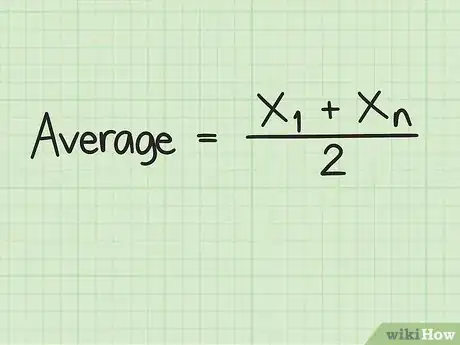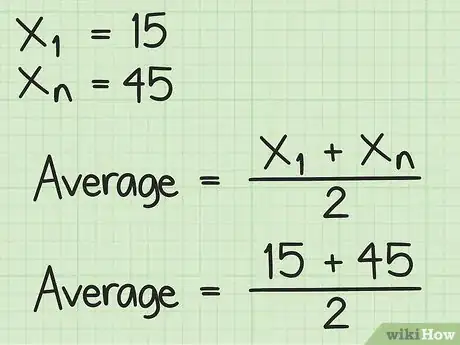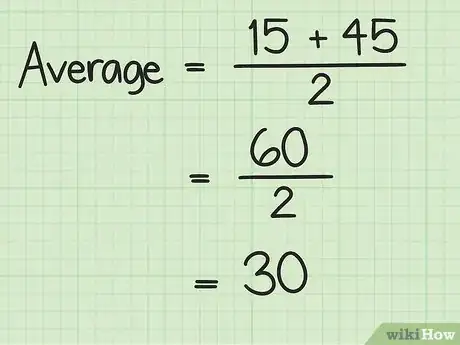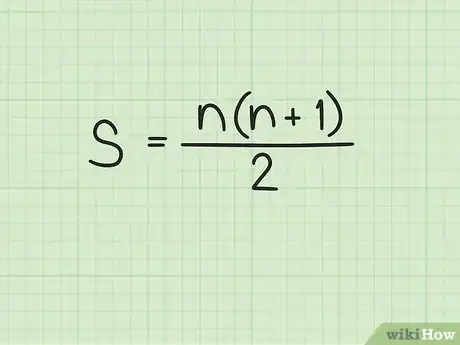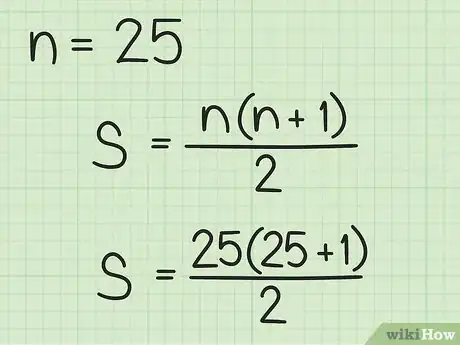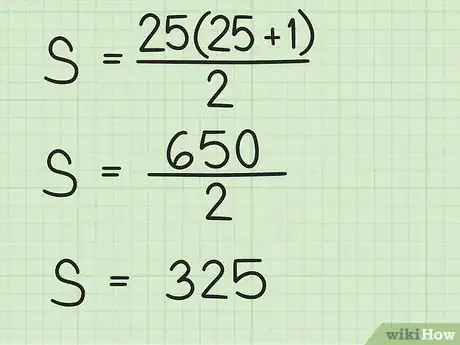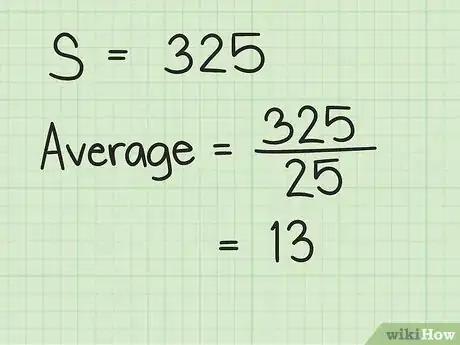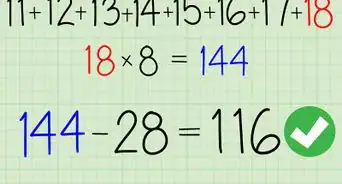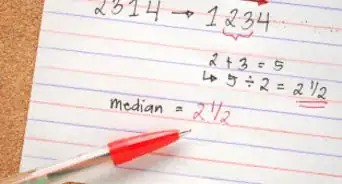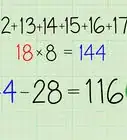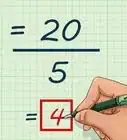This article was co-authored by Jake Adams. Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University.
This article has been viewed 63,537 times.
A sequence of consecutive numbers is called a series. Because a series consists of evenly-spaced numbers, the median and mean (average) of the series will be the same. For a short series of consecutive numbers, it is easy to find the average by finding the middle number in the sequence, or the median. For longer series of numbers, there are formulas you can use to quickly calculate the average, as long as you know what the first term and last term in the series are.
