Chapter 4
Cell Structure of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes
By Boundless
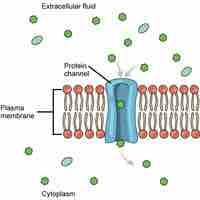
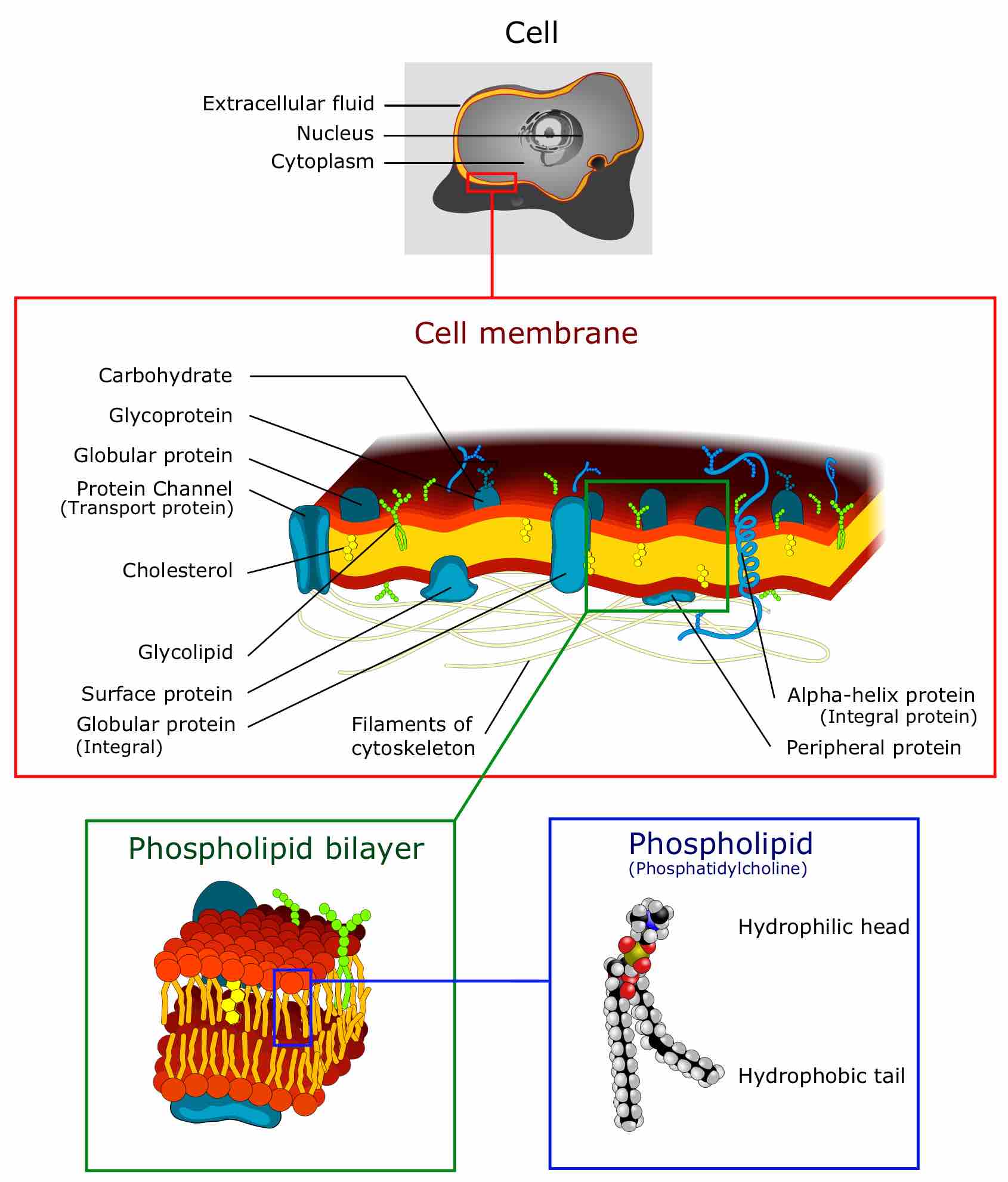
Facilitated diffusion is a process by which molecules are transported across the plasma membrane with the help of membrane proteins.
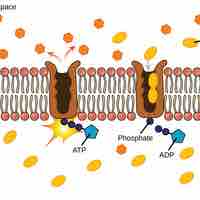
The sodium-potassium pump maintains the electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium out of the cell.
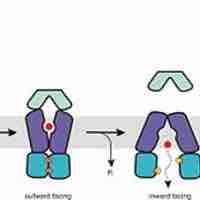
ABC transporters are a protein superfamily that all have an ATP binding cassette and transport substances across membranes.
