept really is that simple, although your math textbook might describe it as the "change in velocity over time." Acceleration also describes the direction something is moving, which you can include as a written description or as part of the math:
- Usually, if an object is accelerating right, up, or forward, people write it as a positive (+) number.
- If an object accelerates left, down, or backward, use a negative (-) number for acceleration instead.
-
2Write the definition as a formula. As mentioned above, acceleration is the change in velocity over the change in time.[2] [3] There are two ways to write this as a math formula:[4]
- aav = Δv/Δt (The symbol Δ or "delta" just means "change.")
- aav = (vf - vi)/(tf - ti) In this equation, vf is the final velocity, and vi is the initial, or starting, velocity
Advertisement -
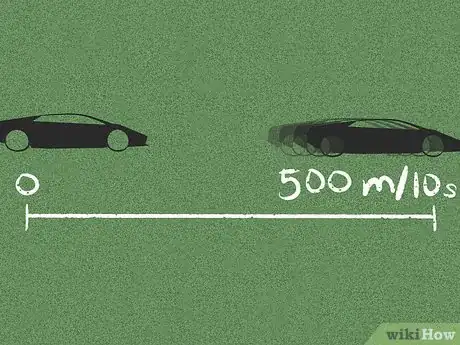
3Find the initial and final velocity of the object. For example, if a car goes from parked on the sidewalk to moving at a velocity of 500 meters/second to the right, the initial velocity is 0 m/s, and the final velocity is 500 m/s right.[5]
- From now on, we'll use positive numbers to describe motion to the right, so we don't have to specify the direction every time.
- If the car starts out going forward and ends up going backward, make sure to write the final velocity as a negative number.
-
4Note the change in time. For instance, the car might take 10 seconds to reach the final velocity. Unless the problem says otherwise, this usually means tf = 10 seconds and ti = 0 seconds.[6]
- Make sure your velocities and times are written in consistent units. For instance, if your velocity is written in miles per hour, the time should be written in hours as well.
-
5Use these numbers to calculate average acceleration. Put the velocities and time into the formula to find the average acceleration.[7] In our example:
- aav = (500 m/s - 0 m/s)/(10s - 0s)
- aav = (500 m/s)/(10 s)
- aav = 50 m / s / s This can also be written as 50 m/s2.
-
6Understand the result. The average acceleration describes how rapidly the velocity changed during the time we're examining, on average.[8] In the example above, the car was speeding up to the right, and each second it sped up by an average of 50 m/s. Note that the details of the exact movement can change, as long as the car ends up with the same total change in velocity and change in time:
- The car could start at 0 m/s and accelerates at a constant rate for 10 seconds, until it reaches 500 m/s.
- The car could start at 0 m/s, accelerate rapidly to 900 m/s, then slow down to 500 m/s by the 10th second.
- The car could start at 0 m/s, stay still for 9 seconds, then jump to 500 m/s very rapidly in the 10th second.
Understanding Positive and Negative Acceleration
-
1Know what positive and negative velocity represents. Although velocity always specifies a direction, it can be tedious to keep writing "up" or "north" or "toward the wall." Instead, most math problems will assume the object is moving along a straight line. Moving in one direction on this line gets described as a positive (+) velocity, and movement in the other direction is negative (-) velocity.[9]
- For example, a blue train is moving east at 500 m/s. A red train is moving west equally fast, but since it is in the opposite direction, it is traveling at -500 m/s instead.
-
2Use the definition of acceleration to determine + or - signs. Acceleration is the change in velocity over time.[10] If you're confused about whether to write acceleration as positive or negative, check the change in velocity and see what comes out:
- vfinal - vinitial = + or - ?
-
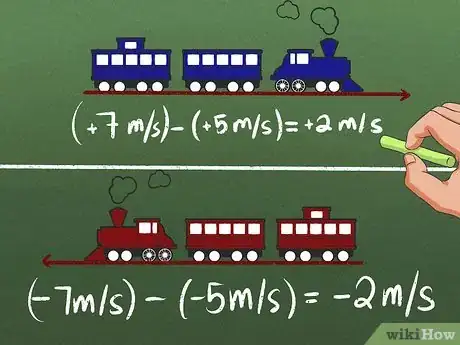
3Understand speeding up in each direction. Let's say a blue train and a red train move away from each other with a speed of 5 m/s. We can picture these on a number line, with the blue train moving at +5 m/s along the positive side of the number line, and the red train moving at -5 m/s along the negative side. If each train starts to accelerate until it reaches 2 m/s faster in the direction it is moving, does each train have positive or negative acceleration?[11] Let's check:
- The blue train is moving faster along the positive side, so it's increasing from +5 m/s to +7 m/s. The final velocity minus the initial velocity is 7 - 5 = +2. Since the change in velocity is positive, so is the acceleration.