Steps
Averaging Any Short Series of Consecutive Numbers
-
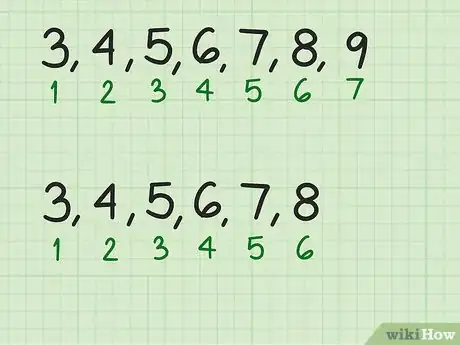
1Count the number of terms in the series. This is the number of numbers in the sequence. Determine whether the series has an odd or even number of terms.
- For example, the sequence 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 has seven terms, an odd amount.
- The sequence 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 has six terms, an even amount.
-
2Identify the middle number of a series with an odd number of terms. This is the number that has the same amount of terms on either side of it. This middle number will be the average of the series.
- For example, in the sequence 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, the middle number is 6. It has three numbers to the left of it, and three numbers to the right of it. So, in this series of numbers, 6 is both the mean and the median.
Advertisement -
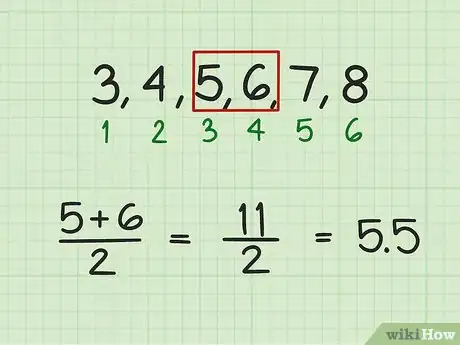
3Average the middle numbers of a series with an even number of terms. To do this, find the pair of numbers that has the same amount of terms on either side of it. To find the average, add these two numbers together and divide by two. Their average will be the average of the series.[1]
- For example, in the sequence 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, the middle pair is 5 and 6. It has two numbers to the left of it, and two numbers to the right of it. So, to calculate the average of the series, calculate the average of these two numbers:
So, in this series of numbers, 5.5 is both the mean and the median.
- For example, in the sequence 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, the middle pair is 5 and 6. It has two numbers to the left of it, and two numbers to the right of it. So, to calculate the average of the series, calculate the average of these two numbers:
Averaging Any Long Series of Consecutive Numbers
-
1Set up the formula for finding the average of an evenly spaced set of numbers. The formula is , where is the first number in the series and is the last number in the series.[2]
-
2Plug the appropriate values into the formula. Remember, for this formula, you are only working with the first number in the sequence () and the last number in the sequence .
- For example, if you were finding the average of sequential numbers beginning with 15 and ending with 45, your formula will look like this: .
-
3Calculate using the order of operations. First you need to add the two values in parentheses. Then divide by 2. The result will be the average of the series of numbers.
- For example:
So, the average of the series of consecutive numbers beginning with 15 and ending with 45 is 30.
- For example:
Averaging Any Consecutive Series Beginning with 1
-
1Set up the formula for calculating the sum of a series of consecutive numbers. The formula is , where equals the sum of all the numbers in the series, and equals the number of terms (numbers) in the series.[3]
-
2Count the number of terms in the series. Since the series begins with 1, the number of terms is equal to the last term in the series. Plug in this value for .
- For example, if you are finding the sum of consecutive numbers 1 through 25, you have 25 numbers in your sequence, so , and your formula will look like this: .
-
3Calculate using the order of operations. First add the numbers in parentheses. Then, multiply their sum by . Finally, divide the product by 2. The result is the sum of the numbers in the series.
- For example:
- For example:
-
4Divide the sum by the number of terms in the series. This will give you the average of the series. [4]
- For example, . So, the average of the series 1-25 is 13.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionIf a, b, c, d, and e are five consecutive odd number, their average is what?
 DonaganTop AnswererThe average of any five consecutive odd numbers is the third number of the sequence (in this case, c). You can prove this by setting a equal to c-4, b = c-2, d= c+2, and e= c+4. Add those four numbers together with c, and the sum of the five numbers is 5c. Divide that sum by 5 to get the average of the five numbers, which is c.
DonaganTop AnswererThe average of any five consecutive odd numbers is the third number of the sequence (in this case, c). You can prove this by setting a equal to c-4, b = c-2, d= c+2, and e= c+4. Add those four numbers together with c, and the sum of the five numbers is 5c. Divide that sum by 5 to get the average of the five numbers, which is c. -
QuestionThe average of 8 consecutive even number is 8. What is the largest even number?
 DonaganTop AnswererThere are no eight consecutive even numbers (integers) whose average is 8.
DonaganTop AnswererThere are no eight consecutive even numbers (integers) whose average is 8. -
QuestionThe mean monthly income of a person is 18190 and his mean monthly expenditure is 17390. What is his average monthly saving income?
 DonaganTop AnswererSubtract 17,390 from 18,190.
DonaganTop AnswererSubtract 17,390 from 18,190.
Warnings
Please note that these methods work only for consecutive numbers.
References
- ↑ https://www.khanacademy.org/math/statistics-probability/summarizing-quantitative-data/mean-median-basics/a/mean-median-and-mode-review
- ↑ https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/ecology/population-ecology/a/population-size-density-and-dispersal
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EkmYAGdxRBY
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/mean.html