Lymphocytes are the only immunologically specific cellular components of the immune system. They are divided into two types based on the pathogen recognition receptors they express on their surface. T cells or T lymphocytes belong to a group of white blood cells known as lymphocytes. They are called T cells because they mature in the thymus. They play a central role in cell-mediated immunity along with initiating rejection of foreign tissues following organ transplantation. B-cells are also white blood cells and are a vital part of the humoral immunity branch of the adaptive immune system. These two cell types can function independently or cooperatively to defend the body against pathogens. T-lymphocytes can be distinguished from other lymphocytes like B cells and natural killer cells (NK cells) by the presence of a T cell receptor (TCR) on the cell surface. Alternatively, B-cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes like T cells and natural killer cells (NK cells) by the presence of a protein on the B-cell's outer surface called a B-cell receptor (BCR).
SEM Lymphocyte
A scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of a single human lymphocyte.
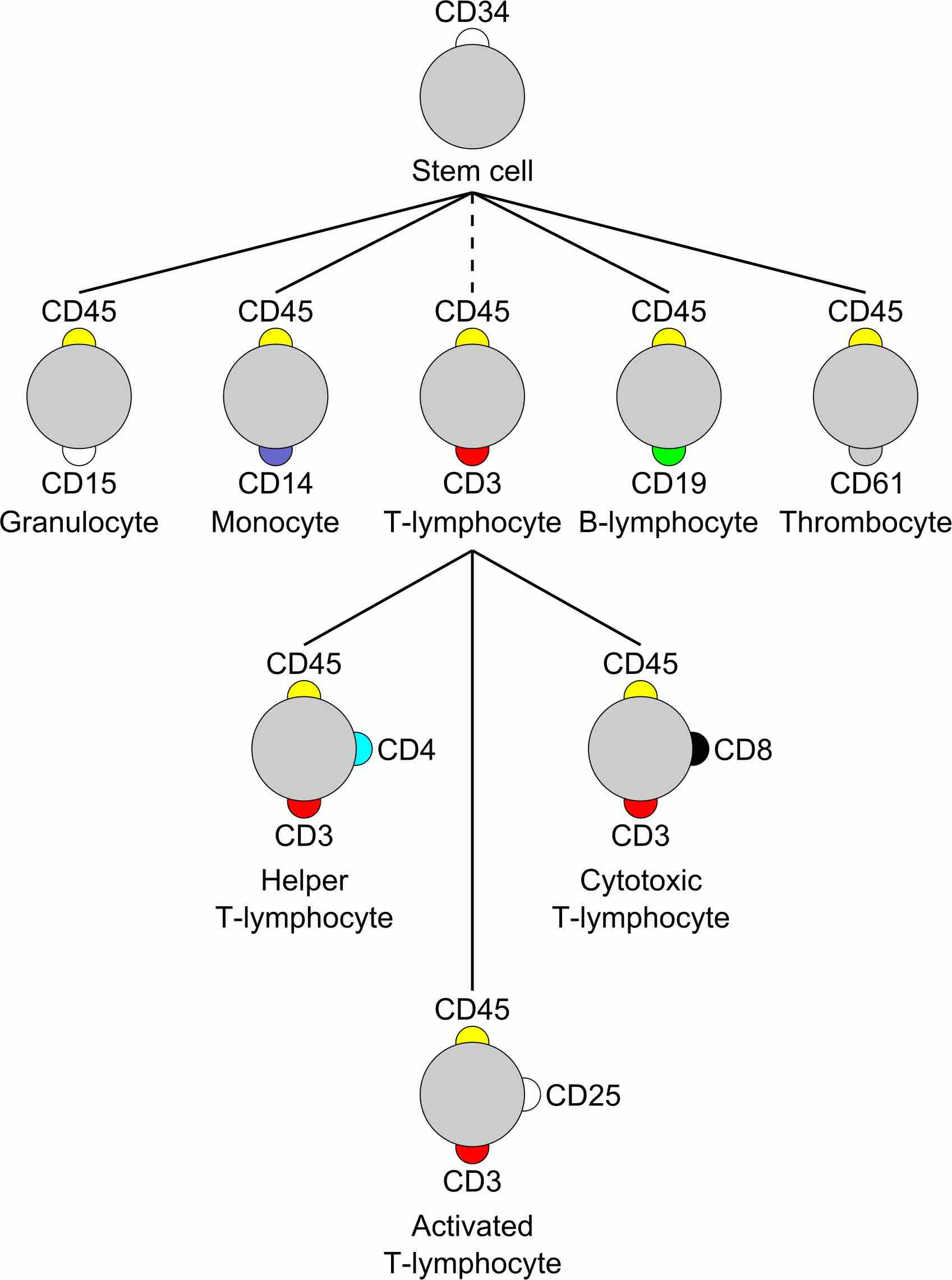
Traditionally, T-lymphocytes were defined by their ability to form E-rosettes when they bind selectively to sheep erythrocytes. T-lymphocytes express CD3, CD4, CD8, or CD25 markers. B-lymphocytes express CD19 marker. The expression of different markers allows the separation/differentiation of T and B cells. Another functional assay used to identify T-lymphocyte is the cytotoxic activity assay. This assay is based on measuring the killing ability that a determined number of T lymphocytes have for a certain number of target cells when both populations are placed together. B-lymphocytes have membrane-bound immunoglobulins that can be stained with anti-immunoglobulin labeled with fluorescent dyes and detected with a fluorescent microscope. More modern techniques like flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry are commonly used and rely on the use of fluorescent antibodies. These techniques are based on staining B and T cells for unique cell surface markers known as cluster of differentiation (CD).
Cluster of differentiation
T and B lymphocytes express unique CD markers.