Chapter 6
Culturing Microorganisms
By Boundless

Microbial cytoplasm is contained within the cytoplasmic membrane and includes the cytosol, macromolecules, and inclusions.
The sources of common essential nutrients are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and sulfur.
Nutrients are necessary for microbial growth and play a vital role in culturing microorganisms outside of their natural environment.
Stringent response is a stress response that occurs in bacteria and plant chloroplasts in reaction to stress conditions.

Oligotrophs are characterized by slow growth, low rates of metabolism, and generally low population density.

Starvation-induced fruiting bodies can aggregate up to 500 micrometres long and contain approximately 100,000 bacterial cells.
Several bacteria alter their morphology in response to the types and concentrations of external compounds.
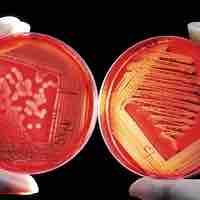
Culture media is the food used to grow and control microbes.

In defined media all the chemical compounds are known, while undefined media has partially unknown chemical constituents.
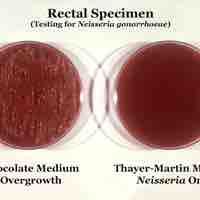
Selective media allows for the growth of specific organisms, while differential media is used to distinguish one organism from another.
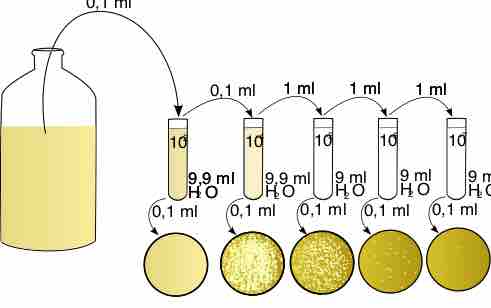
Microbiologists rely on aseptic technique, dilution, colony streaking and spread plates for day-to-day experiments.
Many microbes have special growth conditions or require precautions to grow in a laboratory setting, leading to special culture techniques.
Understanding the nutritional requirements of bacteria can aid their enrichment and isolation.
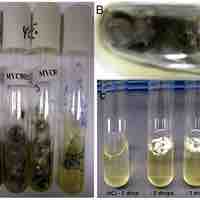
A pure culture is a population of cells or multicellular organisms growing in the absence of other species or types.

