Chapter 27
The Monetary System
By Boundless
Money is any object that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and the repayment of debt.
The monetary economy is a significant improvement over the barter system, in which goods were exchanged directly for other goods.
M1 captures the most liquid components of the money supply, including currency held by the public and checkable deposits in banks.
M2 is a broader measure of the money supply than M1, including all M1 monies and those that could be quickly converted to liquid forms.
In addition to the commonly used M1 and M2 aggregates, several other measures of the money supply are used as well.

Monetary policy is the process by which a monetary authority controls the money supply, often to produce stable prices and low unemployment.
The Federal Reserve was created to promote financial stability, provide regulation and banking services, and conduct monetary policy.

The Federal Reserve System (The Fed) was designed in order to maintain the central bank's independence and promote decentralized power.
The Federal Open Market Committee is responsible for conducting open market operations in order to achieve a target interest rate.
The Fed responded to the financial crisis with conventional open market operations and unconventional credit facilities and bailouts.
While central banks share responsibility for monetary policy, their structures, methods, and primary goals differ across countries.
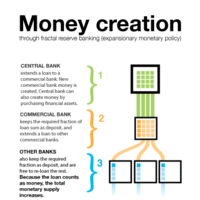
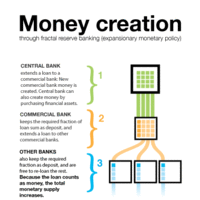
A fractional reserve system is one in which banks hold reserves whose value is less than the sum of claims outstanding on those reserves.
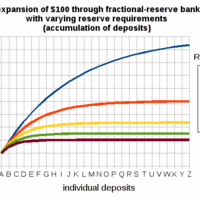
The amount of money created by banks depends on the size of the deposit and the money multiplier.
The money multiplier measures the maximum amount of commercial bank money that can be created by a given unit of central bank money.
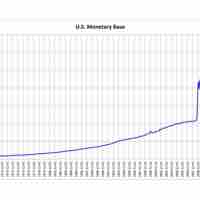
In reality, it is very unlikely that the money supply will be exactly equal to reserves times the money multiplier.