Chapter 1
Principles of Economics
By Boundless
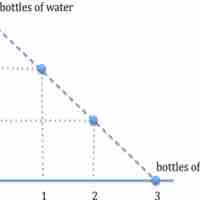
When scarce resources are used, actors are forced to make choices that have an opportunity cost.

Individuals face opportunity costs when they choose one course of action over another.

Individuals will choose the option that yields the greatest net marginal benefit.

Incentives are ways to encourage or discourage certain behaviors or choices.

Firms allow an economy to operate more efficiently and reduce the transaction costs of coordinating production.
Producers and consumers trade because the exchange makes both parties better off.
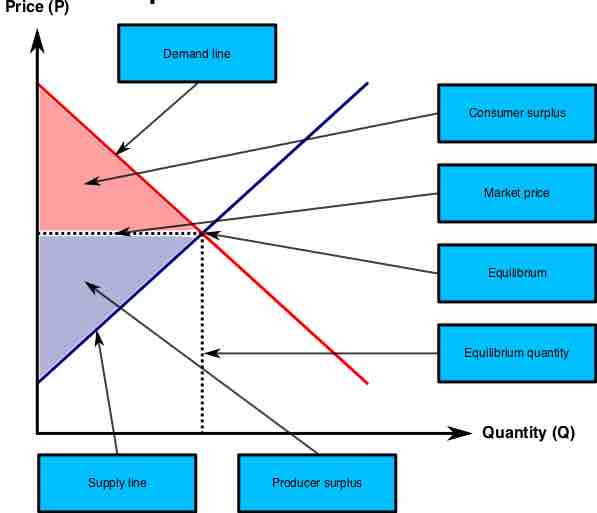
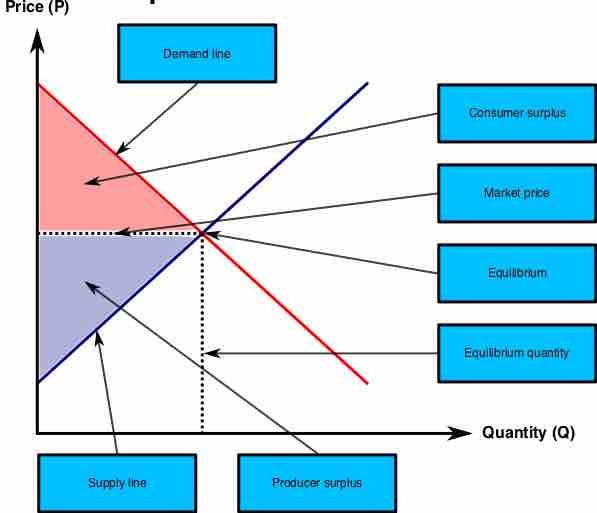
An efficient market maximizes total consumer and producer surplus.

In a free market, the price and quantity of an item are determined by the supply and demand for that item.

A perfectly competitive market with full property rights is typically efficient.

Governments can intervene to make a market more efficient when a market failure, such as externalities or asymmetric information, exists.
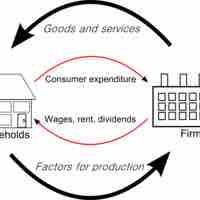
Variables that describe the full economy, such as GDP and unemployment, are determined by the decisions of individual economic actors.

A firm's production outputs are what it creates using its resources: goods or services.

Labor, capital, and land are the three necessary inputs for any production process.
The process of producing and distributing a good or service is called a supply chain, and it is composed of many economic actors.

The key difference between centrally planned and market economies is the degree of individual autonomy.
A mixed economy is a system that embraces elements of centrally planned and free market systems.
Mathematical economics uses mathematical methods, such as algebra and calculus, to represent theories and analyze problems in economics.

Economists use assumptions in order to simplify economics processes so that they are easier to understand.
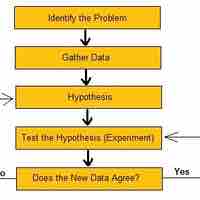
Economics, as a science, follows the scientific method in order to study data, observe patterns, and predict results of stimuli.
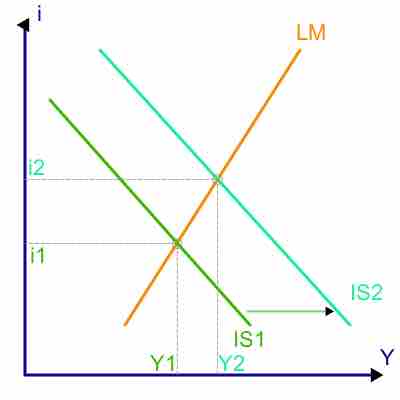
A model is simply a framework that is designed to show complex economic processes.

Positive economics is defined as the "what is" of economics, while normative economics focuses on the "what ought to be".
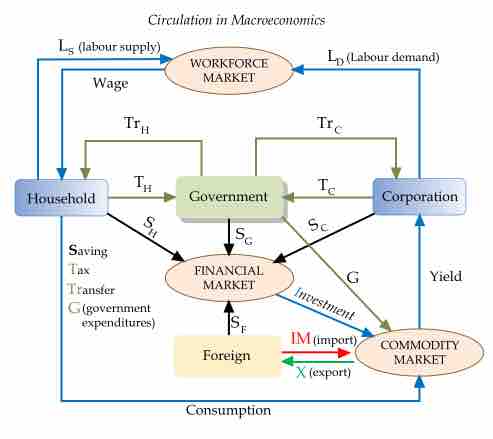
Macroeconomics is the study of the performance, structure, behavior and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
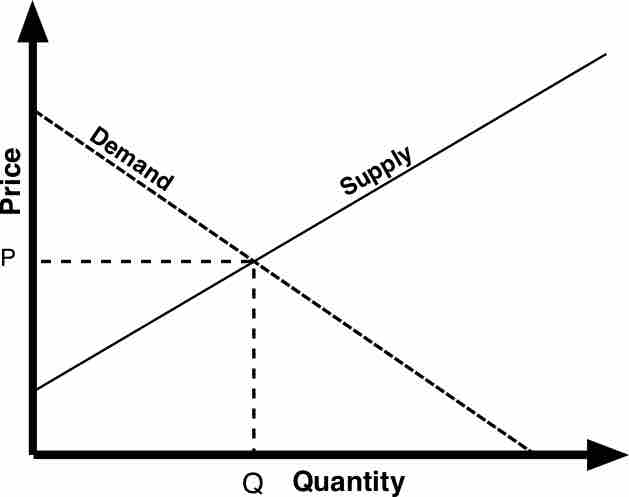
Microeconomics deals with the economic interactions of a specific person, a single entity or a company; it is the study of markets.

Microeconomics focuses on individual markets, while macroeconomics focuses on whole economies.