Bacteria can be stored for months or years if they are stored at -80C and in a high percentage of glycerol.
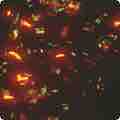
FISH is a hybridization technology which allows the labeling of target RNAs with a fluorescent probe.
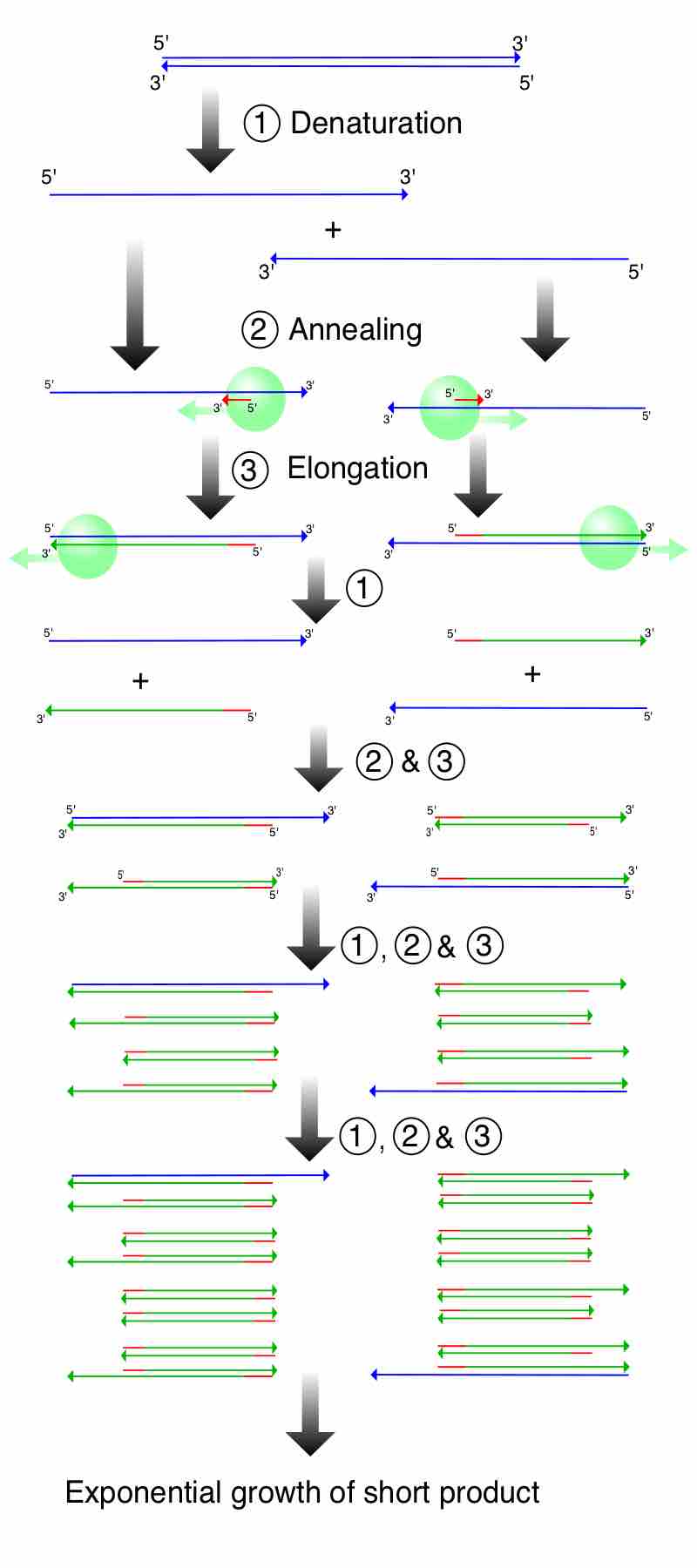
PCR allows for the amplification and mutation of DNA and allowing researchers to study very small samples.
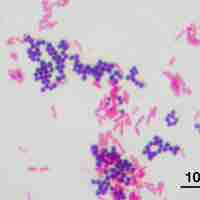
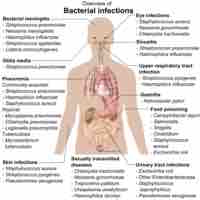
There are numerous tests and assays available that are utilized to aid in bacterial identification in a variety of settings.
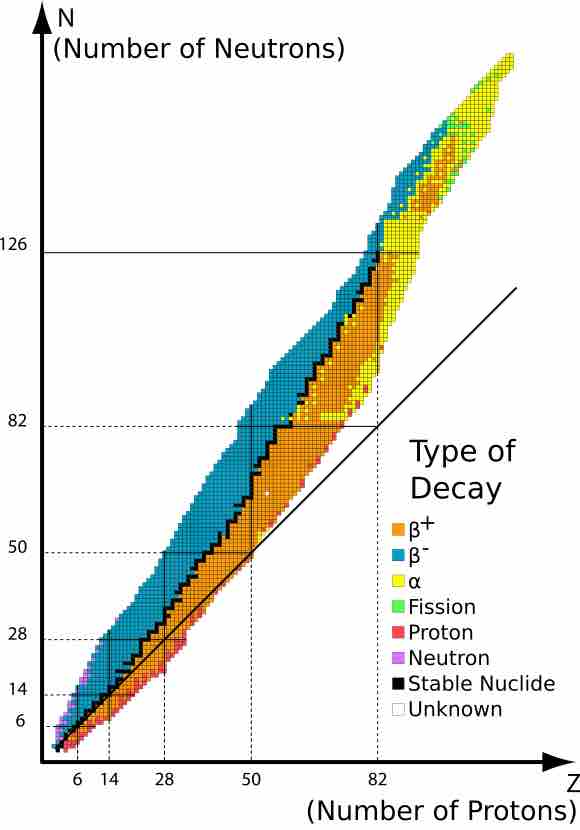
Stable isotopes are atoms that are not radioactive, in other words, they are not going to lose neutrons and decay spontaneously.
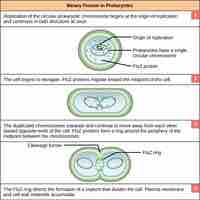
Binary fission is the method by which prokaryotes produce new individuals that are genetically identical to the parent organism.
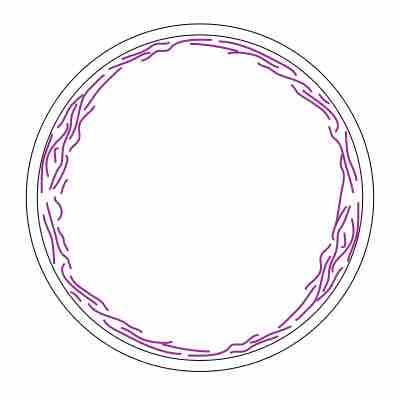
FtsZ is a protein encoded by the ftsZ gene that assembles into a ring at the future site of the septum of bacterial cell division.
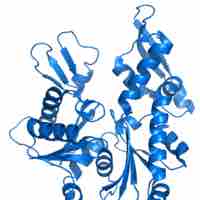
MreB is a protein found in bacteria homologous to actin.
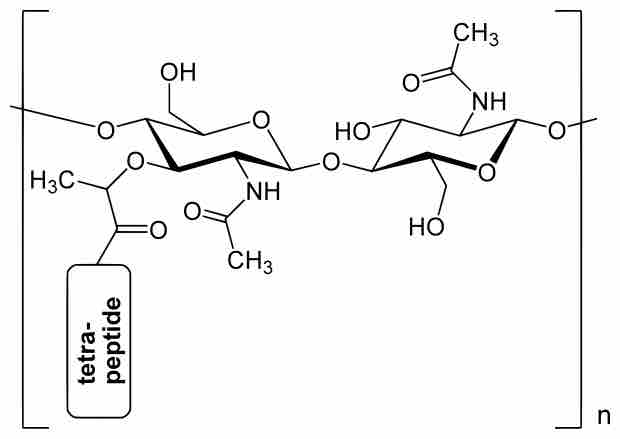
Peptidoglycan, also known as murein, is a polymer and consists of sugars and amino acids which form the cell walls of bacteria.

