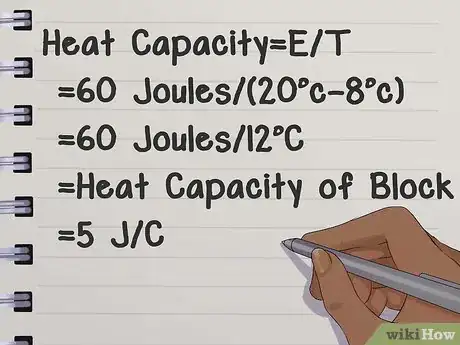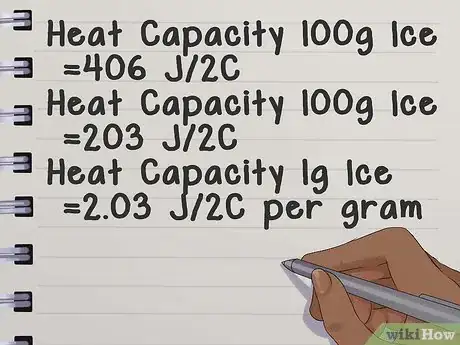wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 23 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 361,716 times.
Learn more...
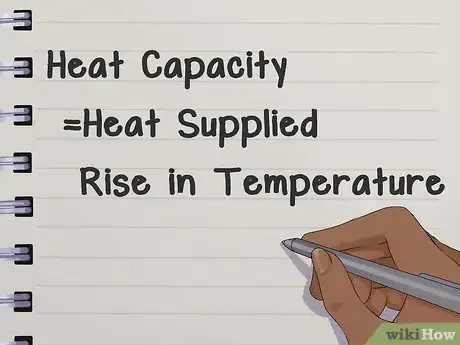
Heat capacity measures how much energy you need to add to something to make it one degree hotter. Finding the heat capacity of something comes down to a simple formula -- just divide the Amount of Heat Energy Supplied by the Change in Temperature to determine how much energy was needed per degree. Every material in the world has a different heat capacity. (Source: Standard 10 Physics book)
Formula: Heat Capacity = (Heat Energy Supplied) / (Rise in Temperature)
Steps
Calculating an Object's Heat Capacity
-
1Know the heat capacity formula. Heat Capacity of an object can be calculated by dividing the amount of heat energy supplied (E) by the corresponding change in temperature (T). Our equation is: Heat Capacity = E / T.[1]
- Example: It takes 2000 Joules of energy to heat a block up 5 degrees Celsius -- what is the heat capacity of the block?
- Heat Capacity = E / T
- Heat Capacity = 2000 Joules / 5 C
- Heat Capacity = 400 Joules per degree Celsius (J/C)
-
2Find the difference in temperature for changes of multiple degrees. For example, if I want to know the heat capacity of a block, and I know it takes 60 Joules to raise the temperature of the block from 8 degrees to 20 degrees, I need to know the difference between the two temperatures to get my heat capacity. Since 20 - 8 = 12, the temperature of the block changed by 12 degrees.[2] Therefore:
- Heat Capacity = E / T
- Heat Capacity of the block = 60 Joules / (20C - 8C)
- 60 Joules / 12 C
- Heat Capacity of the Block = 5 J/C
Advertisement -
3Add the appropriate units to your answer to give it meaning. A heat capacity of 300 means nothing if you don't know how it was measured. Heat Capacity is measured by energy needed per degree. So if we measure the energy in joules, and the change of temperature in Celsius, our final answer will represent how many Joules we needed per degree Celsius. Thus we would represent our answer as 300 J/C, or 300 Joules per degree celsius.
- If you measure heat energy in calories and temperature in Kelvin, your final answer would be 300 C/K.
-
4Know that this equation works for cooling objects as well. When something becomes two degrees colder, it loses the exact same amount of heat as it would gain to become 2 degrees warmers. Thus, if you are asked, "What is the heat capacity of an object if it loses 50 Joules of energy and drops 5 degrees Celsius," you can still use our equation:
- Heat Capacity: 50J / 5C
- Heat Capacity = 10 J/C
Using a Material's Specific Heat
-
1Know that specific heat refers to the energy needed to raise one gram by one degree. When you find the heat capacity of one unit of something (1 gram, 1 ounce, 1 kilogram, etc), you've found this object's specific heat. Specific heat tells you the amount of energy needed to raise each unit one degree. For example, it takes .417 Joules to raise 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius. So, water's specific heat is .417 J/C per gram.[3]
- The specific heat of a material is constant. That means that all pure water has the same specific heat-- .417 J/C.
