Chapter 8
Probability
By Boundless

Probability is the branch of mathematics that deals with the likelihood that certain outcomes will occur. There are five basic rules, or axioms, that one must understand while studying the fundamentals of probability.
The conditional probability of an event is the probability that an event will occur given that another event has occurred.
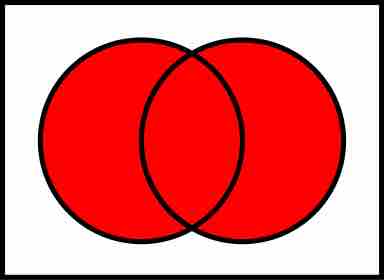
Union and intersection are two key concepts in set theory and probability.

The complement of
The addition rule states the probability of two events is the sum of the probability that either will happen minus the probability that both will happen.
The multiplication rule states that the probability that

To say that two events are independent means that the occurrence of one does not affect the probability of the other.
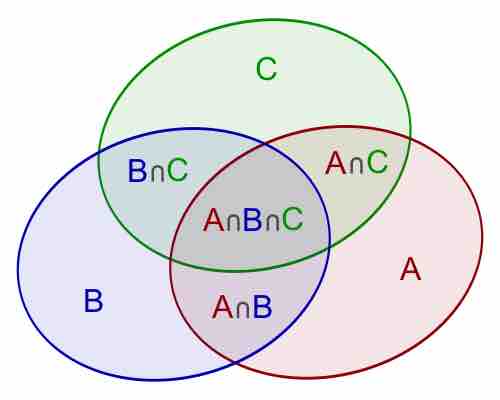
Combinatorics is a branch of mathematics concerning the study of finite or countable discrete structures.
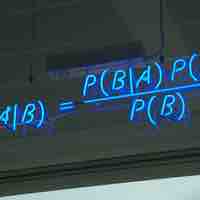
Bayes' rule expresses how a subjective degree of belief should rationally change to account for evidence.

The People of the State of California v. Collins was a 1968 jury trial in California that made notorious forensic use of statistics and probability.