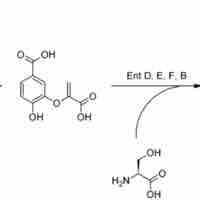
Siderophores are classified by which ligands they use to chelate the ferric iron, including the catecholates, hydroxamates, and carboxylates.
Group translocation is a protein export or secretion pathway found in plants, bacteria, and archaea.
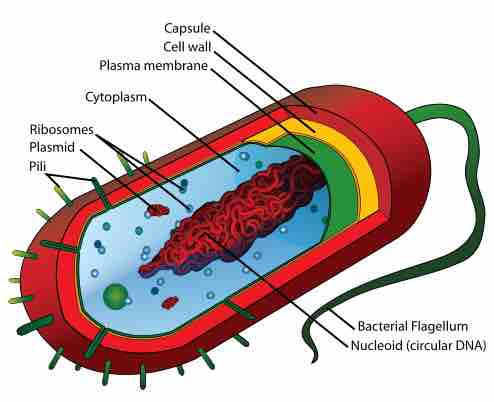
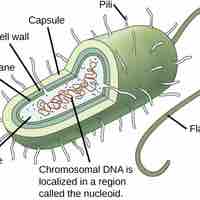
Bacteria are protected by a rigid cell wall composed of peptidoglycans.
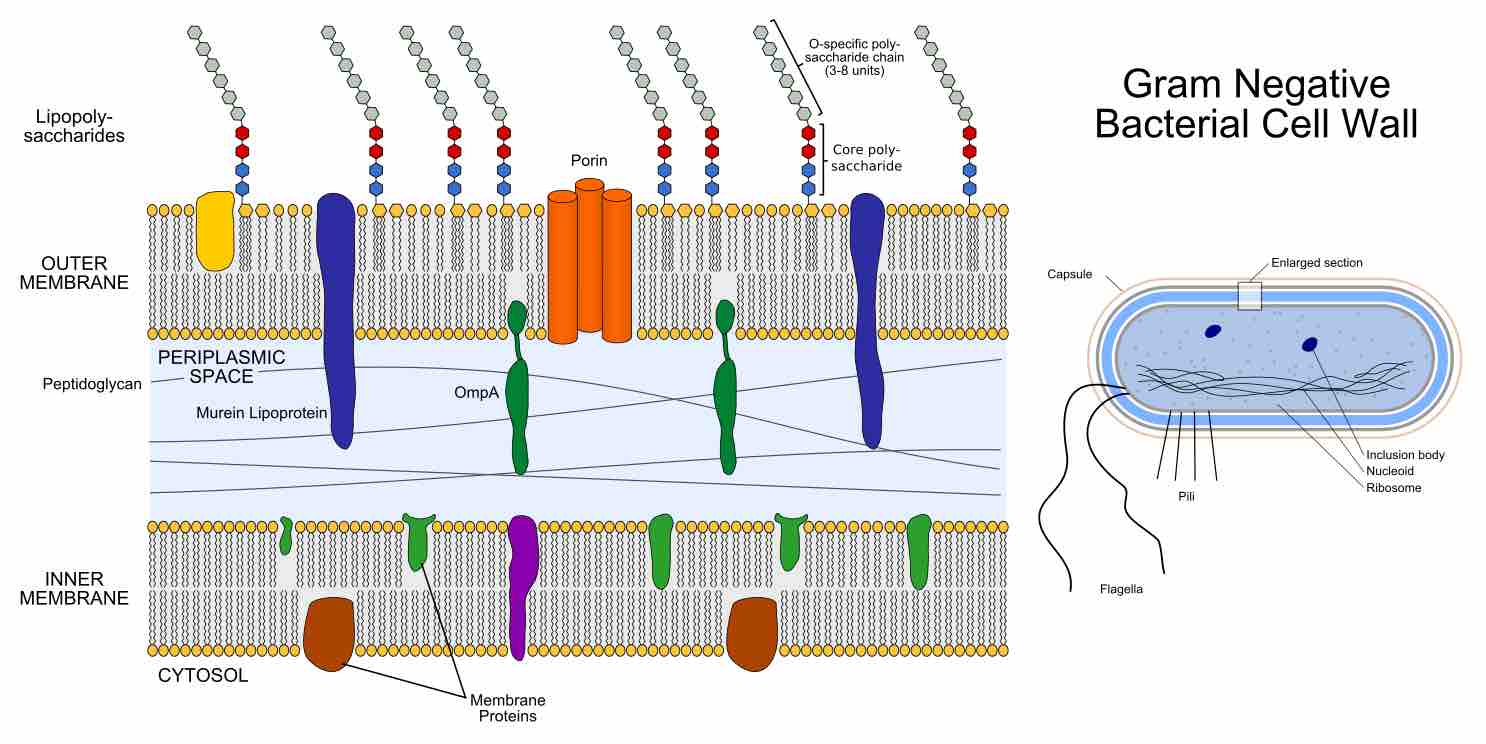
The Gram-negative cell wall is composed of an outer membrane, a peptidoglygan layer, and a periplasm.