Bacterial growth occurs by the division of one bacterium into two daughter cells in a process called binary fission.
Increases in cell size are tightly linked in unicellular organisms and under optimal conditions bacteria can grow and divide rapidly.
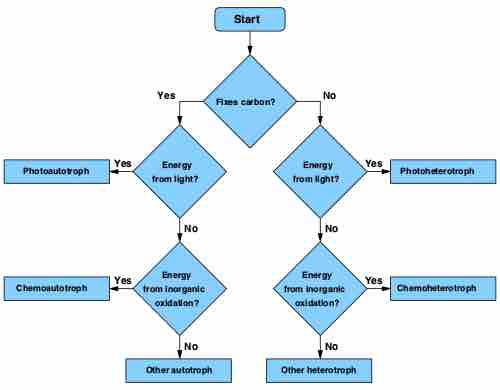
The two ways that microbial organisms can be classified are as autotrophs (supply their own energy) or as heterotrophs (use the products of others).

Direct counting methods are used to determine bacterial concentration without the need for advanced equipment.
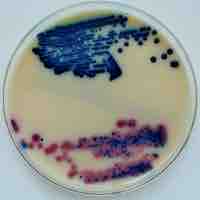
Plate counting is used to estimate the number of viable cells that are present in a sample.

Changes in the number of bacteria can be calculated by a variety of methods that focus on microbial mass.
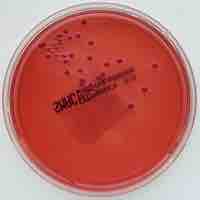
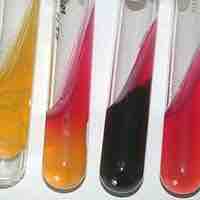
Culture media can be used to differentiate between different kinds of bacteria by detecting acid or gas production.

Bacteria may grow across a wide range of temperatures, from very cold to very hot.
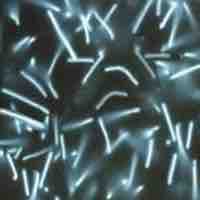
Bacteria can be classified on the basis of cell structure, metabolism or on differences in cell components.
Heat shock response is a cell's response to intense heat, including up-regulation of heat shock proteins.

