Microorganisms have numerous pathways and processes in place to ensure both energy and nutrient production. These pathways are necessary for survival and cellular function. The major metabolic pathways require substrates to be acted upon for the formation of larger, more complex products. Biosynthetic processes are defined by the production of more complex products that are required for growth and maintenance of life. These processes require pathways that are often multi-step. There are various components deemed necessary for biosynthetic processes to occur, including: precursor compounds, chemical energy, and carious catalytic enzymes.
TCA Cycle
The citric acid cycle, commonly referred to as the Krebs cycle, is characterized by the production of energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into carbon dioxide. The cycle is one of the major metabolic processes utilized to generate energy. The citric acid cycle, comprised of a series of chemical reactions, provides precursors for additional biochemical pathways. These precursors are used as substrates for the biogenesis of large complex products. The precursors include amino acids and reducing agents such as NADH. Additional pathways that require precursors formed by the TCA include amino acid and nucleotide synthesis .
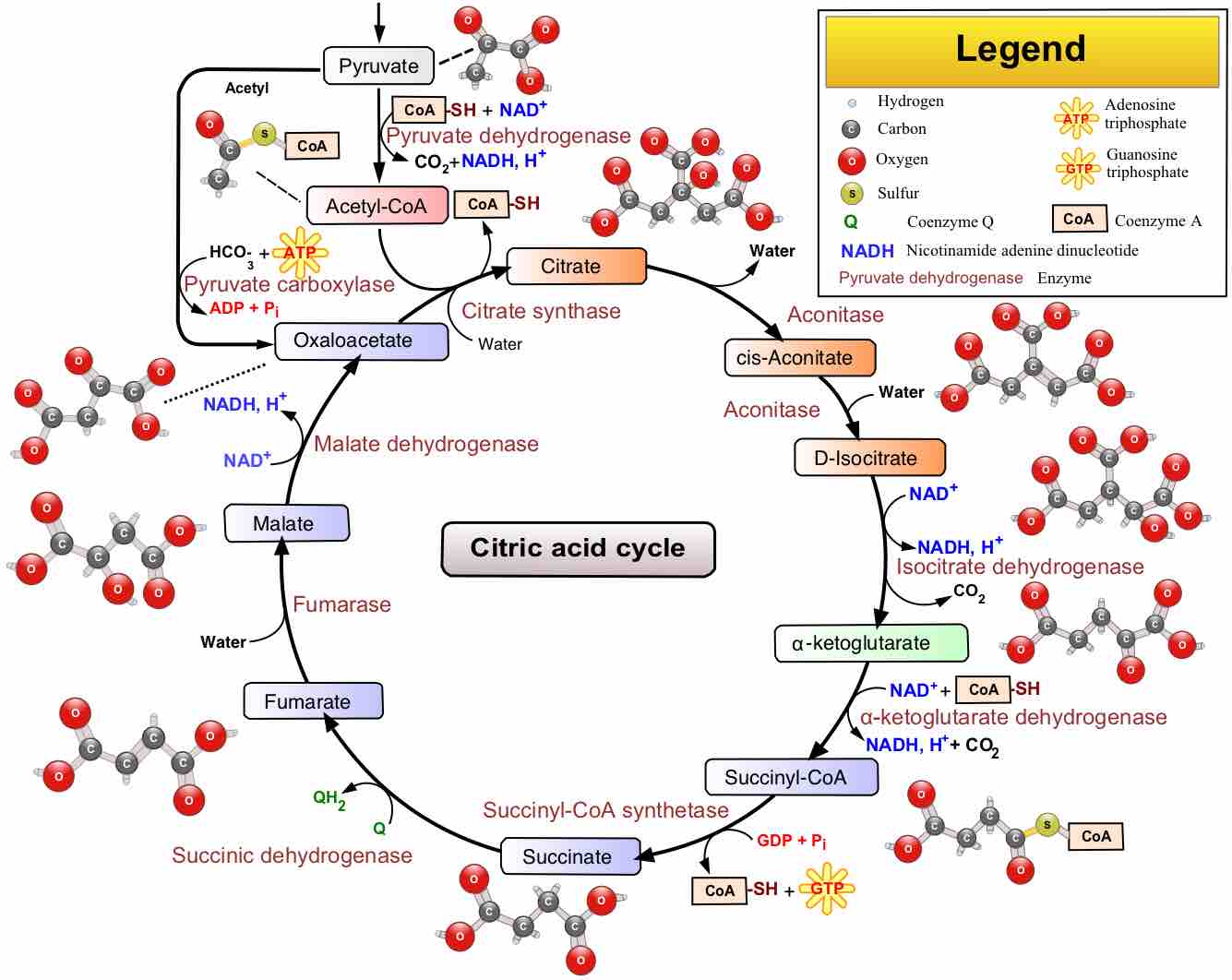
The Citric Acid Cycle
An overview of the Citric Acid Cycle.