- The red train is moving faster along the negative side, so it starts out -5 m/s but ends up going -7 m/s. The final velocity minus the initial velocity is -7 - (-5) = -7 + 5 = -2 m/s. Since the change in velocity is negative, so is the acceleration.
-
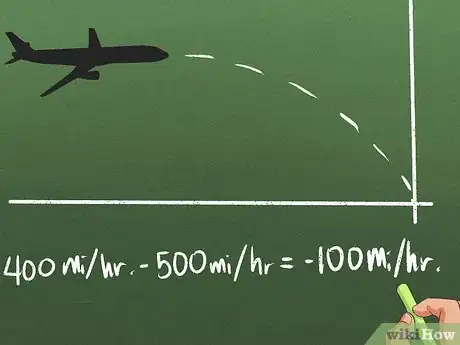
4Understand slowing down.[12] Let's say a plane starts out traveling at 500 miles per hour, but then slows down to 400 miles per hour. Although it's still moving in a positive or forward direction, the plane's acceleration was negative, because it's moving less quickly forward than before. You can check this the same way as the examples above: 400 - 500 = -100, so the acceleration is negative.[13]
- Meanwhile, if a helicopter is moving -100 miles per hour and accelerates to -50 miles per hour, it has experienced positive acceleration. This is because the change in velocity was in the positive direction: -50 - (-100) = +50, even though the change was not enough to reverse the helicopter's direction.
Expert Q&A
-
QuestionHow do you explain acceleration?
 Sean Alexander, MSSean Alexander is an Academic Tutor specializing in teaching mathematics and physics. Sean is the Owner of Alexander Tutoring, an academic tutoring business that provides personalized studying sessions focused on mathematics and physics. With over 15 years of experience, Sean has worked as a physics and math instructor and tutor for Stanford University, San Francisco State University, and Stanbridge Academy. He holds a BS in Physics from the University of California, Santa Barbara and an MS in Theoretical Physics from San Francisco State University.
Sean Alexander, MSSean Alexander is an Academic Tutor specializing in teaching mathematics and physics. Sean is the Owner of Alexander Tutoring, an academic tutoring business that provides personalized studying sessions focused on mathematics and physics. With over 15 years of experience, Sean has worked as a physics and math instructor and tutor for Stanford University, San Francisco State University, and Stanbridge Academy. He holds a BS in Physics from the University of California, Santa Barbara and an MS in Theoretical Physics from San Francisco State University.
Academic Tutor
-
QuestionHow I calculate average acceleration if time is not given only distance and speed is given?
 Community AnswerDivide your distance by speed to get your time.
Community AnswerDivide your distance by speed to get your time. -
QuestionHow do I calculate the average acceleration when given only velocity and distance but not time?
 Community AnswerYou solve for your time first with Xf= Xi+1/2(Vi+Vf)t. Rearrange the formula to solve for t, then input your answer for time and solve for average acceleration.
Community AnswerYou solve for your time first with Xf= Xi+1/2(Vi+Vf)t. Rearrange the formula to solve for t, then input your answer for time and solve for average acceleration.
References
- ↑ https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/one-dimensional-motion/acceleration-tutorial/a/acceleration-article
- ↑ Sean Alexander, MS. Physics Tutor. Expert Interview. 14 May 2020.
- ↑ https://sciencing.com/equations-speed-velocity-acceleration-8407782.html
- ↑ https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/osuniversityphysics/chapter/3-3-average-and-instantaneous-acceleration/
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/guides/z2wy6yc/revision/2
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/guides/z2b9hv4/revision/4
- ↑ https://www.omnicalculator.com/physics/acceleration
- ↑ https://physics.info/acceleration/
- ↑ https://www.physicsclassroom.com/mmedia/kinema/nvpa.cfm
- ↑ https://www.omnicalculator.com/physics/acceleration
- ↑ https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1DKin/Lesson-1/Acceleration
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/guides/z3bqtfr/revision/4
- ↑ https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/osuniversityphysics/chapter/3-3-average-and-instantaneous-acceleration/
- ↑ https://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/1DKin/Lesson-1/Scalars-and-Vectors
About This Article
To find average acceleration, start by remembering that acceleration means how quickly something is speeding up or slowing down. You can write this as a formula like this: a av = (Δv/Δt), where delta represents change. Next, use the information you know to work out the average acceleration. For example, if a car accelerated to 500 m/s over 10 seconds, divide 500 by 10 to get the average acceleration. For tips on how to distinguish between positive and negative acceleration, read on!