Cells are grown and maintained at an appropriate temperature and gas mixture of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen in a cell incubator.
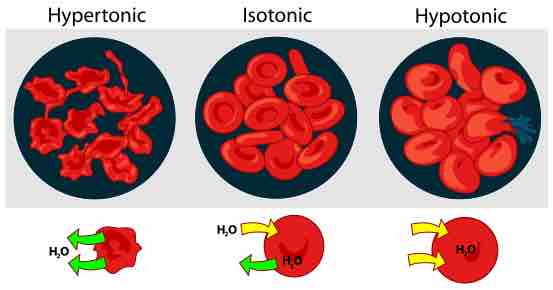
The correct osmotic pressure in the culture medium is essential for the survival of the cells.
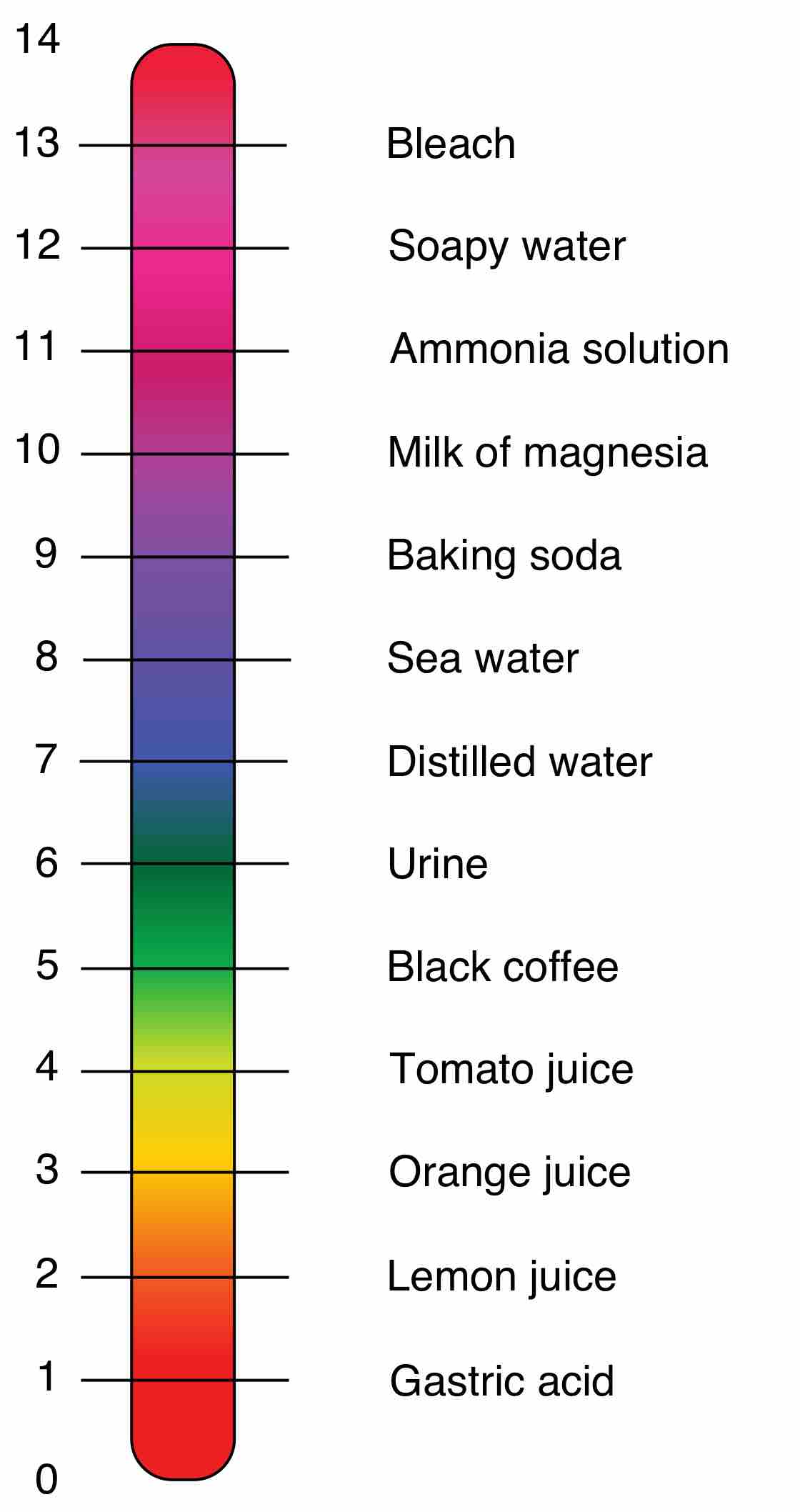
Microorganisms live and thrive within specific pH levels.
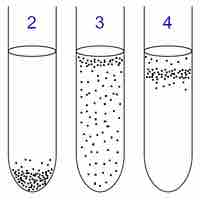
Oxygen requirements vary among microorganisms.

