The Federal Reserve (the Fed) was designed to be independent of the Congress and the government. The idea justification for independence is that it allows the Fed to operate without being put under political pressure to take actions that may not be in the best long-term economic interest of the country.
The Federal Reserve System is composed of five parts :
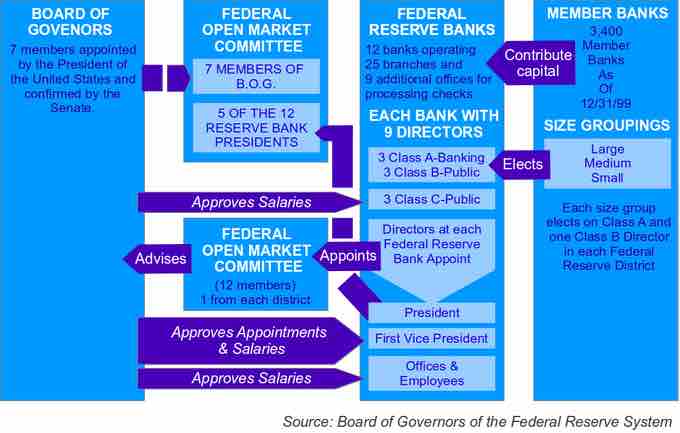
Structure of the Federal Reserve
The diagram shows the relationship between the different organizations that compose the Federal Reserve System
- The presidentially appointed Board of Governors (or Federal Reserve Board), an independent federal government agency located in Washington, D.C. Each governor serves a 14 year term. As of February 2014, the Chair of the Board of Governors is Janet Yellen, who succeeded Ben Bernanke.
- The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), composed of the seven members of the Federal Reserve Board and five of the 12 Federal Reserve Bank presidents, which oversees open market operations, the principal tool of U.S. monetary policy.
- Twelve regional Federal Reserve Banks located in major cities throughout the nation, which divide the nation into twelve Federal Reserve districts. The Federal Reserve Banks act as fiscal agents for the U.S. Treasury, and each has its own nine-member board of directors.
- Numerous other private U.S. member banks, which own required amounts of non-transferable stock in their regional Federal Reserve Banks.
- Various advisory councils.
The Fed can be thought of as having both private and public organization characteristics, though it considers itself to be private. On one hand, the Fed works toward achieving public goals such as moderate inflation and low unemployment. It does not exist to make money. On the other hand, it is, by design, separate from the government. It operates independently, and is not subject to political pressures directly as is Congress or the President.