-
2Use the heat capacity formula to find a material's specific heat. Finding it is easy, simply divide your final answer by the mass of the object. This tells you how much energy was need for each bit of the object, like how many joules changes the temperature in just one gram of ice.
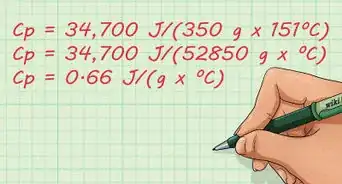
- Example: "I have 100 grams of ice. It takes 406 Joules to raise the temperature of ice 2 degree Celsius-- what is the specific heat of ice?"'
- Heat Capacity for 100g Ice = 406J / 2C
- Heat Capacity for 100g Ice = 203 J/C
- Heat Capacity for 1g Ice = 2.03 J/C per gram
- If you are confused, think of it this way -- it takes 2.03 Joules to raise every single gram of ice one degree. So, if we have 100 grams of ice we need 100 times as many Joules to heat it all.
-
3Use specific heat to find the energy needed to raise any material to any temperature. A material's specific heat is tells you how much energy is needed to raise one unit (usually 1 gram) a single degree. To find the heat needed to raise any object to any temperature, we simply multiply all of the parts together. Energy Needed = Mass x Specific Heat x Temperature Change. The answer is always in your unit of energy such as Joules.[4]
- Example:" If the specific heat of aluminum is .902 Joules per gram, how many Joules does it take to raise 5 grams of aluminum 2 degrees Celsius?
- Energy Needed = 5g x .902J/C x 2C
- Energy Needed = 9.2 J
-
4Know the specific heat of common materials. To help practice, learn the common specific heats that you might see on a test or encounter in real life. What can you learn from them? Notice, for example, that the specific heat of metals is much lower than wood -- this is why a metal spoon heats up quicker than wood if left in a hot cup of chocolate. Lower specific heats mean an object gets hot faster.[5]
- Water: 4.179 J/C
- Air: 1.01 J/C
- Wood: 1.76
- Aluminum: .902 J/C
- Gold: .129 J/C
- Iron: .450[6]
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow big should a water heater tank be to efficiently service a 12-unit condominium with two-bedroom units?
 Community AnswerAs far as the efficiency goes, the difference in efficiency is not that much between sizes. However, for a two-bedroom unit, you will want a minimum volume of 20 liters in your tank.
Community AnswerAs far as the efficiency goes, the difference in efficiency is not that much between sizes. However, for a two-bedroom unit, you will want a minimum volume of 20 liters in your tank. -
QuestionHow do I convert watts into J/KgK?
 Community AnswerWatts and J/KgK measure different things and cannot be "converted" to one another. J/KgK is the heat capacity, which is a property intrinsic to a particular material, while Watt is a unit of power.
Community AnswerWatts and J/KgK measure different things and cannot be "converted" to one another. J/KgK is the heat capacity, which is a property intrinsic to a particular material, while Watt is a unit of power. -
QuestionWhy would we calculate heat capacity of material?
 Octavian OctaCommunity AnswerIt would help you if you wanted to use one of the materials as a radiator, or if you wanted to calculate the temperature of an assembly in different conditions. These are just two examples, but there can be a lot of others.
Octavian OctaCommunity AnswerIt would help you if you wanted to use one of the materials as a radiator, or if you wanted to calculate the temperature of an assembly in different conditions. These are just two examples, but there can be a lot of others.
References
- ↑ https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-chemistry-beta/x2eef969c74e0d802:thermodynamics/x2eef969c74e0d802:heat-capacity-and-calorimetry/v/heat-capacity
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JpNvtxrz0go
- ↑ https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry_Textbook_Maps/Supplemental_Modules_(Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry)/Thermodynamics/Calorimetry/Heat_Capacity
- ↑ https://www.khanacademy.org/science/hs-physics/x215e29cb31244fa1:modeling-energy/x215e29cb31244fa1:thermodynamics/v/specific-heat-capacity
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IHYnOnd8oIU
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pN_6M1SNM4s
About This Article
To calculate heat capacity, use the formula: heat capacity = E / T, where E is the amount of heat energy supplied and T is the change in temperature. For example, if it takes 2,000 Joules of energy to heat up a block 5 degrees Celsius, the formula would look like: heat capacity = 2,000 Joules / 5 C. Then, you would just divide 2,000 by 5 to find that the heat capacity for the block is 400 Joules per degree Celsius. If you want to learn how to calculate heat capacity with the material's specific heat, keep reading!