Chapter 2
Financial Statements, Taxes, and Cash Flow
By Boundless

Financial statements report on a company's income, cash flow and equity.
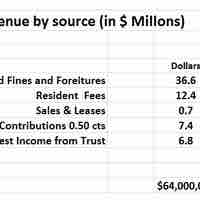
Financial statements are used to understand key facts about the performance and disposition of a business and may influence decisions.
Financial statements can be limited by intentional manipulation, differences in accounting methods, and a sole focus on economic measures.
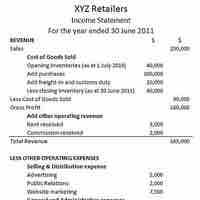
The income statement, or profit and loss statement (P&L), reports a company's revenue, expenses, and net income over a period of time.
Income statements have several limitations stemming from estimation difficulties, reporting error, and fraud.
GAAP's assumptions, principles, and constraints can affect income statements through temporary (timing) and permanent differences.

Noncash items, such as depreciation and amortization, will affect differences between the income statement and cash flow statement.
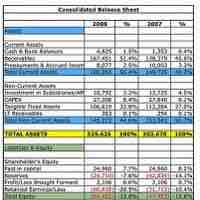
Assets on a balance sheet are classified into current assets and non-current assets. Assets are on the left side of a balance sheet.

The balance sheet contains details on company liabilities and owner's equity.

Working capital is a financial metric which represents operating liquidity available to a business, organization and other entity.
Liquidity, a business's ability to pay obligations, can be assessed using various ratios: current ratio, quick ratio, etc.

The debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) indicates the relative proportion of shareholder's equity and debt used to finance a company's assets.
Book value is the price paid for a particular asset, while market value is the price at which you could presently sell the same asset.
The three limitations to balance sheets are assets being recorded at historical cost, use of estimates, and the omission of valuable non-monetary assets.

Corporate taxes are levied on the income of various entities, stemming from their business operations.
A tax deduction is a reduction of the amount of income subject to tax.
Depreciation is the allocation of expenses associated with assets that contribute to operations over several periods.
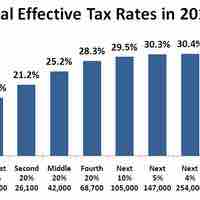
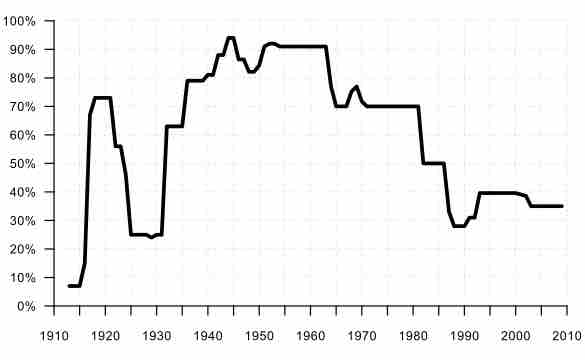
The U.S. federal, state and local governments levy taxes on individuals based on income, property, estate transfers, and/or sales transactions.

The operating cash flows refers to all cash flows that have to do with the actual operations of the business, such as selling products.

Cash flow from investing results from activities related to the purchase or sale of assets or investments made by the company.

Cash flows from financing activities arise from the borrowing, repaying, or raising of money.

Having positive and large cash flow is a good sign for any business, though does not by itself mean the business will be successful.

The statement of equity explains the changes of the company's equity throughout the reporting period.

Depreciation refers to the allocation of the cost of assets to periods in which the assets are used.

Free cash flow (FCF) is cash flow available for distribution among all the securities holders of an organization.

MVA = PV (EVAs); MVA is the difference between current market value and investors' capital., and EVA is an estimate of a firm's economic profit.