Gram-positive bacteria have cell envelopes made of a thick layer of peptidoglycans.
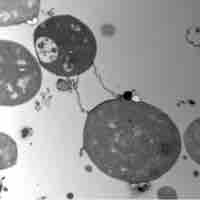
Some bacteria lack a cell wall but retain their ability to survive by living inside another host cell.
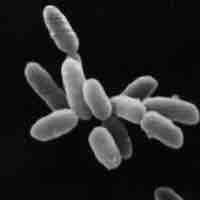
Archaeal cell walls differ from bacterial cell walls in their chemical composition and lack of peptidoglycans.
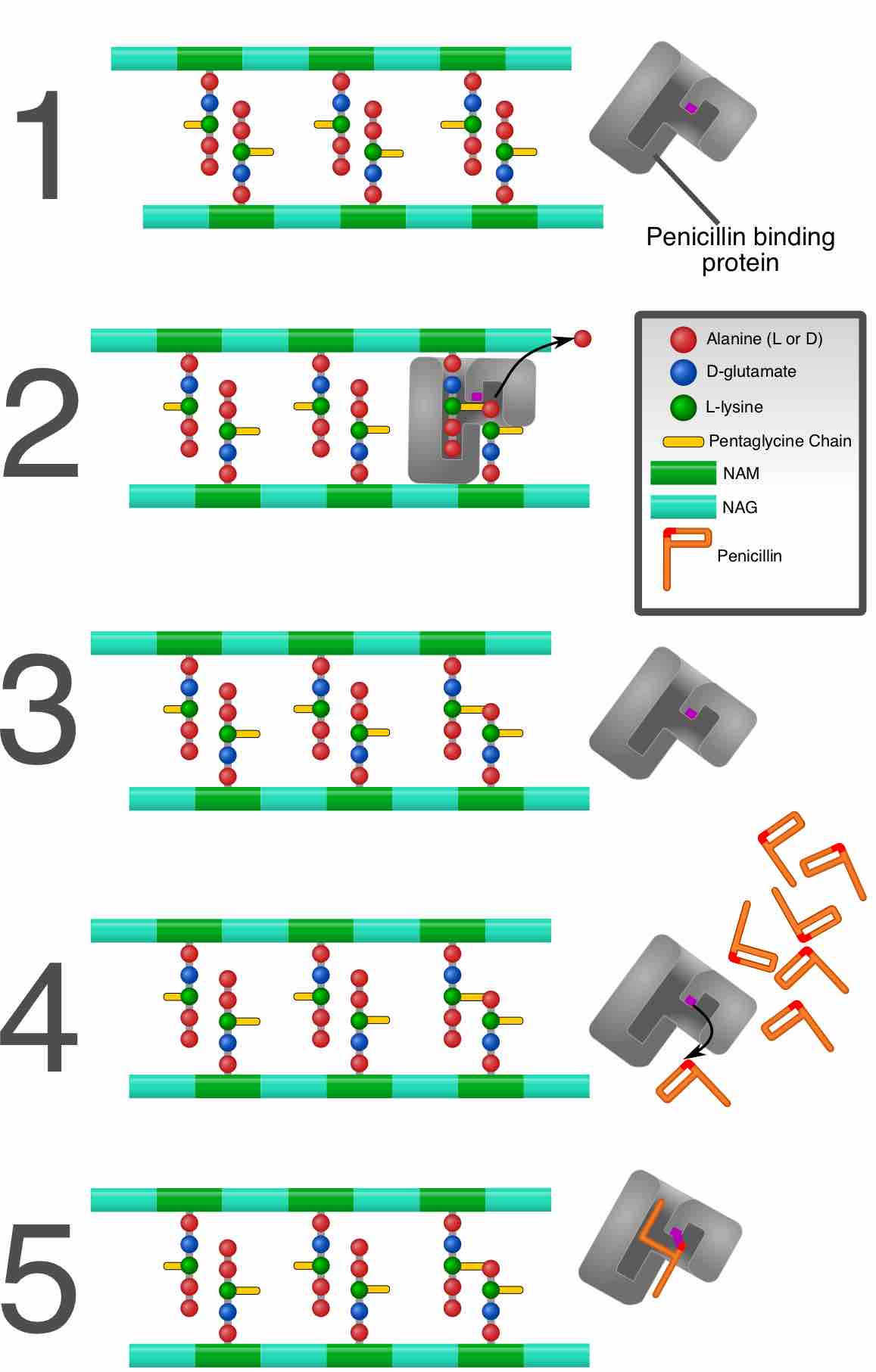
The cell wall is responsible for bacterial cell survival and protection against environmental factors and antimicrobial stress.
