Chapter 3
Microscopy
By Boundless
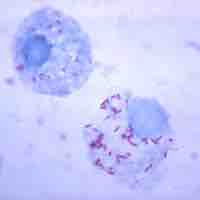
Microbes are often very small, even in comparison to microscopic cells from animals.

Measuring microbes presents challenges because they are very small, requiring indirect measures of microbes to understand them better.

The underlying principal of a microscope is that lenses refract light which allows for magnification.

Magnification is the enlargement of an image; resolution is the ability to tell two objects apart.

Dark-field microscopes show a light silhouette of an organism against a dark background.
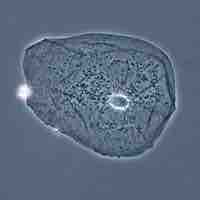
Phase-contrast microscopy visualizes differences in the refractive indexes of different parts of a specimen relative to unaltered light.
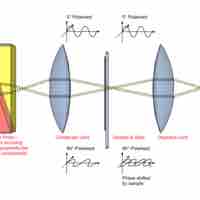
Interference microscopy is a variation of phase-contrast microscopy that uses a prism to split a light beam in two.
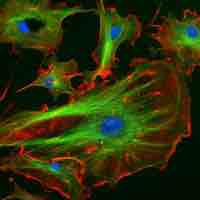
Fluorescence microscopy is used to study specimens that are chemically manipulated to emit light.
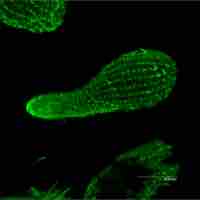
The key to the confocal approach is the use of spatial filtering techniques to eliminate out-of-focus light from biological samples.

Electron microscopy uses magnetic coils to direct a beam of electrons from a tungsten filament through a specimen and onto a monitor.
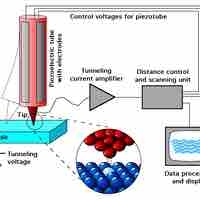
Scanned-probe microscopy uses a fine probe rather than a light-beam or electrons to scan the surface of a specimen and produce a 3D image.
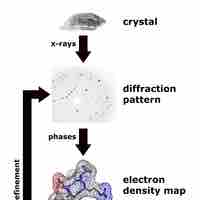
X-ray diffraction is a method that characterizes the structural composition of matter and using mathematical models.