Chapter 2
Chemistry
By Boundless
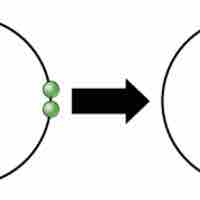
Ionic bonds are attractions between oppositely charged atoms or groups of atoms where electrons are donated and accepted.
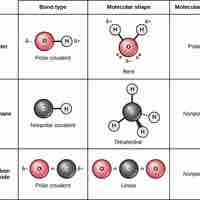
Covalent bonds result from a sharing of electrons between two atoms and hold most biomolecules together.
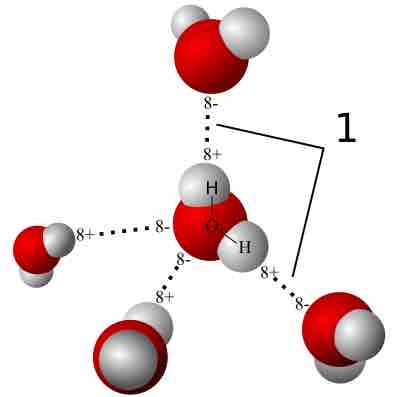
A hydrogen bond is a strong intermolecular force created by the relative positivity of hydrogen atoms.

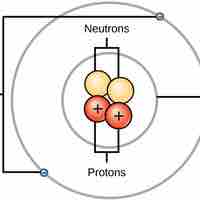
The mole is represented by Avogadro's number, which is 6.02×1023 mol-1.

The average atomic mass of an element is the sum of the masses of its isotopes, each multiplied by its natural abundance.
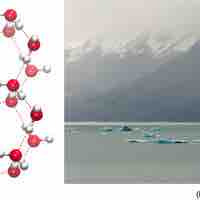
The orientation of hydrogen bonds as water changes states dictates the properties of water in its gaseous, liquid, and solid forms.
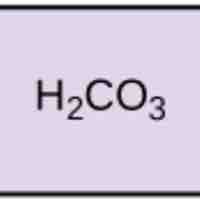
Acids dissociate into H+ and lower pH, while bases dissociate into OH- and raise pH; buffers can absorb these excess ions to maintain pH.
Some salts, such as ammonium bicarbonate (NH4HCO3), contain cations and anions that can both undergo hydrolysis.
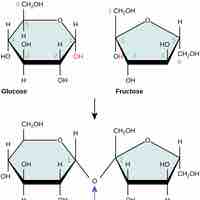
Carbohydrates are essential macromolecules that are classified into three subtypes: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
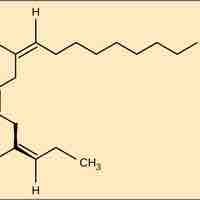
Fats and oils, which may be saturated or unsaturated, can be unhealthy but also serve important functions for plants and animals.
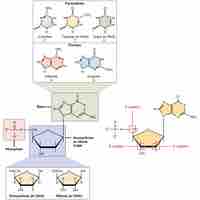
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that carry out cellular processes, especially the regulation and expression of genes.
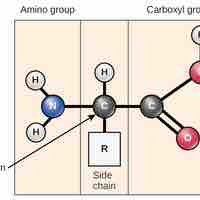
An amino acid contains an amino group, a carboxyl group, and an R group, and it combines with other amino acids to form polypeptide chains.
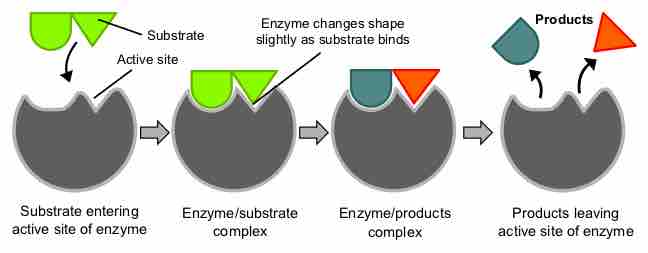
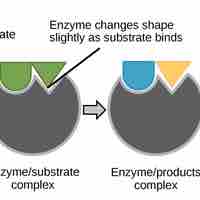
Proteins perform many essential physiological functions, including catalyzing biochemical reactions.
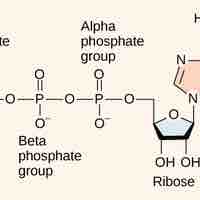
Cells couple the exergonic reaction of ATP hydrolysis with endergonic reactions to harness the energy within the bonds of ATP.

Organisms break down carbohydrates to produce energy for cellular processes, and photosynthetic plants product carbohydrates.
ΔG determines the direction and extent of chemical change.
The enthalpy of reaction measures the heat released/absorbed by a reaction that occurs at constant pressure.