Controlling microbial growth is important in many fields but the degree of acceptable microbial levels can be quite different.
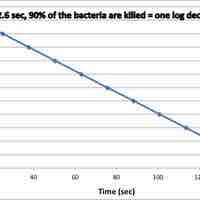
The rate of microbial death is used to develop standard protocols for sterilization in many industries.
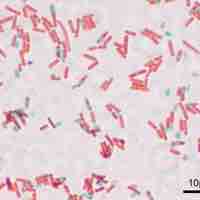
Different microbial structures and types of microbial cells have different level of resistance to antimicrobial agents.

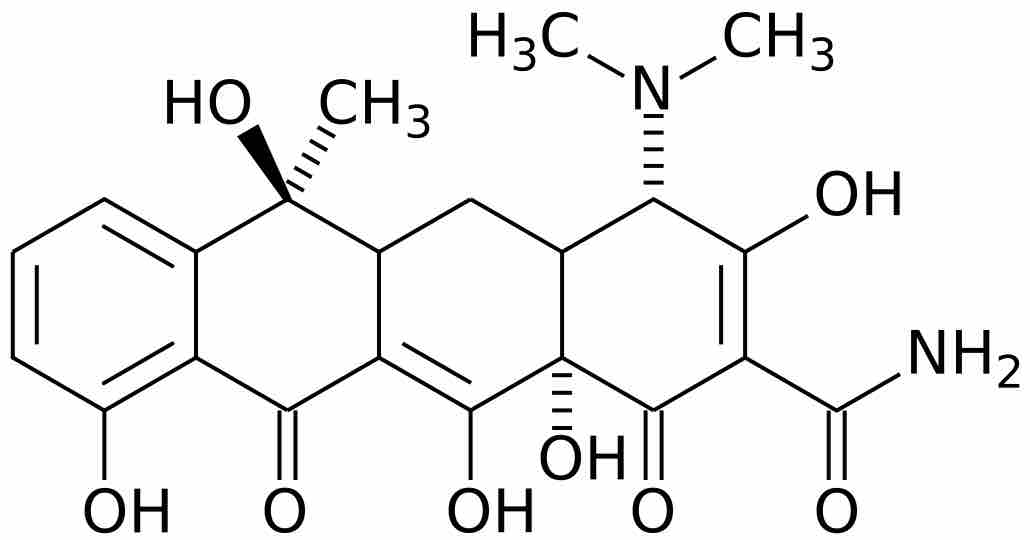
Heat is one of the most common and easily available methods for controlling bacterial growth.

Both non-ionizing and ionizing radiation methods are applied for sterilization.

Low temperatures usually inhibit or stop microbial growth and proliferation but often do not kill bacteria.

Under very high hydrostatic pressure(HHP) of up to 700 MPa, water inactivates pathogens such as E. coli and Salmonella.

Desiccation is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying and can be used to control microbial growth.

Osmotic pressure is the pressure which must be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of water across a semipermeable membrane.

Fluids that would be damaged by heat, irradiation, or chemical sterilization can be sterilized by microfiltration using membrane filters.

A perfect disinfectant would offer full microbiological sterilisation, without harming humans and would also be non-corrosive.

Some antiseptics are germicides, capable of destroying microbes (bacteriocidal), while others are bacteriostatic and prevent their growth.
There are multiple types of disinfectants, including but not limited to air disinfectants, alcohols, and oxidizing agents.
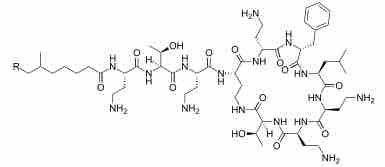
Prior to the advent of antibiotics, live organisms were used directly in attempts to control microbial infections.