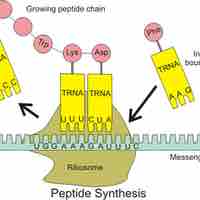
The purpose of the ribosome is to translate messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins with the aid of tRNA.
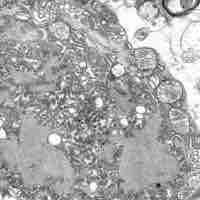
Bacteria have different methods of nutrient storage that are employed in times of plenty, for use in times of want.
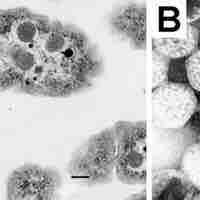
Carboxysomes are intracellular structures that contain enzymes involved in carbon fixation and found in many autotrophic bacteria.
Magnetosomes are intracellular organelles in magnetotactic bacteria that allow them to sense and align themselves along a magnetic field.
Gas vesicles are spindle-shaped structures that provide buoyancy to cells by decreasing their overall cell density.
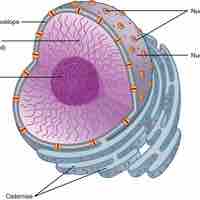
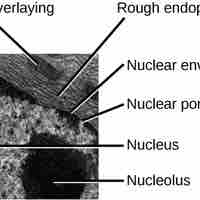
Found within eukaryotic cells, the nucleus contains the genetic material that determines the entire structure and function of that cell.
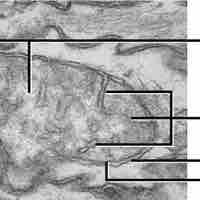
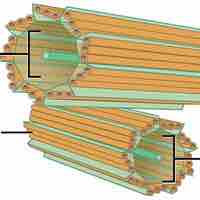
Mitochondria are organelles that are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's main energy-carrying molecule.
Although they are both eukaryotic cells, there are unique structural differences between animal and plant cells.
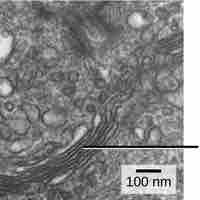
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle that is responsible for the synthesis of lipids and the modification of proteins.
The Golgi apparatus sorts and packages materials before they leave the cell to ensure they arrive at the proper destination.
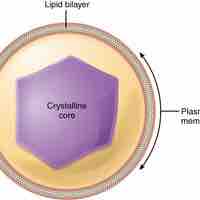
Peroxisomes neutralize harmful toxins and carry out lipid metabolism and oxidation reactions that break down fatty acids and amino acids.
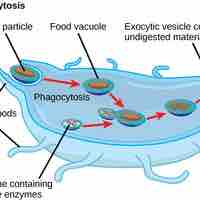
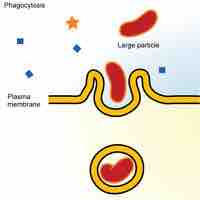
Lysosomes are organelles that digest macromolecules, repair cell membranes, and respond to foreign substances entering the cell.
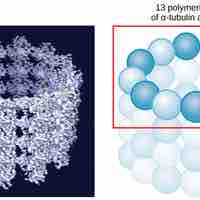
Microtubules are part of the cell's cytoskeleton, helping the cell resist compression, move vesicles, and separate chromosomes at mitosis.
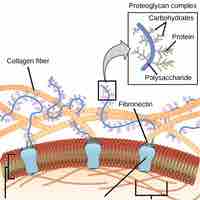
The extracellular matrix of animal cells holds cells together to form a tissue and allow tissues to communicate with each other.

Microscopes allow for magnification and visualization of cells and cellular components that cannot be seen with the naked eye.

Crystallographic analysis reveals the arrangement of atoms in solids that help build the three-dimensional model of molecules.
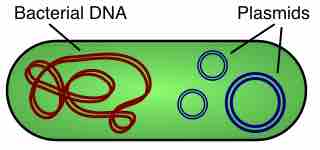
Genetic analysis is a growing field in microbiology that provides information about specific adaptations and the evolution of organisms.