Glycolysis
An additional central metabolic pathway includes glycolysis. Glycolysis is characterized by a series of reactions that results in the conversion of glucose into pyruvate. This process is characterized by the production of various intermediates and molecules that function as substrates in additional pathways . Additional pathways that require substrates or metabolites produced by the glycolytic pathway include: gluconeogenesis, lipid metabolism, the pentose phosphate pathway, and the TCA.
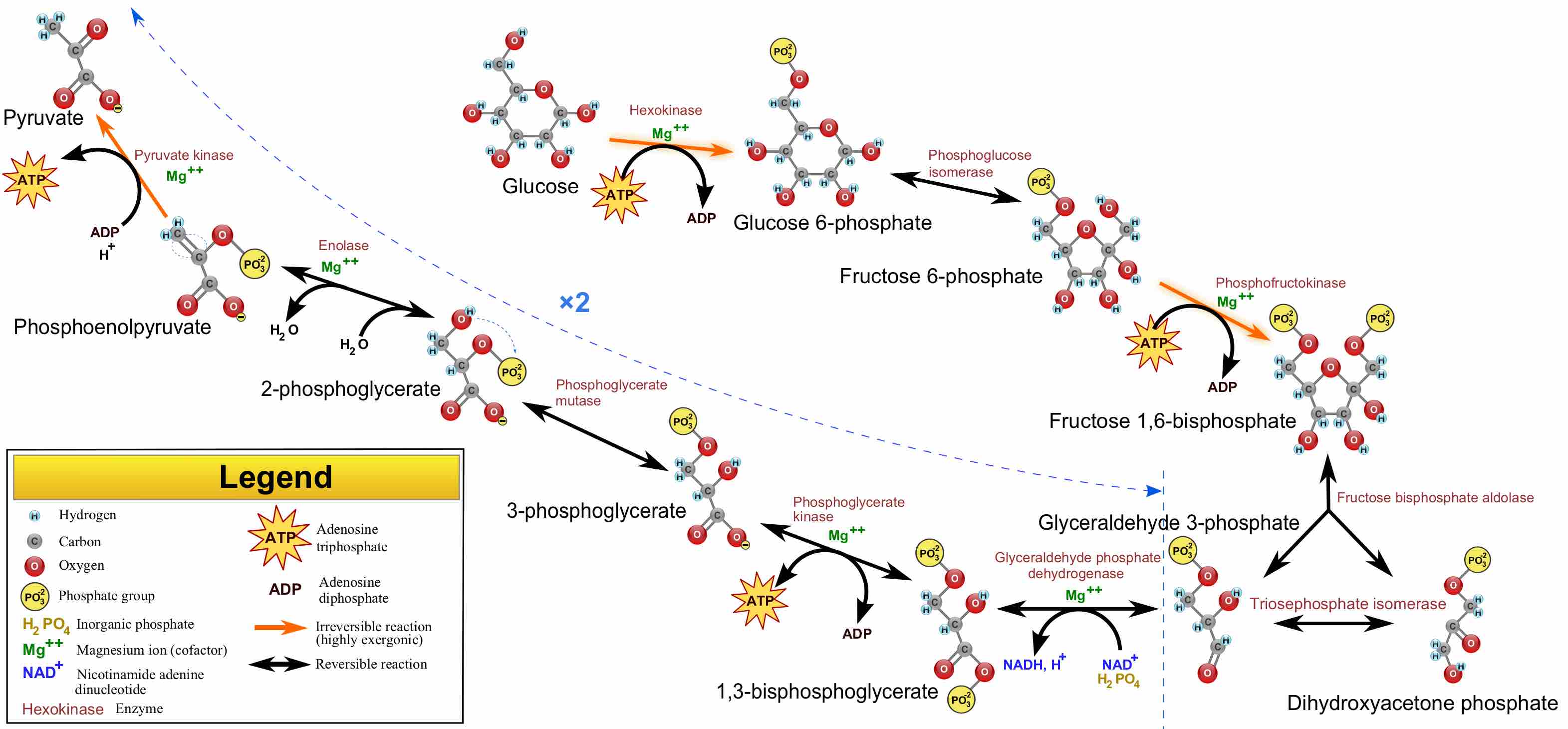
Glycolysis Pathway Overview
An overview of the glycolytic pathway. This pathway, comprised of a series of reactions, produces many intermediates and molecules utilized as substrates for biosynthesis in additional pathways.